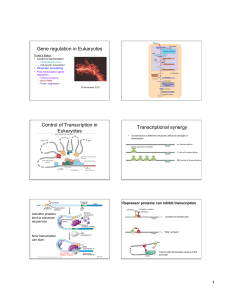
Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Control of Transcription in
... ~1.5% of the human genome, but ~90% of the genome appears to be transcribed… ...
... ~1.5% of the human genome, but ~90% of the genome appears to be transcribed… ...
Leukaemia Section t(7;19)(q34;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Several helix-loop-helix (HLH) proteins are proposed to function as transcriptionnal regulatory factors based on their ability to bind in vitro the E-box motif of transcriptional enhancers. The enhancer binding HLH proteins include E47 and E12, two distinct but related polypeptides encoded by E2A ge ...
... Several helix-loop-helix (HLH) proteins are proposed to function as transcriptionnal regulatory factors based on their ability to bind in vitro the E-box motif of transcriptional enhancers. The enhancer binding HLH proteins include E47 and E12, two distinct but related polypeptides encoded by E2A ge ...
Medical Genetics 2013
... A. The mitochondrial genome comprises circular double-stranded DNA containing ~ 16.6 k bp. B. The mitochondrial genome includes 37 genes: 13 protein coding genes, 22 tRNA genes and 2 ribosomal RNA genes. C. Mitochondrial genes do not contain introns. D. Mitochondria use the universal genetic code fo ...
... A. The mitochondrial genome comprises circular double-stranded DNA containing ~ 16.6 k bp. B. The mitochondrial genome includes 37 genes: 13 protein coding genes, 22 tRNA genes and 2 ribosomal RNA genes. C. Mitochondrial genes do not contain introns. D. Mitochondria use the universal genetic code fo ...
File - Wildcat Biology Review
... A group of individuals belonging to a single species that lives together in a defined area is termed a(an) ...
... A group of individuals belonging to a single species that lives together in a defined area is termed a(an) ...
9 Genetics Vocabulary
... 18. dihybrid cross—predicts the inheritance of TWO traits together (16 boxes) 19. codominance—both alleles are expressed in the heterozygote 20. incomplete dominance—neither allele is expressed; instead, the phenotype of the heterozygote is in between that of the two homozygotes 21. multiple alleles ...
... 18. dihybrid cross—predicts the inheritance of TWO traits together (16 boxes) 19. codominance—both alleles are expressed in the heterozygote 20. incomplete dominance—neither allele is expressed; instead, the phenotype of the heterozygote is in between that of the two homozygotes 21. multiple alleles ...
Point mutation - Chavis Biology
... frame before it is ready to be translated. Often, this enzyme can catch a mutation before it goes through translation, but not always. If the mutation is caught and correct, the organism will never be affected. However, if it doesn’t then the organism will be affected. ...
... frame before it is ready to be translated. Often, this enzyme can catch a mutation before it goes through translation, but not always. If the mutation is caught and correct, the organism will never be affected. However, if it doesn’t then the organism will be affected. ...
populations
... some 400 kilometres south from where it was two decades earlier. Therefore we can see that global climate change can directly affect the alleles in a population. ...
... some 400 kilometres south from where it was two decades earlier. Therefore we can see that global climate change can directly affect the alleles in a population. ...
221_exam_3_2003
... C. blocking host processes may trigger apoptosis. D. blocking host transcription will block cap “stealing”. ____ Mobilizable plasmids require a self-transmissible “helper” plasmid because they lack which of the following? A. oriT B. proteins required to nick the plasmid at its oriT C. genes that enc ...
... C. blocking host processes may trigger apoptosis. D. blocking host transcription will block cap “stealing”. ____ Mobilizable plasmids require a self-transmissible “helper” plasmid because they lack which of the following? A. oriT B. proteins required to nick the plasmid at its oriT C. genes that enc ...
CP Biology Cumulative Final Exam Study Guide write all answers on
... 21. What does the term semipermeable mean? 22. What is the function of the plasma membrane? 23. What is the function of the proteins embedded in the plasma membrane? 24. Explain the terms active transport and passive transport. 25. Describe what would happen to a plant cell placed in hypotonic and h ...
... 21. What does the term semipermeable mean? 22. What is the function of the plasma membrane? 23. What is the function of the proteins embedded in the plasma membrane? 24. Explain the terms active transport and passive transport. 25. Describe what would happen to a plant cell placed in hypotonic and h ...
AP Biology - Renton School District
... 11. Compare and contrast a genetic map, a linkage map, and a cytogenetic map. ...
... 11. Compare and contrast a genetic map, a linkage map, and a cytogenetic map. ...
I have put together a recommendation for teacher assignments
... Now that it has been shown that DNA is what makes up the genetic material, it is time to look more closely at genes. What is a gene? Genes are really packages of information that tell a cell how to make proteins. Proteins are polymers, or long chains, of amino acids. As you learned already, there ar ...
... Now that it has been shown that DNA is what makes up the genetic material, it is time to look more closely at genes. What is a gene? Genes are really packages of information that tell a cell how to make proteins. Proteins are polymers, or long chains, of amino acids. As you learned already, there ar ...
PowerPoint
... However, this was only the first step (gathering information) A lot of new stuff coming from it ...
... However, this was only the first step (gathering information) A lot of new stuff coming from it ...
Implications of Biology
... – Research indicates that denied the benefits of recombining with the X, the Y recombines with itself: “The Y chromosome has been shedding genes furiously over the course of evolutionary time, and it is now a fraction of the size of its partner, the X chromosome. . . . The decay of the Y stems from ...
... – Research indicates that denied the benefits of recombining with the X, the Y recombines with itself: “The Y chromosome has been shedding genes furiously over the course of evolutionary time, and it is now a fraction of the size of its partner, the X chromosome. . . . The decay of the Y stems from ...
Beyond the double helix
... that is adopted at the ragged ends of chromosomes, known as telomeres, where the two sister strands give way to a lone string. Using X-ray crystallography, he showed that this single strand can weave itself into a tidy propeller-like loop, which may help to prevent the molecule from fraying away4.“I ...
... that is adopted at the ragged ends of chromosomes, known as telomeres, where the two sister strands give way to a lone string. Using X-ray crystallography, he showed that this single strand can weave itself into a tidy propeller-like loop, which may help to prevent the molecule from fraying away4.“I ...
Protein Synthesis-Part Two - Halton District School Board
... • Each sequence of nucleotides has a correct reading frame, or grouping of codons. This means that knowing where to start transcription and translation is essential. • There is no mechanism for re-setting transcription or translation if they do not start at the right place. ...
... • Each sequence of nucleotides has a correct reading frame, or grouping of codons. This means that knowing where to start transcription and translation is essential. • There is no mechanism for re-setting transcription or translation if they do not start at the right place. ...
Zebrafish Jeopardy
... DNA Duplication for 300 This component is required for replication in bacterial cells. Its function is to move along the DNA strand ahead of the replication fork, while breaking and sealing bonds in the DNA strand in order to reduce the stress of the twisting. What is DNA gyrase? Home ...
... DNA Duplication for 300 This component is required for replication in bacterial cells. Its function is to move along the DNA strand ahead of the replication fork, while breaking and sealing bonds in the DNA strand in order to reduce the stress of the twisting. What is DNA gyrase? Home ...
Honors Biology: Genetics Quiz 1
... A) RNA DNA Trait Protein B) RNA Protein Trait DNA C) Trait Protein RNA DNA D) DNA RNA Protein Trait _____ 18. In sheep, white fur is dominant to black fur. If two white sheep produce a black offspring, the parent’s genotypes for color must be: A) Heterozygous. B) Homozygous w ...
... A) RNA DNA Trait Protein B) RNA Protein Trait DNA C) Trait Protein RNA DNA D) DNA RNA Protein Trait _____ 18. In sheep, white fur is dominant to black fur. If two white sheep produce a black offspring, the parent’s genotypes for color must be: A) Heterozygous. B) Homozygous w ...
Defining Genes in the Era of Genomics
... and encompasses both coding segment and cis regulatory region. Based on the definition, in principle, it should be possible to use straightforward criteria to identify genes in genomic sequence. Below we discuss five commonly used criteria and why application of them is not, in fact, straightforward ...
... and encompasses both coding segment and cis regulatory region. Based on the definition, in principle, it should be possible to use straightforward criteria to identify genes in genomic sequence. Below we discuss five commonly used criteria and why application of them is not, in fact, straightforward ...
Darwinian Reductionism and Genocentrism
... events. It has not yet. It has been strongly confirmed by homologies in development across species, families, genera, families, orders and kingdoms, e.g. eyeless It has been confirmed by variations within genera—long germ band/short germ band insects ...
... events. It has not yet. It has been strongly confirmed by homologies in development across species, families, genera, families, orders and kingdoms, e.g. eyeless It has been confirmed by variations within genera—long germ band/short germ band insects ...
Biology Chapter 6 Advanced Genetics The Continuity of Life: Part II
... Many ova are fertilized simultaneously, one (sometimes 4) is selected for implantation, and the others are thrown away. The effect IVF will have on a biblical view of marriage motherhood will be affected lead to the breakdown of the family unit ...
... Many ova are fertilized simultaneously, one (sometimes 4) is selected for implantation, and the others are thrown away. The effect IVF will have on a biblical view of marriage motherhood will be affected lead to the breakdown of the family unit ...
lecture 2
... is transcribed from the DNA, ribosomes attach and begin translating the mRNA into protein. Thus, transcription and translation are "coupled" in prokaryotes. 2. Operons Many transcriptional units encode more than one gene, which is termed an OPERON. Genes with related functions are often located toge ...
... is transcribed from the DNA, ribosomes attach and begin translating the mRNA into protein. Thus, transcription and translation are "coupled" in prokaryotes. 2. Operons Many transcriptional units encode more than one gene, which is termed an OPERON. Genes with related functions are often located toge ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.