The Optimal Discovery Procedure II: Applications to Comparative
... are differentially expressed across varying biological conditions based on microarray data (3). It is now possible to simultaneously measure thousands of related variables or “features” in a variety of biological studies. A rich yet largely unknown structure is usually expected to be present among t ...
... are differentially expressed across varying biological conditions based on microarray data (3). It is now possible to simultaneously measure thousands of related variables or “features” in a variety of biological studies. A rich yet largely unknown structure is usually expected to be present among t ...
Chromatin Structure Is a Focus for Regulation 30.2
... • The SWI/SNF, RSC, and NURF remodeling complexes all are very large; • they are classified into groups according to the ATPase subunits. ...
... • The SWI/SNF, RSC, and NURF remodeling complexes all are very large; • they are classified into groups according to the ATPase subunits. ...
- Wiley Online Library
... to be naturally transformable, a number that is probably considerably underestimated (Johnsborg et al., 2007b). In the broadest sense, sex can be defined as any natural process that combines genes from more than one source in a single cell (Margulis & Sagan, 1986). According to this definition, all ...
... to be naturally transformable, a number that is probably considerably underestimated (Johnsborg et al., 2007b). In the broadest sense, sex can be defined as any natural process that combines genes from more than one source in a single cell (Margulis & Sagan, 1986). According to this definition, all ...
File
... DNA in your body cells is not passed on to your children. Germ cells, in contrast, are cells in your reproductive organs, the ovaries or the testes, that develop into gametes. Gametes are sex cells—ova, or eggs, in the female, and spermatozoa, or sperm cells, in the male. DNA in your gametes can be ...
... DNA in your body cells is not passed on to your children. Germ cells, in contrast, are cells in your reproductive organs, the ovaries or the testes, that develop into gametes. Gametes are sex cells—ova, or eggs, in the female, and spermatozoa, or sperm cells, in the male. DNA in your gametes can be ...
nar-02451-data-e-201
... methylated human genes and diseases from any free text without restriction to specific diseases. DEMGD consists of four components. The first is the text pre-processing component in which DEMGD splits free text into sentences, extracts genes, diseases and methylation words using dictionaries. The se ...
... methylated human genes and diseases from any free text without restriction to specific diseases. DEMGD consists of four components. The first is the text pre-processing component in which DEMGD splits free text into sentences, extracts genes, diseases and methylation words using dictionaries. The se ...
Types of chromosome abnormalities
... 45,XY,der(13;14)(q10;q10): A male with a balanced Roberstonian translocation of chromosomes 13 and 14. Karyotype shows that one normal 13 and one normal 14 are missing and replaced with a derivative chromosome 46,XY,t(11;22)(q23;q22): A male with a balanced reciprocal translocation between chromosom ...
... 45,XY,der(13;14)(q10;q10): A male with a balanced Roberstonian translocation of chromosomes 13 and 14. Karyotype shows that one normal 13 and one normal 14 are missing and replaced with a derivative chromosome 46,XY,t(11;22)(q23;q22): A male with a balanced reciprocal translocation between chromosom ...
development, the Linker histone H1 is essential for Drosophila
... a genetically tractable organism where H1 may prove to play an essential role. As mentioned, deletion of the yeast HHO1 gene does not lead to obvious phenotypic effects. Although linker histones are essential for embryonic development in mice, the existence of multiple, nonallelic mouse H1 variant g ...
... a genetically tractable organism where H1 may prove to play an essential role. As mentioned, deletion of the yeast HHO1 gene does not lead to obvious phenotypic effects. Although linker histones are essential for embryonic development in mice, the existence of multiple, nonallelic mouse H1 variant g ...
Pattern of diversity in the genomic region near the
... identity plots to the maize sequence are shown in Fig. 1B. A large region conserved between maize and sorghum extends for ⬇1 kb both 5⬘ and 3⬘ to the known maize cDNA sequence. As expected, less conservation is observed when maize is compared with the more distantly related rice OsTB1, although a sm ...
... identity plots to the maize sequence are shown in Fig. 1B. A large region conserved between maize and sorghum extends for ⬇1 kb both 5⬘ and 3⬘ to the known maize cDNA sequence. As expected, less conservation is observed when maize is compared with the more distantly related rice OsTB1, although a sm ...
Mechanistic Models of Cancer in the Space of Pathways
... Long lists of genes implicated in various stages of cancer exist for many different cancer types. Want to learn about the interaction of these genes via signaling pathways and functional relationships. ...
... Long lists of genes implicated in various stages of cancer exist for many different cancer types. Want to learn about the interaction of these genes via signaling pathways and functional relationships. ...
Identification and Microsatellite Markers of a Resistance Gene to
... is a complex locus, and composed of 4, 10, 2, and 5 alleles, respectively (Hsam et al., 1998; Zeller et al., 1998; Huang et al., 2003). In our study, we located the gene PmDR147 on the distal region of long arm of chromosome 2A. Powdery mildew resistance genes Pm4a and Pm4b are also located on chrom ...
... is a complex locus, and composed of 4, 10, 2, and 5 alleles, respectively (Hsam et al., 1998; Zeller et al., 1998; Huang et al., 2003). In our study, we located the gene PmDR147 on the distal region of long arm of chromosome 2A. Powdery mildew resistance genes Pm4a and Pm4b are also located on chrom ...
Gene quantification using real-time quantitative PCR
... DNA copy number measurements are important in determining the extent of genomic imbalance that underlies most malignancies. There are numerous techniques available for measuring DNA copy number in tumors; each method has specific advantages and disadvantages. Chromosomal CGH can detect imbalances ac ...
... DNA copy number measurements are important in determining the extent of genomic imbalance that underlies most malignancies. There are numerous techniques available for measuring DNA copy number in tumors; each method has specific advantages and disadvantages. Chromosomal CGH can detect imbalances ac ...
DRACULA2 is a dynamic nucleoporin with a role in
... Nonetheless, transgenic seedlings with a mild phenotype had longer hypocotyls than Ws-2 under W; importantly, in these lines the hypocotyl response to W+FR was attenuated compared with Ws-2 (Fig. 1E, Fig. S3C). Together, these results indicated that At1g10390 is the causal gene for the phenotype of ...
... Nonetheless, transgenic seedlings with a mild phenotype had longer hypocotyls than Ws-2 under W; importantly, in these lines the hypocotyl response to W+FR was attenuated compared with Ws-2 (Fig. 1E, Fig. S3C). Together, these results indicated that At1g10390 is the causal gene for the phenotype of ...
Abundance and distribution of Macrolide
... However, high antibiotic concentrations and bacterial densities in biological wastewater systems may favor the proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), which could pose health risks to humans via various pathways (Li et al., 2010; Munir et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2013). Our previous stu ...
... However, high antibiotic concentrations and bacterial densities in biological wastewater systems may favor the proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), which could pose health risks to humans via various pathways (Li et al., 2010; Munir et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2013). Our previous stu ...
Ancestry of neuronal monoamine transporters in the Metazoa
... was the ancestral monoamine transported by the different types of transporter? And what is the relationship between protostome OA and deuterostome NE transporters? To address these questions, we have used both existing and new structural and functional data on SLC6 monoamine transporters representin ...
... was the ancestral monoamine transported by the different types of transporter? And what is the relationship between protostome OA and deuterostome NE transporters? To address these questions, we have used both existing and new structural and functional data on SLC6 monoamine transporters representin ...
MEMCover: integrated analysis of mutual exclusivity and functional
... genes in the same functional pathway prompted the development of computational methods that utilize mutual exclusivity in the context of identifying pathways dysregulated in cancer as well as for the pathway independent identification of mutually exclusive cancer drivers (Ciriello et al., 2012, 2013 ...
... genes in the same functional pathway prompted the development of computational methods that utilize mutual exclusivity in the context of identifying pathways dysregulated in cancer as well as for the pathway independent identification of mutually exclusive cancer drivers (Ciriello et al., 2012, 2013 ...
Department of Biomedical Informatics
... The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) [pronounced "snip"] is the most common form of genetic variation. As the name suggests, each SNP is a difference in a single nucleotide (A,T,C,or G) of an individual's DNA sequence, such as having AAGG instead of ATGG. There may be from 1 to 10 million SNPs i ...
... The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) [pronounced "snip"] is the most common form of genetic variation. As the name suggests, each SNP is a difference in a single nucleotide (A,T,C,or G) of an individual's DNA sequence, such as having AAGG instead of ATGG. There may be from 1 to 10 million SNPs i ...
Molecular Genetics of Autosomal-Dominant Demyelinating Charcot
... mutations. Missense mutations in the PMP22 gene were originally described in two spontaneous mouse mutants termed trembler (Tr) and trembler-J (Tr-J) (Suter et al., 1992a,b) and the same mutations were subsequently found in humans; the Tr mutation (Gly150Asp) causing DSD in a mother and son (Ionases ...
... mutations. Missense mutations in the PMP22 gene were originally described in two spontaneous mouse mutants termed trembler (Tr) and trembler-J (Tr-J) (Suter et al., 1992a,b) and the same mutations were subsequently found in humans; the Tr mutation (Gly150Asp) causing DSD in a mother and son (Ionases ...
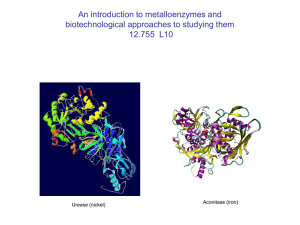
Metalloenzyme Functions
... structural and functional details on each COG and literature references, improvements of the COGNITOR program that is used to fit new proteins into the COGs, and classification of genomes and COGs constructed by ...
... structural and functional details on each COG and literature references, improvements of the COGNITOR program that is used to fit new proteins into the COGs, and classification of genomes and COGs constructed by ...
Title: FISH analysis comparing the gene composition of the Onager
... The onager [E. hemionus onager, EHO] and the domestic horse [E. caballus, ECA] have evolved over the course of 3.7 million years. The closely related EHO and ECA have diploid chromosome numbers of 2n=56 and 2n=64, respectively. Comparative gene mapping was done by FISH [fluorescent in-situ hybridiza ...
... The onager [E. hemionus onager, EHO] and the domestic horse [E. caballus, ECA] have evolved over the course of 3.7 million years. The closely related EHO and ECA have diploid chromosome numbers of 2n=56 and 2n=64, respectively. Comparative gene mapping was done by FISH [fluorescent in-situ hybridiza ...
Bioinformatics Dr. Víctor Treviño Pabellón Tec
... the amino acids have been changed in very similar sequences ...
... the amino acids have been changed in very similar sequences ...
High-Resolution Single-Copy Gene Fluorescence in Situ
... Koumbaris and Bass (2003) have developed a strategy to avoid the cross-hybridization of repetitive sequences using sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) BACs as probes to the maize chromosome 9 in an oat (Avena sativa)–maize addition line. The most direct and effective way to construct cytogenetic maps for orga ...
... Koumbaris and Bass (2003) have developed a strategy to avoid the cross-hybridization of repetitive sequences using sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) BACs as probes to the maize chromosome 9 in an oat (Avena sativa)–maize addition line. The most direct and effective way to construct cytogenetic maps for orga ...
The case for transgenerational epigenetic inheritance in humans
... to be passed to the next generation. Between generations, the epigenetic state of the genome undergoes two dynamic reprogramming events, first in the gametes of the parent and later in the zygote (Dean et al. 2003). This enables the zygote to acquire the totipotent state needed for the differentiati ...
... to be passed to the next generation. Between generations, the epigenetic state of the genome undergoes two dynamic reprogramming events, first in the gametes of the parent and later in the zygote (Dean et al. 2003). This enables the zygote to acquire the totipotent state needed for the differentiati ...
Genetic polymorphism of CSN2 gene in Banat White and Carpatina
... & Grosclaude, 1993; Neveu et al., 2002; Galliano et al., 2004; Cosenza et al., 2005; Caroli et al., 2006). The C variant differs from A in a single amino acid substitution Ala177 → Val177 of the mature protein. Mutation is not detectable on protein level (like IEF), because both amino acids are neut ...
... & Grosclaude, 1993; Neveu et al., 2002; Galliano et al., 2004; Cosenza et al., 2005; Caroli et al., 2006). The C variant differs from A in a single amino acid substitution Ala177 → Val177 of the mature protein. Mutation is not detectable on protein level (like IEF), because both amino acids are neut ...
Case report - HAL
... gene, encoding HNF1 (3). These mutations are inactivating and both alleles are mutated in tumors. Patients with an inherited mutation in one allele of HNF1 may develop maturity onset diabetes of the young type 3 (MODY3, OMIM#600496) and familial liver adenomatosis, when the second allele is inacti ...
... gene, encoding HNF1 (3). These mutations are inactivating and both alleles are mutated in tumors. Patients with an inherited mutation in one allele of HNF1 may develop maturity onset diabetes of the young type 3 (MODY3, OMIM#600496) and familial liver adenomatosis, when the second allele is inacti ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.