Introduction to Patterns of Inheritance/Genetics
... Introduction to Patterns of Inheritance/Genetics INTRODUCTION The pioneer of modern day genetics was an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel, who established the basic laws of heredity from his studies with pea plants in the mid 1800s. Mendel’s fundamental genetic principles may be applied to a variety ...
... Introduction to Patterns of Inheritance/Genetics INTRODUCTION The pioneer of modern day genetics was an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel, who established the basic laws of heredity from his studies with pea plants in the mid 1800s. Mendel’s fundamental genetic principles may be applied to a variety ...
14 – Mendel and the Gene Idea
... a) X-LINKED - carried on X chromosome EX: Color blindness; hemophilia; Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy b) Y-LINKED - carried on Y chromosome EX: Hairy pinnae; SRY=gene for “maleness” 4) MULTIPLE ALLELE TRAIT - More than 2 choices EX: A, B, O blood alleles produce A, B, O, or AB blood types 5) POLYGENIC ...
... a) X-LINKED - carried on X chromosome EX: Color blindness; hemophilia; Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy b) Y-LINKED - carried on Y chromosome EX: Hairy pinnae; SRY=gene for “maleness” 4) MULTIPLE ALLELE TRAIT - More than 2 choices EX: A, B, O blood alleles produce A, B, O, or AB blood types 5) POLYGENIC ...
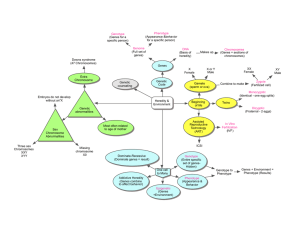
Patterns of Inheritance DNA Chromosome(s) Gene(s) Character(s
... • Specific locations for certain DNA within chromosomes. • 1 gene is one unit of DNA out of all DNA. • There can be many genes within a chromosome. • Chemicals that control the characters of an organism. ...
... • Specific locations for certain DNA within chromosomes. • 1 gene is one unit of DNA out of all DNA. • There can be many genes within a chromosome. • Chemicals that control the characters of an organism. ...
File
... Activity 61 1) What is the relationship between genotype and phenotype? Genotype is which type of genes you have for each trait. Genotype therefore determines what your observable traits are, and that is your phenotype. 2) What is a Punnett square? A table to determine the probabilities of traits in ...
... Activity 61 1) What is the relationship between genotype and phenotype? Genotype is which type of genes you have for each trait. Genotype therefore determines what your observable traits are, and that is your phenotype. 2) What is a Punnett square? A table to determine the probabilities of traits in ...
Evolution
... If chromosomes and loci of the male and female do not match perfectly, reproduction cannot occur (prevents interbreeding) Offspring will resemble parents because genes must match at each locus, but the offspring will differ from both parents in traits for which there was more than one allele Genome ...
... If chromosomes and loci of the male and female do not match perfectly, reproduction cannot occur (prevents interbreeding) Offspring will resemble parents because genes must match at each locus, but the offspring will differ from both parents in traits for which there was more than one allele Genome ...
Tracing Human Evolution with Genetics (Haplotypes)
... Many common medical issues are polygenic Traditionally required a large affected family to identify candidate genes Genome Wide Association (GWA) Articles ...
... Many common medical issues are polygenic Traditionally required a large affected family to identify candidate genes Genome Wide Association (GWA) Articles ...
Jing Zhao - Iowa State University
... RESEARCH FOCUS LD mapping both on a genome-wide scale (GWAS) and restricted to particular genes/genomic regions (Candidate gene/QTL) will be implemented in sorghum using a natural diverse panel that exhibits significant variation in plant height, leaf angel, flowering time, etc. The goal of this typ ...
... RESEARCH FOCUS LD mapping both on a genome-wide scale (GWAS) and restricted to particular genes/genomic regions (Candidate gene/QTL) will be implemented in sorghum using a natural diverse panel that exhibits significant variation in plant height, leaf angel, flowering time, etc. The goal of this typ ...
Genetics PowerPoint
... trait is controlled by a “factor” 2 or more “factors” for each trait •Dominant-more powerful, always shows (R) •Recessive-weaker, sometimes shows (r) ...
... trait is controlled by a “factor” 2 or more “factors” for each trait •Dominant-more powerful, always shows (R) •Recessive-weaker, sometimes shows (r) ...
Ch10planttransformation
... a trait that is measured on a quantitative scale. Examples of quantitative traits are plant height or grain yield. • These traits are typically affected by more than one gene, and also by the environment • Mapping QTL is not as simple as mapping a single gene that affects a qualitative because it in ...
... a trait that is measured on a quantitative scale. Examples of quantitative traits are plant height or grain yield. • These traits are typically affected by more than one gene, and also by the environment • Mapping QTL is not as simple as mapping a single gene that affects a qualitative because it in ...
Big Questions
... How are most traits inherited? How do Genes and the Environment interact? Are all traits inherited? Word Wall: ...
... How are most traits inherited? How do Genes and the Environment interact? Are all traits inherited? Word Wall: ...
Biology
... f. teach someone else the concepts discussed g. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. explain the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics 2. summarize the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment 3. predi ...
... f. teach someone else the concepts discussed g. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. explain the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics 2. summarize the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment 3. predi ...
Barron`s Ch 7 ppt Heredity
... - Therefore if any offspring show recessive trait, parent must be hybrid. ...
... - Therefore if any offspring show recessive trait, parent must be hybrid. ...
Evolution of Populations Summary of Natural Selection
... survive are more likely to pass down the beneficial traits to their offspring Over LONG periods of time the beneficial traits become prevalent throughout the population All species alive today are descended with modifications from ancestral species thus uniting all living things in a tree of life ...
... survive are more likely to pass down the beneficial traits to their offspring Over LONG periods of time the beneficial traits become prevalent throughout the population All species alive today are descended with modifications from ancestral species thus uniting all living things in a tree of life ...
Chapter 5 – Heredity
... 4. Each sex cell now contains ______________ allele for each trait. 5. The study of how traits are inherited is ____________________. B. Gregor Mendel—the father of genetics 1. Mendel was the first to use __________________________ to explain heredity and to trace one trait for _____________________ ...
... 4. Each sex cell now contains ______________ allele for each trait. 5. The study of how traits are inherited is ____________________. B. Gregor Mendel—the father of genetics 1. Mendel was the first to use __________________________ to explain heredity and to trace one trait for _____________________ ...
B1_Biology_Summary_Topic_1
... Classification of veterbrates What terms are used to describe vertebrates and what they mean ...
... Classification of veterbrates What terms are used to describe vertebrates and what they mean ...
chapter 14 - Dublin City Schools
... 8. Describe the inheritance of the ABO blood system and explain why the IA and IB alleles are said to be co-dominant. 9. Define and give examples of pleiotropy and epistasis. 10. Describe a simple model for polygenic inheritance and explain why most polygenic characters are described in quantitative ...
... 8. Describe the inheritance of the ABO blood system and explain why the IA and IB alleles are said to be co-dominant. 9. Define and give examples of pleiotropy and epistasis. 10. Describe a simple model for polygenic inheritance and explain why most polygenic characters are described in quantitative ...
Modern Genetics
... A could be Genotype AA or Ao B could be Genotype BB or Bo AB can only be Genotype AB O can only be Genotype oo ...
... A could be Genotype AA or Ao B could be Genotype BB or Bo AB can only be Genotype AB O can only be Genotype oo ...
Modern Genetics Notes
... Sex — linked traits — traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes. Ex. color blindness Polygenic inheritance — inheritance pattern of a trait that is controlled by two or more genes. Ex. skin color and height *Nutrition, light, chemicals, and infectious agents such as bacteria, fungi, para ...
... Sex — linked traits — traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes. Ex. color blindness Polygenic inheritance — inheritance pattern of a trait that is controlled by two or more genes. Ex. skin color and height *Nutrition, light, chemicals, and infectious agents such as bacteria, fungi, para ...