Lecture-Mic 623-Plasmids-Listeria - Home
... organization of plasmid pIP823, which contains the dfrD gene; dfrD confers high-level trimethoprim resistance to Listeria monocytogenes BM4293 by synthesis of dihydrofolate reductase type S2. pIP823 possessed all the features of the pUB110/pC194 plasmid family, whose members replicate by the rolling ...
... organization of plasmid pIP823, which contains the dfrD gene; dfrD confers high-level trimethoprim resistance to Listeria monocytogenes BM4293 by synthesis of dihydrofolate reductase type S2. pIP823 possessed all the features of the pUB110/pC194 plasmid family, whose members replicate by the rolling ...
Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the gp200 protein of
... United States (AF252298 and CP000107), the gp200 open reading frame was 4,266 bp in length and encoded a protein of 1,421 amino acids. The complete gp200 coding sequences derived from 17 Taiwanese samples were identical or nearly identical to each other (99.9∼100% identities), even though the canine ...
... United States (AF252298 and CP000107), the gp200 open reading frame was 4,266 bp in length and encoded a protein of 1,421 amino acids. The complete gp200 coding sequences derived from 17 Taiwanese samples were identical or nearly identical to each other (99.9∼100% identities), even though the canine ...
Genetic polymorphism of epoxide hydrolase and glutathione S-transferase in COPD S-L. Cheng
... disease (COPD). Nevertheless, only 10–20% of chronic smokers develop the severe impairment of pulmonary function associated with COPD [1, 2]. This indicates the possible contribution of environmental or genetic cofactors to the development of COPD. Although cofactors, such as childhood viral infecti ...
... disease (COPD). Nevertheless, only 10–20% of chronic smokers develop the severe impairment of pulmonary function associated with COPD [1, 2]. This indicates the possible contribution of environmental or genetic cofactors to the development of COPD. Although cofactors, such as childhood viral infecti ...
MS#5_(Cueno and Laude).indd - Philippine Journal of Science
... of the coconut endosperm and, as seen in Figure 1, visible differences in terms of PCR band intensity were observed, we did expect sequence differences even in the 3’UTR. The major sequence difference between DCT1-5mo and DCT1-6mo transcripts is the 52 nt missing from DCT16mo transcripts (Table 1 an ...
... of the coconut endosperm and, as seen in Figure 1, visible differences in terms of PCR band intensity were observed, we did expect sequence differences even in the 3’UTR. The major sequence difference between DCT1-5mo and DCT1-6mo transcripts is the 52 nt missing from DCT16mo transcripts (Table 1 an ...
Expression of floricaula in single cell layers of
... (Fig. 2). This gave a 9.0 kb band for flo-613 and a 5.5 kb band for wild-type plants that lack the 3.5 kb Tam3 element (Fig. 2A, left two lanes). Most of the chimeras had a 9.0 kb band, showing that they carried Tam3 in the flo gene. In addition, all chimeras had a 5.5 kb band of varying intensity, ...
... (Fig. 2). This gave a 9.0 kb band for flo-613 and a 5.5 kb band for wild-type plants that lack the 3.5 kb Tam3 element (Fig. 2A, left two lanes). Most of the chimeras had a 9.0 kb band, showing that they carried Tam3 in the flo gene. In addition, all chimeras had a 5.5 kb band of varying intensity, ...
fulltext - DiVA portal
... addition, upon screening of several different Salmonella enterica serovars, functional homologues to the clyA gene were identified in the typhoid Salmonella serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A [9]. The presence of the clyA gene in wild-type isolates of Salmonella suggests a conserved function of the gene ...
... addition, upon screening of several different Salmonella enterica serovars, functional homologues to the clyA gene were identified in the typhoid Salmonella serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A [9]. The presence of the clyA gene in wild-type isolates of Salmonella suggests a conserved function of the gene ...
Complete genome sequence of the thermophilic Thermus sp
... are easier to crystallize than their mesophilic counterparts [7]. Some of the breakthrough examples of large complexes from thermophiles that have been crystallized are structures of the 70S ribosome [8], the bacterial RNA polymerase [9, 10] and the respiratory complex I [11] from Thermus spp. that ...
... are easier to crystallize than their mesophilic counterparts [7]. Some of the breakthrough examples of large complexes from thermophiles that have been crystallized are structures of the 70S ribosome [8], the bacterial RNA polymerase [9, 10] and the respiratory complex I [11] from Thermus spp. that ...
The role of Dby mRNA in early development of male mouse zygotes
... be limited to the male haploid genome and the spermatozoa RNA, but may also be involved in early zygotic and embryonic development. Recently, we reported that transcripts of three Ychromosome genes, DBY, SRY and RPS4Y, are selectively retained in human ejaculated spermatozoa [6]. Functional analysis ...
... be limited to the male haploid genome and the spermatozoa RNA, but may also be involved in early zygotic and embryonic development. Recently, we reported that transcripts of three Ychromosome genes, DBY, SRY and RPS4Y, are selectively retained in human ejaculated spermatozoa [6]. Functional analysis ...
Comparison of Genes Encoding Enzymes of Sterol Biosynthesis
... follows different routes in photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic organisms. Accordingly, to open the cyclopropane ring of cycloartenol, the photosynthetic organisms require different set of enzymes, such as cycloartenol synthase and cycloeucalenol-obtusifoliol isomerase. Nevertheless, the sterol bio ...
... follows different routes in photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic organisms. Accordingly, to open the cyclopropane ring of cycloartenol, the photosynthetic organisms require different set of enzymes, such as cycloartenol synthase and cycloeucalenol-obtusifoliol isomerase. Nevertheless, the sterol bio ...
DNA Genetics
... d. they do not produce abnormal hemoglobin. ____ 47. Most sex-linked genes are located on a. the autosomes. b. the X chromosome only. c. the Y chromosome only. d. both the X chromosome and the Y chromosome. ____ 48. The formation of a Barr body a. causes the genes on one of the X chromosomes in a fe ...
... d. they do not produce abnormal hemoglobin. ____ 47. Most sex-linked genes are located on a. the autosomes. b. the X chromosome only. c. the Y chromosome only. d. both the X chromosome and the Y chromosome. ____ 48. The formation of a Barr body a. causes the genes on one of the X chromosomes in a fe ...
Picoplankton Bloom in Global South? A High Fraction of Aerobic
... Lami et al., 2007; Schwalbach and Fuhrman, 2005) and despite initial reports, they support the hypothesis proposed by Kolber (2001) that these organisms would have an advantage in oligotrophic conditions. Recent studies, however, suggest that AAPs thrive better in more eutrophic environments (Cottre ...
... Lami et al., 2007; Schwalbach and Fuhrman, 2005) and despite initial reports, they support the hypothesis proposed by Kolber (2001) that these organisms would have an advantage in oligotrophic conditions. Recent studies, however, suggest that AAPs thrive better in more eutrophic environments (Cottre ...
PDF
... an adaptation important for the evolution of behavioural phenotypes in the worker caste. This could be because the evolution of eusociality entailed rapid evolution and specialisation of workers [39]. Alternatively, high intra-colony variability in worker phenotypes could be beneficial because it re ...
... an adaptation important for the evolution of behavioural phenotypes in the worker caste. This could be because the evolution of eusociality entailed rapid evolution and specialisation of workers [39]. Alternatively, high intra-colony variability in worker phenotypes could be beneficial because it re ...
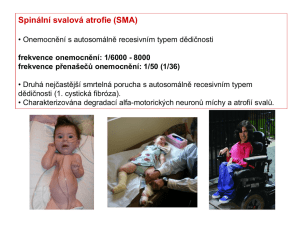
SMN1
... Mechanisms proposed to explain how reduced SMN levels cause SMA According to one hypothesis, reduced SMN levels result in reduced assembly of Sm proteins onto snRNA. This unevenly alters the levels of specific endogenous snRNPs, such as those used to splice minor introns (particularly U11) from pr ...
... Mechanisms proposed to explain how reduced SMN levels cause SMA According to one hypothesis, reduced SMN levels result in reduced assembly of Sm proteins onto snRNA. This unevenly alters the levels of specific endogenous snRNPs, such as those used to splice minor introns (particularly U11) from pr ...
Package `fcros`
... Title A Method to Search for Differentially Expressed Genes and to Detect Recurrent Chromosomal Copy Number Aberrations Version 1.5.4 Date 2017-04-03 Author Doulaye Dembele Maintainer Doulaye Dembele
Depends R (>= 3.1.0)
Description A fold change rank based method is presented to ...
... Title A Method to Search for Differentially Expressed Genes and to Detect Recurrent Chromosomal Copy Number Aberrations Version 1.5.4 Date 2017-04-03 Author Doulaye Dembele Maintainer Doulaye Dembele
Maternal-Effect Genes That Alter the Fate Map of the Drosophila
... wild-type embryo at the cellular blastoderm stage (3 hr) exhibits seven stripes offtz protein. (b) A wild-type embryo at the end of embryogenesis (22 hr). Some segments are indicated. T, thoracic; A, abdominal; tl, telson. (c) vdpD/vc&? The broad region offtz staining that occurs in place of stripes ...
... wild-type embryo at the cellular blastoderm stage (3 hr) exhibits seven stripes offtz protein. (b) A wild-type embryo at the end of embryogenesis (22 hr). Some segments are indicated. T, thoracic; A, abdominal; tl, telson. (c) vdpD/vc&? The broad region offtz staining that occurs in place of stripes ...
Genetic Control of X Chromosome Inactivation in Mice: Definition of
... factors that in turn regulate the expression of other loci in the Xic, such as Xist or Tsix. The various Xce alleles are thus predicted to have differential binding affinities for this factor (or factors), leading to a bias in the choice between chromosomes. While no such factors have been identifie ...
... factors that in turn regulate the expression of other loci in the Xic, such as Xist or Tsix. The various Xce alleles are thus predicted to have differential binding affinities for this factor (or factors), leading to a bias in the choice between chromosomes. While no such factors have been identifie ...
Respiratory terminal oxidases in the facultative chemoheterotrophic
... microns, Sigma-Aldrich) for 4 min. Two-step RT-PCR was performed using the enhanced avian RT-PCR kit (SigmaAldrich). Total RNA was denatured together with the specific primer for 10 min at 85 8C and the reverse transcriptase reaction was performed for 40 min at 48 8C followed by 20 min at 60 8C. PCR ...
... microns, Sigma-Aldrich) for 4 min. Two-step RT-PCR was performed using the enhanced avian RT-PCR kit (SigmaAldrich). Total RNA was denatured together with the specific primer for 10 min at 85 8C and the reverse transcriptase reaction was performed for 40 min at 48 8C followed by 20 min at 60 8C. PCR ...
Identification and removal of colanic acid from plasmid DNA
... solvents such as ethanol (EtOH) and by polyethylene glycol. Because polysaccharides are anionic, they co-purify with DNA by anion-exchange chromatography. The commercially available laboratory scale purification methods, including Qiagen, use anionexchange chromatography for at least one major step ...
... solvents such as ethanol (EtOH) and by polyethylene glycol. Because polysaccharides are anionic, they co-purify with DNA by anion-exchange chromatography. The commercially available laboratory scale purification methods, including Qiagen, use anionexchange chromatography for at least one major step ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Breakage of a chromosome can lead to four types of changes in chromosome structure. A deletion - chromosome fragment lacking a centromere is lost during cell division. A duplication -a fragment becomes attached as an extra segment to a sister chromatid. ...
... Breakage of a chromosome can lead to four types of changes in chromosome structure. A deletion - chromosome fragment lacking a centromere is lost during cell division. A duplication -a fragment becomes attached as an extra segment to a sister chromatid. ...
meiosis
... – The only difference from mitotic division is that chromosomes do not replicate before they divide at centromeres. ...
... – The only difference from mitotic division is that chromosomes do not replicate before they divide at centromeres. ...
Genetic mapping of mutations using phenotypic pools and
... We have previously reported a map of the Arabidopsis genome constructed with RAPD markers and recombinant inbred lines derived from a cross between the Arabidopsis strain WS and the multiple marker line W100, which carries nine visible markers (3,4). To test this pooling approach to mapping we selec ...
... We have previously reported a map of the Arabidopsis genome constructed with RAPD markers and recombinant inbred lines derived from a cross between the Arabidopsis strain WS and the multiple marker line W100, which carries nine visible markers (3,4). To test this pooling approach to mapping we selec ...
Evaluation of genomic DNA from paraffin
... many genes are linked to the disorder, possibly giving rise to different phenotypes (Fatkin & Graham 2002). When comparing individuals affected by DCM within dog breeds it appears to be relatively homogenous in separate breeds. This makes the dogs a good model to study the genetic background of spon ...
... many genes are linked to the disorder, possibly giving rise to different phenotypes (Fatkin & Graham 2002). When comparing individuals affected by DCM within dog breeds it appears to be relatively homogenous in separate breeds. This makes the dogs a good model to study the genetic background of spon ...
Anterior boundaries of Hox gene expression in mesoderm
... segments by specifying positional information during embryogenesis (for reviews see [l, 20-22,441. That mammalian homeobox-containing genes also are controlling factors required for the physical determination of the body plan has not been demonstrated, primarily because mutations in the respective l ...
... segments by specifying positional information during embryogenesis (for reviews see [l, 20-22,441. That mammalian homeobox-containing genes also are controlling factors required for the physical determination of the body plan has not been demonstrated, primarily because mutations in the respective l ...
the sequence alignment itself is a hypothesis about the homology of
... genes/sequences • We must determine homology for each and every nucleotide/amino acid position within the sequences. • This is accomplished via sequence alignment • It is THE CRITICAL first step in most phylogenetic analyses • Always remember that the sequence alignment itself is a hypothesis about ...
... genes/sequences • We must determine homology for each and every nucleotide/amino acid position within the sequences. • This is accomplished via sequence alignment • It is THE CRITICAL first step in most phylogenetic analyses • Always remember that the sequence alignment itself is a hypothesis about ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.