NonMendelian Inheritance Patterns
... how much and in what order you mix them on a white page dictates the final color. • http://www.thetech.org/genetics/ask.php?id=203 ...
... how much and in what order you mix them on a white page dictates the final color. • http://www.thetech.org/genetics/ask.php?id=203 ...
Biology
... f. teach someone else the concepts discussed g. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. explain the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics 2. summarize the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment 3. predi ...
... f. teach someone else the concepts discussed g. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. explain the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics 2. summarize the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment 3. predi ...
exercise mendelian-genetics
... • Differentiate between homozygous and heterozygous genotypes • Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype • Describe the difference between monohybrid and dihybrid cross • Apply Mendel’s laws to several crosses • Demonstrate how chromosome alignment in metaphase I affects the alleles in ...
... • Differentiate between homozygous and heterozygous genotypes • Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype • Describe the difference between monohybrid and dihybrid cross • Apply Mendel’s laws to several crosses • Demonstrate how chromosome alignment in metaphase I affects the alleles in ...
Genetics - My CCSD
... A. Heredity = passing of characteristics from parent to offspring a.Trait = characteristics that are inherited b. Gregor Mendel = “Father of Genetics” (1822-1884) I. Monk, scientist, gardener, teacher II. Studied thousand of pea plants; with distinct traits III. Simplify problems; meticulous data co ...
... A. Heredity = passing of characteristics from parent to offspring a.Trait = characteristics that are inherited b. Gregor Mendel = “Father of Genetics” (1822-1884) I. Monk, scientist, gardener, teacher II. Studied thousand of pea plants; with distinct traits III. Simplify problems; meticulous data co ...
Ch11 notes Master
... hybrids: offspring (F1) of crosses between parents (P) with different traits. true-bred short male(tt) X true-bred tall mom(TT) ...
... hybrids: offspring (F1) of crosses between parents (P) with different traits. true-bred short male(tt) X true-bred tall mom(TT) ...
What are the advantages to sexual reproduction? Disadvantages?
... recessive alleles are present; can be masked or suppressed by dominant ...
... recessive alleles are present; can be masked or suppressed by dominant ...
Ch 11 Standards Test Practice
... B It is coded for a sex-linked gene. C It affects only females. D The trait shows polygenic inheritance. individual has type AB blood. His father has 9 An type A blood and his mother has type B blood. What is the individual’s phenotype an example of? A simple recessive heredity B simple dominant her ...
... B It is coded for a sex-linked gene. C It affects only females. D The trait shows polygenic inheritance. individual has type AB blood. His father has 9 An type A blood and his mother has type B blood. What is the individual’s phenotype an example of? A simple recessive heredity B simple dominant her ...
BIO 290
... Chapter 4: Mapping Eukaryote Chromosomes by Recombination Terminology: linked genes, loci, crossover, cis and trans conformations, genetic map unit/centimorgan, recombinant frequency (RF), molecular markers, SNPs, RFLPs, haplotype, linkage disequilibrium, VNTRs, microsatellites, minisatellites, Lod ...
... Chapter 4: Mapping Eukaryote Chromosomes by Recombination Terminology: linked genes, loci, crossover, cis and trans conformations, genetic map unit/centimorgan, recombinant frequency (RF), molecular markers, SNPs, RFLPs, haplotype, linkage disequilibrium, VNTRs, microsatellites, minisatellites, Lod ...
Class Starter
... develop different traits? • Certain offspring may be born with a combination of genes that is more successful than his/her parents or siblings. • This will make the individual ‘more fit’ and therefore more likely to survive in their environment and pass on their DNA to future ...
... develop different traits? • Certain offspring may be born with a combination of genes that is more successful than his/her parents or siblings. • This will make the individual ‘more fit’ and therefore more likely to survive in their environment and pass on their DNA to future ...
Mendel and Genetics
... • Heterozygous- zygote or individual whose genotype contains 2 different or contrasting forms of an allele (like a gene for blue eyes and a gene for brown eyes) • Homozygous- zygote or individual with 2 identical genes for a trait. ...
... • Heterozygous- zygote or individual whose genotype contains 2 different or contrasting forms of an allele (like a gene for blue eyes and a gene for brown eyes) • Homozygous- zygote or individual with 2 identical genes for a trait. ...
BSC 219
... Determined by multiple genetic and environmental factors, and can be measured in whole numbers. Animal litter size. Threshold characteristics Measured by presence or absence Susceptibility to disease Types of Quantitative Characteristics Polygenic inheritance Refers to quantitative characteristics c ...
... Determined by multiple genetic and environmental factors, and can be measured in whole numbers. Animal litter size. Threshold characteristics Measured by presence or absence Susceptibility to disease Types of Quantitative Characteristics Polygenic inheritance Refers to quantitative characteristics c ...
Concept 2: Living things inherit TRAITS in PATTERNS* We can
... •Seed color •Flower color •Pod color • Using one trait at a time, Mendel crossed two plants who were opposite forms of the same trait • Example: Trait – plant height ▫ Tall plant vs. a dwarf plant ...
... •Seed color •Flower color •Pod color • Using one trait at a time, Mendel crossed two plants who were opposite forms of the same trait • Example: Trait – plant height ▫ Tall plant vs. a dwarf plant ...
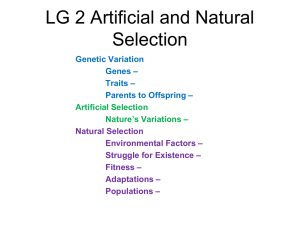
Presentation: Artificial and Natural Selection
... Describe the effects of environmental factors on artificial and natural selection. ...
... Describe the effects of environmental factors on artificial and natural selection. ...
11-1 The Work of Mendel
... • Ex: probability of flipping a coin to heads = ½ or _____% • Probability of head 3 times in a row = ½ x ½ x ½ = _____ • The ________ the number or trials, the closer to the expected ratio • _______ outcomes do not affect _______ outcomes • Alleles segregate randomly (like a coin) ...
... • Ex: probability of flipping a coin to heads = ½ or _____% • Probability of head 3 times in a row = ½ x ½ x ½ = _____ • The ________ the number or trials, the closer to the expected ratio • _______ outcomes do not affect _______ outcomes • Alleles segregate randomly (like a coin) ...
Mendel
... Pictorial genealogy of a family showing the inheritance of a particular trait Individuals are shown and connected using symbols on pg 88 Can be used ...
... Pictorial genealogy of a family showing the inheritance of a particular trait Individuals are shown and connected using symbols on pg 88 Can be used ...
Presentation
... from parents to offspring • traits = characteristics that are inherited • Genetics = branch of biology that studies ...
... from parents to offspring • traits = characteristics that are inherited • Genetics = branch of biology that studies ...
Networks of Genes, Epistasis and a Functionally
... Autism is highly genotypically heterogenous disorder, to which variants in a large number of genes likely to contribute. Identifying the molecular pathways in which these genes act provides not only insight into the pathoetiology but also translational routes to diagnosis, patient stratification and ...
... Autism is highly genotypically heterogenous disorder, to which variants in a large number of genes likely to contribute. Identifying the molecular pathways in which these genes act provides not only insight into the pathoetiology but also translational routes to diagnosis, patient stratification and ...
STUDY GUIDE-5Mendelian Genetics
... a. segregation and independent assortment apply to genes on different chromosomes b. adjacent genes on the same chromosome tend to move as a unit c. the pattern of inheritance (monohybrid, dihybrid, sex-linked, and linked genes) can be predicted from genotype/phenotype data 14.3 I can use an example ...
... a. segregation and independent assortment apply to genes on different chromosomes b. adjacent genes on the same chromosome tend to move as a unit c. the pattern of inheritance (monohybrid, dihybrid, sex-linked, and linked genes) can be predicted from genotype/phenotype data 14.3 I can use an example ...
The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
... Correlating Behavior of a Gene’s Alleles with Behavior of a Chromosome Pair •1 of Morgan’s crosses: (mutant) X (wild type) ...
... Correlating Behavior of a Gene’s Alleles with Behavior of a Chromosome Pair •1 of Morgan’s crosses: (mutant) X (wild type) ...
Non-Mendelian Inheritance and Exceptions to Mendel`s Rules
... cause cystic fibrosis. About 70% of these are caused by the dF508 mutation, but different allelic combinations produce different phenotypes (multiple alleles), a factor that also alters Mendelian phenotypic ratios. ...
... cause cystic fibrosis. About 70% of these are caused by the dF508 mutation, but different allelic combinations produce different phenotypes (multiple alleles), a factor that also alters Mendelian phenotypic ratios. ...