Arabidopsis hair cell morphogenesis in encodes a cellulose
... al. 1992; Wymer et al. 1997). Growth ceases on vacuolation of the hair tip. The genetic analysis of root hair development has identified several genes that are required for the initiation and growth of the root hair. RHL1, RHL2, and RHL3 genes are active during the formation of a bulge early in root ...
... al. 1992; Wymer et al. 1997). Growth ceases on vacuolation of the hair tip. The genetic analysis of root hair development has identified several genes that are required for the initiation and growth of the root hair. RHL1, RHL2, and RHL3 genes are active during the formation of a bulge early in root ...
Genetic Factors Affecting Facial Growth
... which they do not (Harris, 2008); 2) the presumption that whatever genetic factors may have contributed to the occlusion will also affect how the patient responds to treatment, which they may not; and 3) a lack of understanding to the extent at which genetic factors may interact with environmental f ...
... which they do not (Harris, 2008); 2) the presumption that whatever genetic factors may have contributed to the occlusion will also affect how the patient responds to treatment, which they may not; and 3) a lack of understanding to the extent at which genetic factors may interact with environmental f ...
Positive Selection of Deleterious Alleles through Interaction with a
... and among herds, and the null models, which reflected only differences among herds. In logistic regression analyses, which were performed with SPSS 19, correction for population stratification was performed by including the latitude of each herd. We chose to include latitude as a continuous variable ...
... and among herds, and the null models, which reflected only differences among herds. In logistic regression analyses, which were performed with SPSS 19, correction for population stratification was performed by including the latitude of each herd. We chose to include latitude as a continuous variable ...
Virp1 Is a Host Protein with a Major Role in Potato - IMBB
... Viroids are small, circular, single-stranded RNA molecules that, while not coding for any protein, cause several plant diseases. Viroids rely for their infectious cycle on host proteins, most of which are likely to be involved in endogenous RNA-mediated phenomena. Therefore, characterization of host ...
... Viroids are small, circular, single-stranded RNA molecules that, while not coding for any protein, cause several plant diseases. Viroids rely for their infectious cycle on host proteins, most of which are likely to be involved in endogenous RNA-mediated phenomena. Therefore, characterization of host ...
Entering the second century of maize quantitative genetics
... As high-throughput genotyping and GWAS studies became possible, two major questions in the field of quantitative genetics were, first, how many genes influenced each trait, and second, what was the allele distribution within those genes? This debate was most visible for human genetic diseases, but i ...
... As high-throughput genotyping and GWAS studies became possible, two major questions in the field of quantitative genetics were, first, how many genes influenced each trait, and second, what was the allele distribution within those genes? This debate was most visible for human genetic diseases, but i ...
Association between toluene diisocyanate-induced aspartic acid at position 57
... are involved in antigen presentation and that a correct binding between these glycoproteins and the antigen is necessary for a functional antigen recognition by Tlymphocytes. We do not know what the TDI antigen looks like. It seems unlikely that TDI itself is the antigen, since it is a low molecular ...
... are involved in antigen presentation and that a correct binding between these glycoproteins and the antigen is necessary for a functional antigen recognition by Tlymphocytes. We do not know what the TDI antigen looks like. It seems unlikely that TDI itself is the antigen, since it is a low molecular ...
Identity-by-descent filtering of exome sequence data for disease
... over at least two generations and are not optimized for the relatively high error rates of variant calls in NGS data. In this work, we describe a procedure for efficiently filtering exome sequencing data obtained from two or more affected siblings with an autosomal recessive Mendelian disorder based ...
... over at least two generations and are not optimized for the relatively high error rates of variant calls in NGS data. In this work, we describe a procedure for efficiently filtering exome sequencing data obtained from two or more affected siblings with an autosomal recessive Mendelian disorder based ...
Strand
... Read example from standard Understand that DNA which comprises the organism’s chromosomes is like a “recipe book” containing the code for each protein the organism needs. ...
... Read example from standard Understand that DNA which comprises the organism’s chromosomes is like a “recipe book” containing the code for each protein the organism needs. ...
Genetic Codes with No Dedicated Stop Codon: Context
... While the genetic code is classically taught as being unambiguous, and indeed may largely be so, we now know this is an oversimplification. Since the original discovery of the standard genetic code, alternative translational interpretations of codons have been found, most notably in the use of the U ...
... While the genetic code is classically taught as being unambiguous, and indeed may largely be so, we now know this is an oversimplification. Since the original discovery of the standard genetic code, alternative translational interpretations of codons have been found, most notably in the use of the U ...
Analysis of the Molecular Basis of Flowering Time Variation in
... al., 2000), and this is supported by the early flowering of F1 plants derived from the Shakhdara ⫻ FRI(Sf-2) flc-3 cross (Table I). Kondara and Kz-9 were not as early flowering in our conditions as had been reported previously (Karlsson et al., 1993; Nordborg and Bergelson, 1999), but the F1 plants ...
... al., 2000), and this is supported by the early flowering of F1 plants derived from the Shakhdara ⫻ FRI(Sf-2) flc-3 cross (Table I). Kondara and Kz-9 were not as early flowering in our conditions as had been reported previously (Karlsson et al., 1993; Nordborg and Bergelson, 1999), but the F1 plants ...
Quantitative analysis of SMN1 and SMN2 genes based on DHPLC
... Autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a common, fatal neuromuscular disease caused by homozygous absence of the SMN1 gene in approximately 94% of patients. However, a highly homologous SMN2 gene exists in the same chromosome interval, centromeric to SMN1, and hampers detection of SMN1 ...
... Autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a common, fatal neuromuscular disease caused by homozygous absence of the SMN1 gene in approximately 94% of patients. However, a highly homologous SMN2 gene exists in the same chromosome interval, centromeric to SMN1, and hampers detection of SMN1 ...
Building Individualized Medicine: Prevention of Adverse Reactions
... large groups of patients stratified according to their dose requirements. This approach uses genetic markers rather than functional polymorphisms and therefore does not provide information about possible mechanisms behind alterations in drug response. Instead, it relies on the assumption that a muta ...
... large groups of patients stratified according to their dose requirements. This approach uses genetic markers rather than functional polymorphisms and therefore does not provide information about possible mechanisms behind alterations in drug response. Instead, it relies on the assumption that a muta ...
Mendelian genetics
... will always be on different chromosomes. • We CAN determine how two different traits can be passed down, though. This requires the use of a ...
... will always be on different chromosomes. • We CAN determine how two different traits can be passed down, though. This requires the use of a ...
Autotrophic CO2 fixation via the reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle in
... inorganic carbon as the source for cell carbon – are likely to have been among the first types of organisms on Earth (e.g. Huber and Wächtershäuser, 1997; Russell and Hall, 1997). Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA and whole genomes place autotrophic hyperthermophiles at the base of the evoluti ...
... inorganic carbon as the source for cell carbon – are likely to have been among the first types of organisms on Earth (e.g. Huber and Wächtershäuser, 1997; Russell and Hall, 1997). Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA and whole genomes place autotrophic hyperthermophiles at the base of the evoluti ...
Gene Section EVI1 (ecotropic viral integration site 1 (EVI1) and
... Similar Evi1 expression patterns were also observed in Xenopus, chicken, and zebrafish. ...
... Similar Evi1 expression patterns were also observed in Xenopus, chicken, and zebrafish. ...
Basic Principles of Heredity
... where the shape of seeds is determined. This locus might be occupied by an allele for round seeds or one for wrinkled seeds. We will use the term allele when referring to a specific version of a gene; we will use the term gene to refer more generally to any allele at a locus. The genotype is the set ...
... where the shape of seeds is determined. This locus might be occupied by an allele for round seeds or one for wrinkled seeds. We will use the term allele when referring to a specific version of a gene; we will use the term gene to refer more generally to any allele at a locus. The genotype is the set ...
22q12 and 22q13 duplications
... Chromosomes are structures which contain our DNA and are found in almost every cell of the body. Every chromosome contains thousands of genes which may be thought of as individual instruction booklets (or recipes) that contain all the genetic information telling the body how to develop, grow and fun ...
... Chromosomes are structures which contain our DNA and are found in almost every cell of the body. Every chromosome contains thousands of genes which may be thought of as individual instruction booklets (or recipes) that contain all the genetic information telling the body how to develop, grow and fun ...
Classification of Centers for Disease Control Group Eugonic
... organisms found in the oral cavity of dogs and cats, although systemic infections in humans and animals have also been reported (Ganière et al., 1995). Two biotypes can be distinguished based on the presence (EF-4a) or absence (EF-4b) of arginine dihydrolase activity (Holmes & Ahmed, 1981). In addi ...
... organisms found in the oral cavity of dogs and cats, although systemic infections in humans and animals have also been reported (Ganière et al., 1995). Two biotypes can be distinguished based on the presence (EF-4a) or absence (EF-4b) of arginine dihydrolase activity (Holmes & Ahmed, 1981). In addi ...
thymine dimers - Glen Research
... with smaller pyrimidines) and hydrogen bonding (hydrogen bond donors from one nucleobase pair with hydrogen bond acceptors from the other). The former is necessary to permit the structure that underlies enzyme recognition. The latter achieves the specificity that gives rise to the simple rules for b ...
... with smaller pyrimidines) and hydrogen bonding (hydrogen bond donors from one nucleobase pair with hydrogen bond acceptors from the other). The former is necessary to permit the structure that underlies enzyme recognition. The latter achieves the specificity that gives rise to the simple rules for b ...
Fanconi anemia and RAD50 deficiency: genetic and functional
... the different types of molecular events that lead to the restoration of heterozygosity, and thereby normal function, of the self-corrected cell types in individuals constitutionally homozygous or compound heterozygous for disease causing gene mutations. ...
... the different types of molecular events that lead to the restoration of heterozygosity, and thereby normal function, of the self-corrected cell types in individuals constitutionally homozygous or compound heterozygous for disease causing gene mutations. ...
Strains to Theiler`s Virus Persistent Infection the Difference of
... The D10Pas4 deletion could have been responsible for the susceptibility of the SJL/J strain for two reasons. First, it is present in the only strain for which the H-2D haplotype does not correlate with susceptibility to persistent infection. Second, it is located 44 nt upstream of the TATA box, betw ...
... The D10Pas4 deletion could have been responsible for the susceptibility of the SJL/J strain for two reasons. First, it is present in the only strain for which the H-2D haplotype does not correlate with susceptibility to persistent infection. Second, it is located 44 nt upstream of the TATA box, betw ...
Ribotyping of Clostridium perfringens from industrially produced
... Among 111 Cl. perfringens isolates from ground meat 107 distinctly different ribotype patterns were detected. In only four cases two Cl. perfringens isolates showed an identical ribopattern. Figure 1 shows an example of the variability of the ribotype patterns. The number of DIG labelled bands of Cl ...
... Among 111 Cl. perfringens isolates from ground meat 107 distinctly different ribotype patterns were detected. In only four cases two Cl. perfringens isolates showed an identical ribopattern. Figure 1 shows an example of the variability of the ribotype patterns. The number of DIG labelled bands of Cl ...
DNA supercoiling factor contributes to dosage
... counteracts ISWI action and forms (and/or maintains) transcriptionally active open chromatin. ...
... counteracts ISWI action and forms (and/or maintains) transcriptionally active open chromatin. ...
Design-O-Saur - Beyond Benign
... cross to select the genotype of your F1 Generation (dinosaur offspring). 7. Make a list of your offspring’s genotype and phenotype. 8. Make a model of your offspring that includes a representation of all the traits listed in step #7. This model must be made by you, not store bought. Students may use ...
... cross to select the genotype of your F1 Generation (dinosaur offspring). 7. Make a list of your offspring’s genotype and phenotype. 8. Make a model of your offspring that includes a representation of all the traits listed in step #7. This model must be made by you, not store bought. Students may use ...
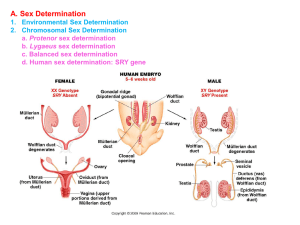
III. Linkage
... A. Sex Determination B. Sex Linkage C. Dosage Compensation Which X condenses is random. So, in heterozygous female cats (XOXo), when the X with the gene for orange color condenses, the ‘non-orange’ allele allows genes for other colors at other loci to be expressed (black, brown, ‘blue’). The X that ...
... A. Sex Determination B. Sex Linkage C. Dosage Compensation Which X condenses is random. So, in heterozygous female cats (XOXo), when the X with the gene for orange color condenses, the ‘non-orange’ allele allows genes for other colors at other loci to be expressed (black, brown, ‘blue’). The X that ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.