DETECTING AND CHARACTERIZING PLEIOTROPY: NEW
... Whether pleiotropy is universal or modular has an impact on how pleiotropic genes are influenced by selection. Complex organisms have vastly more cell types than prokaryotes, but only about four-fold more genes.10 The necessary increase in pleiotropy per gene that this statistic suggests could limit ...
... Whether pleiotropy is universal or modular has an impact on how pleiotropic genes are influenced by selection. Complex organisms have vastly more cell types than prokaryotes, but only about four-fold more genes.10 The necessary increase in pleiotropy per gene that this statistic suggests could limit ...
Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 13:
... 1.6.1.19) activity was determined with a colorimetric reaction according to Yonaha and Toyama (1980). Glutamate decarboxylase (GAD, EC 4.1.1.15) activity was measured by the method of Fonda (1985) as modified by Vézina et al. (1988). The bacteria used to measure GAD activity were grown in a minimal ...
... 1.6.1.19) activity was determined with a colorimetric reaction according to Yonaha and Toyama (1980). Glutamate decarboxylase (GAD, EC 4.1.1.15) activity was measured by the method of Fonda (1985) as modified by Vézina et al. (1988). The bacteria used to measure GAD activity were grown in a minimal ...
primer on genetic epidemiology
... heritability with consideration of shared and non-shared environment effects by collecting diverse environmental variables [32]. Recently, Yang et al. has developed a GCTA model, a tool that estimates heritability using genome-wide association study (GWAS) data and unrelated individuals for both qua ...
... heritability with consideration of shared and non-shared environment effects by collecting diverse environmental variables [32]. Recently, Yang et al. has developed a GCTA model, a tool that estimates heritability using genome-wide association study (GWAS) data and unrelated individuals for both qua ...
Application of rpoB sequence similarity analysis, REP‐PCR and
... 2004). Therefore, studying phylogenetic relations and diversity in this novel bacterial genus is not only a taxonomical concern, but also a necessity in order to exploit its biotechnological potential completely. ...
... 2004). Therefore, studying phylogenetic relations and diversity in this novel bacterial genus is not only a taxonomical concern, but also a necessity in order to exploit its biotechnological potential completely. ...
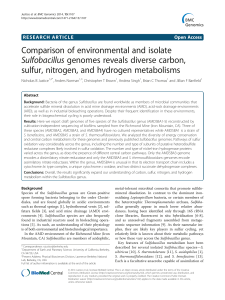
Comparison of environmental and isolate Sulfobacillus genomes
... regions were extracted and trimmed with Sickle (available https://github.com/najoshi/sickle), allowing only paired-end reads with length >60 and quality scores >20. For the reference database, 186 sequences were downloaded from the SILVA SSU database representing the 174 sequences of ‘Family XVII In ...
... regions were extracted and trimmed with Sickle (available https://github.com/najoshi/sickle), allowing only paired-end reads with length >60 and quality scores >20. For the reference database, 186 sequences were downloaded from the SILVA SSU database representing the 174 sequences of ‘Family XVII In ...
Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)
... Changes that affect the structure of chromosomes can cause problems with growth, development, and function of the body’s systems. These changes can affect many genes along the chromosome and disrupt the proteins made from those genes. Structural changes can occur during the formation of egg or sperm ...
... Changes that affect the structure of chromosomes can cause problems with growth, development, and function of the body’s systems. These changes can affect many genes along the chromosome and disrupt the proteins made from those genes. Structural changes can occur during the formation of egg or sperm ...
Keverne et al (2001)
... gene families while maintaining each cell’s specificity at the same time. Likewise, expansion of gene control mechanisms has required cooperative binding of transcription factors regulated by a variety of signaling pathways. When a number of these factors must be present for any of them to bind, thi ...
... gene families while maintaining each cell’s specificity at the same time. Likewise, expansion of gene control mechanisms has required cooperative binding of transcription factors regulated by a variety of signaling pathways. When a number of these factors must be present for any of them to bind, thi ...
Purine Biosynthesis. Big in Cell Division, Even
... for their synthesis also. Thus, it is reasonable to ask: why purine/ureides in some species and not in others and what advantages/disadvantages might accrue as a result of this trait? Despite the biochemical complexity of the pathway, the “cost” in terms of ATP and reductant expended per N assimilat ...
... for their synthesis also. Thus, it is reasonable to ask: why purine/ureides in some species and not in others and what advantages/disadvantages might accrue as a result of this trait? Despite the biochemical complexity of the pathway, the “cost” in terms of ATP and reductant expended per N assimilat ...
- Wiley Online Library
... 70% activity of the wild-type NHase still remained in this mutant (Table 1), indicating that these His residues only partially participate in P14K function. In addition, residue Arg96, which is conserved among the self-subunit swapping chaperones (Fig. 2), was also changed to investigate any effect ...
... 70% activity of the wild-type NHase still remained in this mutant (Table 1), indicating that these His residues only partially participate in P14K function. In addition, residue Arg96, which is conserved among the self-subunit swapping chaperones (Fig. 2), was also changed to investigate any effect ...
BLAST Exercise: Detecting and Interpreting Genetic Homology
... making when we use BLAST in our analysis. The theory of evolution proposes that all organisms descend by speciation from common ancestors. At the molecular level, an ancestral DNA sequence diverges over time (through accumulation of point mutations, duplications, deletions, transpositions, recombina ...
... making when we use BLAST in our analysis. The theory of evolution proposes that all organisms descend by speciation from common ancestors. At the molecular level, an ancestral DNA sequence diverges over time (through accumulation of point mutations, duplications, deletions, transpositions, recombina ...
recessive allele
... 2. By the law of segregation, the two alleles for a character are packaged into separate gametes 3. By the law of independent assortment, each pair of alleles segregates into gametes independently 4. Mendelian inheritance reflects rules of probability 5. Mendel discovered the particulate behavior of ...
... 2. By the law of segregation, the two alleles for a character are packaged into separate gametes 3. By the law of independent assortment, each pair of alleles segregates into gametes independently 4. Mendelian inheritance reflects rules of probability 5. Mendel discovered the particulate behavior of ...
Using a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism to Predict Bitter
... Some sequences are found at only one site -- a single locus - in the human genome. For many tandem repeats, the number of repeated units vary between individuals. Such loci are termed VNTRs. One VNTR in humans is a 17 bp sequence of DNA repeated between 70 and 450 times in the genome. The total numb ...
... Some sequences are found at only one site -- a single locus - in the human genome. For many tandem repeats, the number of repeated units vary between individuals. Such loci are termed VNTRs. One VNTR in humans is a 17 bp sequence of DNA repeated between 70 and 450 times in the genome. The total numb ...
Chapter 12
... Chapter 12 - DNA Technology and the Human Genome How can we use bacteria to manipulate DNA and protein? Recall how a bacterium defends itself when a bacteriophage injects its DNA into a bacterium… The bacterium has enzymes called restriction enzymes that attempt to cut up the bacteriophage DNA befo ...
... Chapter 12 - DNA Technology and the Human Genome How can we use bacteria to manipulate DNA and protein? Recall how a bacterium defends itself when a bacteriophage injects its DNA into a bacterium… The bacterium has enzymes called restriction enzymes that attempt to cut up the bacteriophage DNA befo ...
Chapter 15
... If these two genes were on different chromosomes, the alleles from the F1 dihybrid would sort into gametes independently, and we would expect to see equal numbers of the four types of offspring. If these two genes were on the same chromosome, we would expect each allele combination, B+ vg+ and b vg, ...
... If these two genes were on different chromosomes, the alleles from the F1 dihybrid would sort into gametes independently, and we would expect to see equal numbers of the four types of offspring. If these two genes were on the same chromosome, we would expect each allele combination, B+ vg+ and b vg, ...
Molecular genetics analysis of in vitro produced
... 1970’s with the first normal calf born in 1981 (Brackett et al. 1982), three years later after the first IVF baby was born in 1978 (Steptoe and Edwards 1978). However, until the beginning of 1990’s fewer than 150 calves were born and has not been used commercially at all in cattle (Seidel and Seidel ...
... 1970’s with the first normal calf born in 1981 (Brackett et al. 1982), three years later after the first IVF baby was born in 1978 (Steptoe and Edwards 1978). However, until the beginning of 1990’s fewer than 150 calves were born and has not been used commercially at all in cattle (Seidel and Seidel ...
Fishing for the Secrets of Vertebrate Evolution in Threespine
... 1994). Despite this diversity, sticklebacks from virtually any two populations from around the world can be crossed in the laboratory to generate a large number of viable and fertile progeny, thereby facilitating the forward genetic approach outlined in Figure 1 to identify the molecular basis of na ...
... 1994). Despite this diversity, sticklebacks from virtually any two populations from around the world can be crossed in the laboratory to generate a large number of viable and fertile progeny, thereby facilitating the forward genetic approach outlined in Figure 1 to identify the molecular basis of na ...
A comprehensive computational model of facilitated diffusion in
... the relevant molecules in a cell and the entire DNA sequence. This type of approach can address several questions, e.g. how crowding can influence the search process at genome-wide level, in a dynamical context (Chu et al., 2009) and not as static barriers (Li et al., 2009). In addition, one could i ...
... the relevant molecules in a cell and the entire DNA sequence. This type of approach can address several questions, e.g. how crowding can influence the search process at genome-wide level, in a dynamical context (Chu et al., 2009) and not as static barriers (Li et al., 2009). In addition, one could i ...
Mutations in the MicroRNA Complementarity Site
... ICU4 gene, which we previously mapped to chromosome 1 between the T27K12-Sp6 and nga128 microsatellite markers (Serrano-Cartagena et al., 2000). The genotyping of 130 icu4-1 homozygotes selected from an F2 mapping population derived from a Columbia-0 (Col-0) 3 icu4-1/icu4-1 cross allowed us to narro ...
... ICU4 gene, which we previously mapped to chromosome 1 between the T27K12-Sp6 and nga128 microsatellite markers (Serrano-Cartagena et al., 2000). The genotyping of 130 icu4-1 homozygotes selected from an F2 mapping population derived from a Columbia-0 (Col-0) 3 icu4-1/icu4-1 cross allowed us to narro ...
Van, C., Williams, J.S., Kunkel, T.A., and
... customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the co ...
... customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the co ...
Deciphering the molecular phylogenetics of the Asian honey bee
... The Asian honey bee, Apis cerana are honey producers and pollinators of cultivated crops and wild plants. They occur in Asia, from Afghanistan to China and from Japan to southern Indonesia. A. cerana have yellow stripes on their abdomen and are habituated to Indian plains. These are less aggressive ...
... The Asian honey bee, Apis cerana are honey producers and pollinators of cultivated crops and wild plants. They occur in Asia, from Afghanistan to China and from Japan to southern Indonesia. A. cerana have yellow stripes on their abdomen and are habituated to Indian plains. These are less aggressive ...
Identification of Genes Needed for Regeneration, Stem Cell
... such as regeneration and adult somatic stem cells. Therefore, studies of planarian biology will help the understanding of processes relevant to human development and health not easily studied in current invertebrate genetic systems. Neoblasts are the only known proliferating cells in adult planarian ...
... such as regeneration and adult somatic stem cells. Therefore, studies of planarian biology will help the understanding of processes relevant to human development and health not easily studied in current invertebrate genetic systems. Neoblasts are the only known proliferating cells in adult planarian ...
Yet viruses cannot be included in the tree of life - Université Paris-Sud
... genes (fIG. 1). Similarly, ESV-1 appears nested within the eukaryotic groups (the slowest evolving ESV-1 gene — paralogue 2 — even branches with a stramenopile sequence), far from any of the Mimivirus copies. This demonstrates that the viral clamp loader genes were recently, and independently, acqui ...
... genes (fIG. 1). Similarly, ESV-1 appears nested within the eukaryotic groups (the slowest evolving ESV-1 gene — paralogue 2 — even branches with a stramenopile sequence), far from any of the Mimivirus copies. This demonstrates that the viral clamp loader genes were recently, and independently, acqui ...
Forkhead Transcription Factors: Key Players in Development and
... This has been confirmed by NMR structural analysis of the DNA binding domains of three additional forkhead proteins: FOXC2, Foxd3, and FOXO4 (Jin et al., 1999; Marsden et al., 1998; van Dongen et al., 2000; Weigelt et al., 2001). While Clark et al. (1993) identified three ␣-helices in FoxA3, the NMR ...
... This has been confirmed by NMR structural analysis of the DNA binding domains of three additional forkhead proteins: FOXC2, Foxd3, and FOXO4 (Jin et al., 1999; Marsden et al., 1998; van Dongen et al., 2000; Weigelt et al., 2001). While Clark et al. (1993) identified three ␣-helices in FoxA3, the NMR ...
Autosomal aberrations associated with testicular dysgenesis or
... maps of Y related to spermatogenesis have been constructed [22]. In the present review it was indicated that there exist many latent aberrant autosomal regions which may be regarded as significant genetic sources that may be of help to the study of novel gene cloning and their functions. For example ...
... maps of Y related to spermatogenesis have been constructed [22]. In the present review it was indicated that there exist many latent aberrant autosomal regions which may be regarded as significant genetic sources that may be of help to the study of novel gene cloning and their functions. For example ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.