Genetics Powerpoint 2/7/17
... • He made observations of his father’s orchard and decided he could predict the kinds of flowers a plant could produce…if he knew something about the parent ...
... • He made observations of his father’s orchard and decided he could predict the kinds of flowers a plant could produce…if he knew something about the parent ...
Gene Section SEPT5 (septin 5) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Other names: hCDCRel-1 (human cell division cycle regulation 1); PNUTL1 (peanut (drosophila)- like 1); CDCREL; AF22 (ALL1 fused gene from chromosome ...
... Other names: hCDCRel-1 (human cell division cycle regulation 1); PNUTL1 (peanut (drosophila)- like 1); CDCREL; AF22 (ALL1 fused gene from chromosome ...
Chapter 13- RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Some mutations are caused by physical agents in the environment, called mutagens The effects of mutations can have little/no effect, or can negatively disrupt gene ...
... Some mutations are caused by physical agents in the environment, called mutagens The effects of mutations can have little/no effect, or can negatively disrupt gene ...
Chapter 13- RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Some mutations are caused by physical agents in the environment, called mutagens The effects of mutations can have little/no effect, or can negatively disrupt gene ...
... Some mutations are caused by physical agents in the environment, called mutagens The effects of mutations can have little/no effect, or can negatively disrupt gene ...
DNA Test Review What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which
... 12. Why is tRNA important in translation? 13. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? 14. How many amino acids does this DNA sequence represent: TAAAGGCCC? 15. How can only 20 amino acids make thousands of proteins? 16. What is the ratio of A:T and C:G? 17. Why is DNA replication called semicons ...
... 12. Why is tRNA important in translation? 13. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? 14. How many amino acids does this DNA sequence represent: TAAAGGCCC? 15. How can only 20 amino acids make thousands of proteins? 16. What is the ratio of A:T and C:G? 17. Why is DNA replication called semicons ...
Unit I
... Each link of a protein chain is a simple organic unit called an amino acid. There are 20 amino acids that are used to form protein chains. The proteins we eat are broken down and then rearranged into the proteins we need. DNA, a type of nucleic acid, is a long, double-stranded molecule made up of un ...
... Each link of a protein chain is a simple organic unit called an amino acid. There are 20 amino acids that are used to form protein chains. The proteins we eat are broken down and then rearranged into the proteins we need. DNA, a type of nucleic acid, is a long, double-stranded molecule made up of un ...
Card Match
... A person who has the recessive allele for a characteristic or disease and can pass it on, but who does not have the characteristic or disease itself. ...
... A person who has the recessive allele for a characteristic or disease and can pass it on, but who does not have the characteristic or disease itself. ...
Transcription/Translation foldable
... foldable Fold your paper so the two ends meet in the middle. Label Transcription on one side and Translation on the other. ...
... foldable Fold your paper so the two ends meet in the middle. Label Transcription on one side and Translation on the other. ...
DNA Handout KEY - Iowa State University
... start codon and what amino acid does it code for? 3 genes that code for one amino acid. The same code is used for all organisms, viruses, chloroplast, mitochondria AUG- methionine 16. The substitution of the nitrogenous base _Thymine___ for ___Uracil___ is a key difference in DNA and RNA. 17. What a ...
... start codon and what amino acid does it code for? 3 genes that code for one amino acid. The same code is used for all organisms, viruses, chloroplast, mitochondria AUG- methionine 16. The substitution of the nitrogenous base _Thymine___ for ___Uracil___ is a key difference in DNA and RNA. 17. What a ...
Evolution and Natural Selection
... Organisms can be affected by their environment. Variation caused by the environment is not heritable, so it is not subject to natural selection. However, the ability of organisms to develop differently in different environments can be genetic. This means organisms can evolve to be flexible. Plants a ...
... Organisms can be affected by their environment. Variation caused by the environment is not heritable, so it is not subject to natural selection. However, the ability of organisms to develop differently in different environments can be genetic. This means organisms can evolve to be flexible. Plants a ...
Gene Section PMS1 (PMS1 postmeiotic segregation increased 1 (S. cerevisiae))
... Amino acids: 932. Molecular Weight: 105830 Daltons. PMS1 is a protein involved in the mismatch repair process after DNA replication. ...
... Amino acids: 932. Molecular Weight: 105830 Daltons. PMS1 is a protein involved in the mismatch repair process after DNA replication. ...
REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION
... When a cell no longer needs the protein, the gene is inactivated and transcription and translation can’t occur Some genes are active in some cells but not in others. ...
... When a cell no longer needs the protein, the gene is inactivated and transcription and translation can’t occur Some genes are active in some cells but not in others. ...
Notes - marric
... –Gene Mapping Tracking crossing over helps determine where genes are located on the chromosome –Genes that are far apart have a ______________chance of crossing over –Genes that are closer have a _________________________ chance of crossing over •Genes that stay together are said to be _____________ ...
... –Gene Mapping Tracking crossing over helps determine where genes are located on the chromosome –Genes that are far apart have a ______________chance of crossing over –Genes that are closer have a _________________________ chance of crossing over •Genes that stay together are said to be _____________ ...
FREE Sample Here
... a. demonstrate the connection between Mendel’s principles of inheritance and evolution. *b. propose that evolution occurs by natural selection. c. develop the theory of evolution, based on earlier theories of ...
... a. demonstrate the connection between Mendel’s principles of inheritance and evolution. *b. propose that evolution occurs by natural selection. c. develop the theory of evolution, based on earlier theories of ...
Exam II
... talked about in class : Transponson tagging; homologous recombination; and the Arabidopsis model developed by Dr Young (insertion of t-DNA). If you were given a gene from the RNAi study involving C. elegans, and all you knew about that gene is its sequence and that it produces a phenotype that disru ...
... talked about in class : Transponson tagging; homologous recombination; and the Arabidopsis model developed by Dr Young (insertion of t-DNA). If you were given a gene from the RNAi study involving C. elegans, and all you knew about that gene is its sequence and that it produces a phenotype that disru ...
Chapter 17 * from gene to protein
... amino acid, creating 43 (64) possible code words. During transcription, one DNA strand, the template strand, provides a template for ordering the sequence of nucleotide bases in an mRNA transcript. The mRNA base triplets are called codons. Each codon specifies which one of the 20 amino acids will be ...
... amino acid, creating 43 (64) possible code words. During transcription, one DNA strand, the template strand, provides a template for ordering the sequence of nucleotide bases in an mRNA transcript. The mRNA base triplets are called codons. Each codon specifies which one of the 20 amino acids will be ...
Worms Have as Many Genes as We Do? But They Lack Alu
... Although Ast and his research team discovered that while Alu sequences are familiar to the slicing system, only in half of these incidences, the system deals with the sequences as “coding”, and adjoins them to existing genes, and so a new protein is formed. In the other half of the cases, the splici ...
... Although Ast and his research team discovered that while Alu sequences are familiar to the slicing system, only in half of these incidences, the system deals with the sequences as “coding”, and adjoins them to existing genes, and so a new protein is formed. In the other half of the cases, the splici ...
File - NCEA Level 3 Biology
... few tens of bases. The significance of minisatellites is that the patterns in different people or other organisms vary considerably. These can be electrophoresed to identify or fingerprint individuals ...
... few tens of bases. The significance of minisatellites is that the patterns in different people or other organisms vary considerably. These can be electrophoresed to identify or fingerprint individuals ...
Test review Warm-up
... SYSTEM (don’t eat things that you are allergic too…..70% of immune system is in ...
... SYSTEM (don’t eat things that you are allergic too…..70% of immune system is in ...
PERSONAL GENOMICS
... “They fully sequenced the genes of both his cancer cells and healthy cells for comparison, and at the same time analyzed his RNA, a close chemical cousin to DNA, for clues to what his genes were doing.” “And they found a culprit - a normal gene that was in overdrive, churning out huge amounts of a p ...
... “They fully sequenced the genes of both his cancer cells and healthy cells for comparison, and at the same time analyzed his RNA, a close chemical cousin to DNA, for clues to what his genes were doing.” “And they found a culprit - a normal gene that was in overdrive, churning out huge amounts of a p ...
Mutagenesis and Genetic Screens
... that could be involved in the process under study • Last step: confirm gene identification – Rescue of phenotype – Mutations in same gene in different alleles ...
... that could be involved in the process under study • Last step: confirm gene identification – Rescue of phenotype – Mutations in same gene in different alleles ...
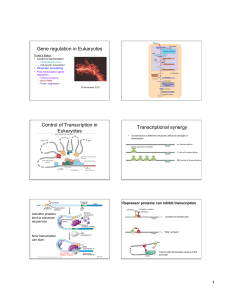
Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Control of Transcription in
... ~1.5% of the human genome, but ~90% of the genome appears to be transcribed… ...
... ~1.5% of the human genome, but ~90% of the genome appears to be transcribed… ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.