The Co-Evolution of Genes and Culture Pedigrees and the
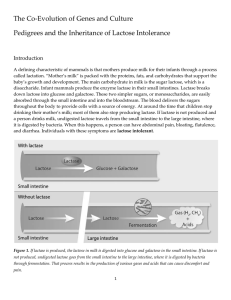
... lactose tolerant. They can also be referred to as being lactase persistent, meaning that lactase production persists beyond childhood. (People who no longer produce lactase as adults are called lactase nonpersistent.) Genetic studies suggest that lactose tolerance arose among human populations in th ...
... lactose tolerant. They can also be referred to as being lactase persistent, meaning that lactase production persists beyond childhood. (People who no longer produce lactase as adults are called lactase nonpersistent.) Genetic studies suggest that lactose tolerance arose among human populations in th ...
First report of a tetracycline-inducible gene
... Mollicutes are a class of wall-less bacteria having arisen from ancestors common to low-G+C Gram-positive bacteria by a so-called regressive evolution (Weisburg et al., 1989). Various species are pathogenic to man, animals and plants, in which they may cause severe diseases. Due to their small genom ...
... Mollicutes are a class of wall-less bacteria having arisen from ancestors common to low-G+C Gram-positive bacteria by a so-called regressive evolution (Weisburg et al., 1989). Various species are pathogenic to man, animals and plants, in which they may cause severe diseases. Due to their small genom ...
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology
... (Stanley et al. 1983). When M. capsulatus is used for SCP production, pMMO formation is preferred because this enzyme allows a more efficient carbon to biomass conversion than sMMO (Jørgensen and Degn 1987). Besides methane, both sMMO and pMMO oxidise several other substrates (Colby and Dalton 1978; ...
... (Stanley et al. 1983). When M. capsulatus is used for SCP production, pMMO formation is preferred because this enzyme allows a more efficient carbon to biomass conversion than sMMO (Jørgensen and Degn 1987). Besides methane, both sMMO and pMMO oxidise several other substrates (Colby and Dalton 1978; ...
BMC Developmental Biology
... Eya3 is one of four mammalian orthologous genes (Eya14) of eyes absent (eya) in Drosophila melanogaster [1,2]. Previous investigations demonstrated that a homozygous knockout of eya function in D. melanogaster results in severe embryonic defects and absence of compound eyes due to eye progenitor cel ...
... Eya3 is one of four mammalian orthologous genes (Eya14) of eyes absent (eya) in Drosophila melanogaster [1,2]. Previous investigations demonstrated that a homozygous knockout of eya function in D. melanogaster results in severe embryonic defects and absence of compound eyes due to eye progenitor cel ...
Constituent Grammatical Evolution
... improves the success rate of the algorithm. Consequently, it is not fair to compare GE with GP when semantically different search spaces are used. However, if the bias could emerge or be enforced during the evolution through some other mechanism (and not by design) this would be a different case; fo ...
... improves the success rate of the algorithm. Consequently, it is not fair to compare GE with GP when semantically different search spaces are used. However, if the bias could emerge or be enforced during the evolution through some other mechanism (and not by design) this would be a different case; fo ...
Genetics of Male Infertility - the Infertility Center of St. Louis
... and elsewhere, but the repetitive nucleotide sequences which characterize much of the Y chromosome made it very difficult with standard STS markers to define smaller deletions (104). The unusually repetitive sequence structure of the AZFc region of the Y plagued even the first attempts at constructi ...
... and elsewhere, but the repetitive nucleotide sequences which characterize much of the Y chromosome made it very difficult with standard STS markers to define smaller deletions (104). The unusually repetitive sequence structure of the AZFc region of the Y plagued even the first attempts at constructi ...
Conservation of Gene Order between Horse and Human X
... of ECAX. Cytogenetic alignment of the RH map was improved by fluorescent in situ hybridization mapping of six of the markers. The map integrates and refines the currently available genetic linkage, syntenic, and cytogenetic maps, and adds new loci. Comparison of the physical location of the 16 genes ...
... of ECAX. Cytogenetic alignment of the RH map was improved by fluorescent in situ hybridization mapping of six of the markers. The map integrates and refines the currently available genetic linkage, syntenic, and cytogenetic maps, and adds new loci. Comparison of the physical location of the 16 genes ...
RiboT
... 5) Evolvability of RiboT to identify gain-of-function mutations that facilitate synthesis of problematic protein sequences The model: SecM polypeptide presents a classic example of an amino acid sequence for which translation is problematic for the ribosome Programmed ribosome stalling at the Pro166 ...
... 5) Evolvability of RiboT to identify gain-of-function mutations that facilitate synthesis of problematic protein sequences The model: SecM polypeptide presents a classic example of an amino acid sequence for which translation is problematic for the ribosome Programmed ribosome stalling at the Pro166 ...
Alternative isoleucine synthesis pathway in
... Cyanothece 51142 (from the Joint Genome Institute: http:// www.jgi.doe.gov), the gene for threonine-ammonia lyase (EC 4.3.1.19) catalysing the conversion of threonine to 2ketobutyrate is missing. We also confirmed the absence of this gene from the Cyanothece 51142 genome by BLAST analysis (Table 2). ...
... Cyanothece 51142 (from the Joint Genome Institute: http:// www.jgi.doe.gov), the gene for threonine-ammonia lyase (EC 4.3.1.19) catalysing the conversion of threonine to 2ketobutyrate is missing. We also confirmed the absence of this gene from the Cyanothece 51142 genome by BLAST analysis (Table 2). ...
A family of diatom-like silicon transporters in the siliceous loricate
... to the S. diplocostata SITs over 193 amino acids. The remaining contigs, mostly shorter than 250 bp, encode protein fragments similar to short stretches within this region of the protein, but the fragmentary genome data precludes determination of how many genes they represent. We conclude that D. gr ...
... to the S. diplocostata SITs over 193 amino acids. The remaining contigs, mostly shorter than 250 bp, encode protein fragments similar to short stretches within this region of the protein, but the fragmentary genome data precludes determination of how many genes they represent. We conclude that D. gr ...
The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
... The First Studies of Linked Genes • To determine whether linked genes behave as predicted, Morgan performed an experiment using Drosophila, in which he mated two flies that were heterozygous for two sex-linked traits. • The results of this experiment included some fruit flies with novel phenotypes. ...
... The First Studies of Linked Genes • To determine whether linked genes behave as predicted, Morgan performed an experiment using Drosophila, in which he mated two flies that were heterozygous for two sex-linked traits. • The results of this experiment included some fruit flies with novel phenotypes. ...
Monoallelic Expression and Dominance
... methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme digestion and by genomic bisulfite sequencing (Clark et al., 1994). We detected no consistent differences between SaSa and SaSb plants in the methylation state of SCRa within the two exons and one intron of the gene and within approximately 500 bp of sequence ...
... methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme digestion and by genomic bisulfite sequencing (Clark et al., 1994). We detected no consistent differences between SaSa and SaSb plants in the methylation state of SCRa within the two exons and one intron of the gene and within approximately 500 bp of sequence ...
Bacteroides mobilizable and conjugative genetic elements
... rteA and rteB have been shown to be in the same operon as tetQ, production of these proteins is presumably due to translational coupling one ribosomes begin to translate the operon mRNA. RteA and RteB have no role in tetracycline regulation of operon expression. This was somewhat surprising because ...
... rteA and rteB have been shown to be in the same operon as tetQ, production of these proteins is presumably due to translational coupling one ribosomes begin to translate the operon mRNA. RteA and RteB have no role in tetracycline regulation of operon expression. This was somewhat surprising because ...
Bioinformatics Toolbox
... Open environment — Access the source code for the Bioinformatics Toolbox functions. The toolbox includes many of the basic bioinformatics functions you will need to use, and it includes prototypes for some of the more advanced functions. Modify these functions to create your own custom solutions. In ...
... Open environment — Access the source code for the Bioinformatics Toolbox functions. The toolbox includes many of the basic bioinformatics functions you will need to use, and it includes prototypes for some of the more advanced functions. Modify these functions to create your own custom solutions. In ...
The CHARGE Targeted Sequencing Study
... in part) the observed rare variant association at any of the 5 genes at 11p11.2. The conditional analysis was conducted by including the 2 common variants along with the rare variants at each of 5 gene regions in SKAT. In CHS and FHS, we used rs794584 and rs10838687, and in ARIC study, rs4752979 was ...
... in part) the observed rare variant association at any of the 5 genes at 11p11.2. The conditional analysis was conducted by including the 2 common variants along with the rare variants at each of 5 gene regions in SKAT. In CHS and FHS, we used rs794584 and rs10838687, and in ARIC study, rs4752979 was ...
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK MANAGEMENT AUTHORITY DECISION
... The Committee considers that the eradication of the organisms, should escape occur and a population establish, could be difficult since they may not be able to be detected, and any eradication method is likely to adversely effect other microorganisms already present in that environment. The Committe ...
... The Committee considers that the eradication of the organisms, should escape occur and a population establish, could be difficult since they may not be able to be detected, and any eradication method is likely to adversely effect other microorganisms already present in that environment. The Committe ...
Differential expression of six genes in fat
... A-FABP was found to be upregulated in a selected highfat line of Duroc pigs when compared to the low-fat Duroc group (Canovas et al., 2010). Differential A-FABP expression was also detected between Berkshire and Yorkshire pigs, where highest levels were measured in Berkshire, a breed well known for ...
... A-FABP was found to be upregulated in a selected highfat line of Duroc pigs when compared to the low-fat Duroc group (Canovas et al., 2010). Differential A-FABP expression was also detected between Berkshire and Yorkshire pigs, where highest levels were measured in Berkshire, a breed well known for ...
Solid Tumour Section Soft tissue tumors: an overview in Oncology and Haematology
... detected by conventional G-banding and affect the seemingly normal chromosome 11. Atypical lipomatous tumor/Well-differentiated liposarcoma: Supernumerary ring or/and giant marker chromosomes have been observed mostly as the sole chromosome aberration. Cells containing ring and/or giant markers vary ...
... detected by conventional G-banding and affect the seemingly normal chromosome 11. Atypical lipomatous tumor/Well-differentiated liposarcoma: Supernumerary ring or/and giant marker chromosomes have been observed mostly as the sole chromosome aberration. Cells containing ring and/or giant markers vary ...
Chapter 11 Mutation: The Source of Genetic Variation
... Chapter 11 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings ©2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning ...
... Chapter 11 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings ©2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning ...
The Optimal Discovery Procedure II: Applications to Comparative
... are differentially expressed across varying biological conditions based on microarray data (3). It is now possible to simultaneously measure thousands of related variables or “features” in a variety of biological studies. A rich yet largely unknown structure is usually expected to be present among t ...
... are differentially expressed across varying biological conditions based on microarray data (3). It is now possible to simultaneously measure thousands of related variables or “features” in a variety of biological studies. A rich yet largely unknown structure is usually expected to be present among t ...
Chapter 1 A Perspective on Human Genetics
... Chapter 11 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings ©2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning ...
... Chapter 11 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings ©2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning ...
Expressed Sequence Tag (EST)
... • High redundancy in the data (“native” databases: clone frequency reflects mRNA abundance) • Databases are skewed for sequences near 3’-end of mRNAs (normalization) • For most ESTs, no indication as to the gene from which they are derived ...
... • High redundancy in the data (“native” databases: clone frequency reflects mRNA abundance) • Databases are skewed for sequences near 3’-end of mRNAs (normalization) • For most ESTs, no indication as to the gene from which they are derived ...
Biomolecular chemistry 3. Translating the genetic code
... opposed to RNA, level) which may or may not be in the correct frame. If the next ATG encodes an in frame methionine, the translated protein will be missing the N-terminal sequence between its first two methionine residues. If the next ATG is out of frame (see +2 translation) then a nonsensical prote ...
... opposed to RNA, level) which may or may not be in the correct frame. If the next ATG encodes an in frame methionine, the translated protein will be missing the N-terminal sequence between its first two methionine residues. If the next ATG is out of frame (see +2 translation) then a nonsensical prote ...
Metabolomic and Gene Expression Profiles Exhibit Modular Genetic
... profiles and metabolomic profiles and found that the genotype-by-diet interaction effect explained a surprisingly large portion of the total phenotypic variance (Figure S1) (Reed et al. 2010, 2014). Building from the dataset originally reported in Reed et al. (2014), here we have presented the analyse ...
... profiles and metabolomic profiles and found that the genotype-by-diet interaction effect explained a surprisingly large portion of the total phenotypic variance (Figure S1) (Reed et al. 2010, 2014). Building from the dataset originally reported in Reed et al. (2014), here we have presented the analyse ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.