Gene Section ID4 (inhibitor of DNA binding 4, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein)
... of the cell cycle machinery. Other ID genes are not redondant with ID4 during telencephalic develop-ment, supporting the idea that ID4 function is unique in this context (Yun et al., 2004). In immature neurons with high expression of ID proteins, heterodimers of bHLHID prevent DNA binding and expres ...
... of the cell cycle machinery. Other ID genes are not redondant with ID4 during telencephalic develop-ment, supporting the idea that ID4 function is unique in this context (Yun et al., 2004). In immature neurons with high expression of ID proteins, heterodimers of bHLHID prevent DNA binding and expres ...
Bacterial plasmids - Micro-Rao
... Mobilizable plasmids are those plasmids that lack genes to initiate self transfer but do encode the functions needed specifically for transfer of their own DNA. The initiation function is provided by other conjugative plasmid present in the same cell. Suicide plasmids are referred to those plasmids ...
... Mobilizable plasmids are those plasmids that lack genes to initiate self transfer but do encode the functions needed specifically for transfer of their own DNA. The initiation function is provided by other conjugative plasmid present in the same cell. Suicide plasmids are referred to those plasmids ...
ANP 307 - National Open University of Nigeria
... repeatability and heritability estimates, genes and genes action as well as quantitative and qualitative characters and their inheritance. This course guide tells you briefly what the course is about. What course materials you will be using and how you can work your way through these materials. In a ...
... repeatability and heritability estimates, genes and genes action as well as quantitative and qualitative characters and their inheritance. This course guide tells you briefly what the course is about. What course materials you will be using and how you can work your way through these materials. In a ...
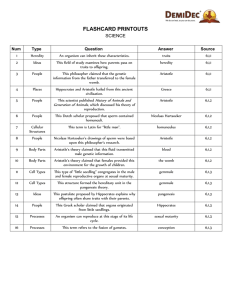
Science Flashcard Printouts.doc
... This type of “little seedling” congregates in the male and female reproductive organs at sexual maturity. ...
... This type of “little seedling” congregates in the male and female reproductive organs at sexual maturity. ...
Generation and analysis of mutated clonal scFv Jiya George
... Human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) incorporates host cellular protein, beta-2-microglobulin (β2m), into its surface envelope during budding. β2m is a cellular protein that belongs to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Class I molecules. Studies have shown anti-β2m monoclonal antibodies (mAb ...
... Human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) incorporates host cellular protein, beta-2-microglobulin (β2m), into its surface envelope during budding. β2m is a cellular protein that belongs to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Class I molecules. Studies have shown anti-β2m monoclonal antibodies (mAb ...
chapter 11 section 1 notes
... An individual’s characteristics are determined by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. ...
... An individual’s characteristics are determined by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. ...
Single-copy nuclear genes resolve the phylogeny of the
... often placed as sister to Mecopterida and the latter traditionally included either within, or as sister to, Coleoptera [9,10]. The consensus view is that most morphological features of Hymenoptera and Strepsiptera are too highly modified to unequivocally resolve their phylogenetic positions [11,12]. ...
... often placed as sister to Mecopterida and the latter traditionally included either within, or as sister to, Coleoptera [9,10]. The consensus view is that most morphological features of Hymenoptera and Strepsiptera are too highly modified to unequivocally resolve their phylogenetic positions [11,12]. ...
results and discussion discussion
... starvation induced protein (GsiB) of Bacillus subtilis, which is a hydrophilic protein of 123 amino acids and is composed almost entirely of five repeating motifs (Stacy and Aalen, 1998). Sequence analysis of GspM by radar repeat finder revealed that it was not formed of perfect repeats similar to G ...
... starvation induced protein (GsiB) of Bacillus subtilis, which is a hydrophilic protein of 123 amino acids and is composed almost entirely of five repeating motifs (Stacy and Aalen, 1998). Sequence analysis of GspM by radar repeat finder revealed that it was not formed of perfect repeats similar to G ...
Point Mutation Analysis of PMP22 in Patients Referred for Hereditary
... causality (loss of PMP22 function) for the three unclassified amino acid substitutions (c.328G>A p.(Val110Met), c.392C>G p.(Ser131Cys) and c.395A>G p.(Tyr132Cys)), while the c.320-1_320delGGinsTA (destruction of splice site) and c.434delT (protein reading frame shift) mutations are clearly deleterio ...
... causality (loss of PMP22 function) for the three unclassified amino acid substitutions (c.328G>A p.(Val110Met), c.392C>G p.(Ser131Cys) and c.395A>G p.(Tyr132Cys)), while the c.320-1_320delGGinsTA (destruction of splice site) and c.434delT (protein reading frame shift) mutations are clearly deleterio ...
Complete comparative genomic analysis of two field isolates of
... 2002; Li et al., 2002a), eight ORFs have amino acid substitutions in their encoded products. These include me53, lef-1, tlp-20, lef-8, lef-9, orf80, odv-e66 (orf144) and ie-1. Five of 12 ORFs that are unique to v90/2 and v90/4, orf5, orf10, orf18, orf23 and orf64 (Li et al., 2002b), have amino acid ...
... 2002; Li et al., 2002a), eight ORFs have amino acid substitutions in their encoded products. These include me53, lef-1, tlp-20, lef-8, lef-9, orf80, odv-e66 (orf144) and ie-1. Five of 12 ORFs that are unique to v90/2 and v90/4, orf5, orf10, orf18, orf23 and orf64 (Li et al., 2002b), have amino acid ...
Comparative analysis of two-component signal transduction systems
... are often encoded on adjacent genes. A typical HK contains an N-terminal, membrane-associated sensor domain and a C-terminal, cytosolic H-box and HATPase domain. Together, these cytoplasmic domains make up the phosphotransferase domain. A typical RR is a cytosolic protein consisting of an N-terminal ...
... are often encoded on adjacent genes. A typical HK contains an N-terminal, membrane-associated sensor domain and a C-terminal, cytosolic H-box and HATPase domain. Together, these cytoplasmic domains make up the phosphotransferase domain. A typical RR is a cytosolic protein consisting of an N-terminal ...
Investigating the link between tRNA and mRNA - EMBL-EBI
... manifests itself in the cell as trna molecules, which fall into several classes of anticodon isoacceptors, each decoding a single codon into its corresponding amino acid. In this thesis I discuss the central importance of the codon– anticodon interface to mrna-to-protein translation, and how its sta ...
... manifests itself in the cell as trna molecules, which fall into several classes of anticodon isoacceptors, each decoding a single codon into its corresponding amino acid. In this thesis I discuss the central importance of the codon– anticodon interface to mrna-to-protein translation, and how its sta ...
Genetics of Primary ciliary dyskinesia - HAL
... The diagnosis of PCD is therefore based on the identification of functional and structural abnormalities of cilia (Fig.2). In most patients with PCD, all the cilia share the same ultrastructural defect, as expected for a congenital disease. However, depending on the patients, cilia have been shown t ...
... The diagnosis of PCD is therefore based on the identification of functional and structural abnormalities of cilia (Fig.2). In most patients with PCD, all the cilia share the same ultrastructural defect, as expected for a congenital disease. However, depending on the patients, cilia have been shown t ...
PDF
... mitochondria was predicted based on identified similarities to mitochondrial localization motifs in other eukaryotes, whereas protein localization to plastids was based on the presence of signal peptide motifs in combination with plastid localization motifs previously shown to be required in diatoms ...
... mitochondria was predicted based on identified similarities to mitochondrial localization motifs in other eukaryotes, whereas protein localization to plastids was based on the presence of signal peptide motifs in combination with plastid localization motifs previously shown to be required in diatoms ...
Metabolomics based gene function annotation in Escherichia coli
... mutants. Additionally, metabolomics can be used to explore metabolic diversity of different accessions/strains, tissues, and cell types of an organism. Once the metabolic diversity has been described, the genetic-basis for the metabolic and/or phenotypic differences can be elucidated using other omi ...
... mutants. Additionally, metabolomics can be used to explore metabolic diversity of different accessions/strains, tissues, and cell types of an organism. Once the metabolic diversity has been described, the genetic-basis for the metabolic and/or phenotypic differences can be elucidated using other omi ...
Odyssey of Agrobacterium T-DNA.
... most likely by replacement DNA strand synthesis. The replacement reaction presumably removes the VirD2 molecule attached to the 5¢ end of the left border, restoring the circular DNA molecule of the Ti plasmid. Purified VirD2 protein cleaves single-stranded oligonucleotides containing border sequence ...
... most likely by replacement DNA strand synthesis. The replacement reaction presumably removes the VirD2 molecule attached to the 5¢ end of the left border, restoring the circular DNA molecule of the Ti plasmid. Purified VirD2 protein cleaves single-stranded oligonucleotides containing border sequence ...
Quantitative inheritance
... thus the polygenic model This can be described by looking at the variation ~ shown in following slides ...
... thus the polygenic model This can be described by looking at the variation ~ shown in following slides ...
of Lactobacillus pentosus
... downstream of the xylAB promoter site and its complex formation with XyIR was demonstrated in 8. subtilis, B. licheniformis, and S. xylosus by gel mobility experiments and DNA-footprinting studies (Gârtner et al., 1992, Scheler and Hillen, 1994, Sizemore et al., 1992). The 8. subtilis xyl operator s ...
... downstream of the xylAB promoter site and its complex formation with XyIR was demonstrated in 8. subtilis, B. licheniformis, and S. xylosus by gel mobility experiments and DNA-footprinting studies (Gârtner et al., 1992, Scheler and Hillen, 1994, Sizemore et al., 1992). The 8. subtilis xyl operator s ...
POPULATION GENETICS LECTURE NOTES
... homozygote state. If the mutation is caused by a dominant lethal allele, the heterozygote for the allele will show the lethal phenotype, the homozygote dominant is impossible. If the mutation is caused by a recessive lethal allele, the homozygote for the allele will have the lethal phenotype. Most l ...
... homozygote state. If the mutation is caused by a dominant lethal allele, the heterozygote for the allele will show the lethal phenotype, the homozygote dominant is impossible. If the mutation is caused by a recessive lethal allele, the homozygote for the allele will have the lethal phenotype. Most l ...
Analyzing microRNA Data and Integrating microRNA with Gene
... regulate many genes, the PutativeGenes list will be much longer than the input microRNA list. The PutativeGenes list might be used for Biological Interpretation. Another useful way to examine the data would be to right-click on the Gene Symbol column (last one on the right) and select Create List w ...
... regulate many genes, the PutativeGenes list will be much longer than the input microRNA list. The PutativeGenes list might be used for Biological Interpretation. Another useful way to examine the data would be to right-click on the Gene Symbol column (last one on the right) and select Create List w ...
docx
... AmpliChip p53 assay was designed to detect single base pair substitutions and deletions in the entire coding region of the TP53 gene, including splice sites of exons 2–11. The AmpliChip p53 microarray consists of over 33,000 probe sets of more than 220,000 individual oligonucleotides tiled for a tot ...
... AmpliChip p53 assay was designed to detect single base pair substitutions and deletions in the entire coding region of the TP53 gene, including splice sites of exons 2–11. The AmpliChip p53 microarray consists of over 33,000 probe sets of more than 220,000 individual oligonucleotides tiled for a tot ...
Myriad--Ambry -- Final Version of Ambry Preliminary Injunction
... Chromosomes in a human cell are made up of two complementary strands of DNA molecules—one strand is on one side of the double helix and the second strand is on the other side. For any given gene, only one molecule strand (the “template strand”) is actually transcribed into mRNA and ultimately used t ...
... Chromosomes in a human cell are made up of two complementary strands of DNA molecules—one strand is on one side of the double helix and the second strand is on the other side. For any given gene, only one molecule strand (the “template strand”) is actually transcribed into mRNA and ultimately used t ...
Mendel`s Principles of Heredity
... in F1 p progeny g y is the dominant form • Trait that is hidden in the F1 progeny is the recessive form • Progeny inherit one unit from the maternal parent and the other unit from the paternal parent ...
... in F1 p progeny g y is the dominant form • Trait that is hidden in the F1 progeny is the recessive form • Progeny inherit one unit from the maternal parent and the other unit from the paternal parent ...
biojeopardy evolution
... 15cm. What is the most likely explanation for difference in sizes of members of these populations What is genetic bottleneck or founder Continue ...
... 15cm. What is the most likely explanation for difference in sizes of members of these populations What is genetic bottleneck or founder Continue ...
3. Inheritance and hereditary
... exemplary genetic characteristics to illustrate general principles that also apply to other organisms, including new model organisms for which new technologies now or soon will allow some aspects of genetic manipulation and study. The general nomenclature used in this book is described in Box 3-1. ...
... exemplary genetic characteristics to illustrate general principles that also apply to other organisms, including new model organisms for which new technologies now or soon will allow some aspects of genetic manipulation and study. The general nomenclature used in this book is described in Box 3-1. ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.