Principle of Dominance
... determined not only by their inherited genes. • Characteristics are determined by the interaction between the genes & the environment • Genes provide a plan for development, but how that plan unfolds also depends on the environment Drug Use ...
... determined not only by their inherited genes. • Characteristics are determined by the interaction between the genes & the environment • Genes provide a plan for development, but how that plan unfolds also depends on the environment Drug Use ...
genetics
... Genes Segment of DNA that codes for one protein/trait Most traits are determined by TWO genes. Remember chromosomes have a homologous match…two chromosomes with similar genetic information EXAMPLE: Hair color, eye color, height in pea plants ...
... Genes Segment of DNA that codes for one protein/trait Most traits are determined by TWO genes. Remember chromosomes have a homologous match…two chromosomes with similar genetic information EXAMPLE: Hair color, eye color, height in pea plants ...
U4 Schedule Fall
... 1. Chromosome – threadlike structure within the cell nucleus that contains the genetic material (DNA) that is passed from one generation to the next 2. Diploid – two of each kind of chromosome; one from each parent (2n) 3. Haploid – one of each kind of chromosome; gametes (1n) 4. Karyotype – picture ...
... 1. Chromosome – threadlike structure within the cell nucleus that contains the genetic material (DNA) that is passed from one generation to the next 2. Diploid – two of each kind of chromosome; one from each parent (2n) 3. Haploid – one of each kind of chromosome; gametes (1n) 4. Karyotype – picture ...
Ch. 15 Chromosomal Inheritance
... Leads to aneuploidy: • Aneuploidy is the condition of having less than or more than the normal diploid number of chromosomes, and is the most frequently observed type of cytogenetic abnormality. ...
... Leads to aneuploidy: • Aneuploidy is the condition of having less than or more than the normal diploid number of chromosomes, and is the most frequently observed type of cytogenetic abnormality. ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Behavior Genetics: The study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior ...
... Behavior Genetics: The study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior ...
2. Mendelian Pedigree patterns
... pairing region segregate like autosomal genes and not like sex-limnked genes and thus are called pseudoautosomal genes. ...
... pairing region segregate like autosomal genes and not like sex-limnked genes and thus are called pseudoautosomal genes. ...
Chapter 6
... proposed the chromosome theory of inheritance. Morgan found that his experimental results could be explained if genes were arranged in a linear manner along chromosomes. He proposed the gene-chromosome theory. • Linked genes do not assort independently. Instead, the probability of recombination amon ...
... proposed the chromosome theory of inheritance. Morgan found that his experimental results could be explained if genes were arranged in a linear manner along chromosomes. He proposed the gene-chromosome theory. • Linked genes do not assort independently. Instead, the probability of recombination amon ...
Inheritance Patterns_Ch.12_2012 - OCC
... Parents can be tested for marker before conceiving a child. ...
... Parents can be tested for marker before conceiving a child. ...
Cornell Notes Template
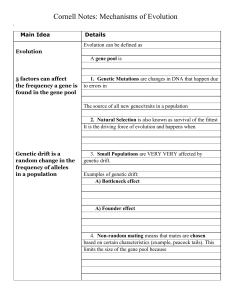
... 2. Natural Selection is also known as survival of the fittest It is the driving force of evolution and happens when ...
... 2. Natural Selection is also known as survival of the fittest It is the driving force of evolution and happens when ...
Important questions from the unit genetics and
... Answer: Convergent evolution When more than one adaptive radiation occurs in an isolated geographical area, the phenomenon is called convergent evolution. The best example for convergent evolution is the case of Australian marsupials. A number of marsupial animals evolved from a single stock but the ...
... Answer: Convergent evolution When more than one adaptive radiation occurs in an isolated geographical area, the phenomenon is called convergent evolution. The best example for convergent evolution is the case of Australian marsupials. A number of marsupial animals evolved from a single stock but the ...
Genetic Diseases and Diagnosis: Word Scramble Read each clue
... A diagnostic technique in which sound waves are used to obtain an image of a fetus. TRULDNSAUO The technique that allows one to see a fetus by using a camera on an endoscope. ETOCYFSOP The term used for something in the environment capable of causing a gene mutation. AGENMUT ...
... A diagnostic technique in which sound waves are used to obtain an image of a fetus. TRULDNSAUO The technique that allows one to see a fetus by using a camera on an endoscope. ETOCYFSOP The term used for something in the environment capable of causing a gene mutation. AGENMUT ...
Genetics of Complex Disease - Association for Molecular Pathology
... • Values > 1.0 are generally taken to indicate evidence in favor of a genetic component. In general, the higher the value, the stronger the genetic component. • Values can be used to estimate the number of genes under different genetic models. • Note that the magnitude of the estimate is very depend ...
... • Values > 1.0 are generally taken to indicate evidence in favor of a genetic component. In general, the higher the value, the stronger the genetic component. • Values can be used to estimate the number of genes under different genetic models. • Note that the magnitude of the estimate is very depend ...
8th Grade Unit Plan: Genetics
... SWBAT explain that an offspring’s traits are the result of the contribution of genetic material carried in each cell. SWBAT explain the relationship between genes, DNA, and chromosomes. SWBAT identify alleles as different forms of the same gene. SWBAT differentiate between dominant and recessive all ...
... SWBAT explain that an offspring’s traits are the result of the contribution of genetic material carried in each cell. SWBAT explain the relationship between genes, DNA, and chromosomes. SWBAT identify alleles as different forms of the same gene. SWBAT differentiate between dominant and recessive all ...
Mendelian Genetics Objectives (Chapter 14)
... Define the concept "random event" and explain why it is significant that allele segregation during meiosis and fusion of gametes at fertilization are random events Apply the "multiplication" rule to predicting probabilities of specific outcomes from genetic crosses Apply the "addition" rule to predi ...
... Define the concept "random event" and explain why it is significant that allele segregation during meiosis and fusion of gametes at fertilization are random events Apply the "multiplication" rule to predicting probabilities of specific outcomes from genetic crosses Apply the "addition" rule to predi ...
Genes on Chromosomes - Capital High School
... • females inactivate one of the two X chromosomes in each cell during embryonic development. This is called a Barr body – an inactive and dense stainable structure found in the nucleus. • X carries hundreds of genes but few, if any, of these have anything to do directly ...
... • females inactivate one of the two X chromosomes in each cell during embryonic development. This is called a Barr body – an inactive and dense stainable structure found in the nucleus. • X carries hundreds of genes but few, if any, of these have anything to do directly ...
Example of selective breeding in cats
... agriculture is responsible for many modern day vegetables. Cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, collards and kale are have all originated from the same wild mustard plant. ...
... agriculture is responsible for many modern day vegetables. Cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, collards and kale are have all originated from the same wild mustard plant. ...
zChap00_Front_140901
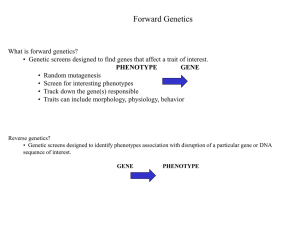
... 4.2 Origins of mutations 4.3 Genetic screening for mutations: forward genetics 4.4 Types of mutations 4.5 Some mutations may not have detectible phenotypes 4.6 Complementation tests and allelism 4.7 Example of human mutations Chapter 5 ...
... 4.2 Origins of mutations 4.3 Genetic screening for mutations: forward genetics 4.4 Types of mutations 4.5 Some mutations may not have detectible phenotypes 4.6 Complementation tests and allelism 4.7 Example of human mutations Chapter 5 ...
GENETICS AND INHERITANCE
... • Law of segregation: reproductive cells carry only one copy of each gene • Law of independent assortment: genes for different traits are separated from each other independently during meiosis; applies in most cases Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. ...
... • Law of segregation: reproductive cells carry only one copy of each gene • Law of independent assortment: genes for different traits are separated from each other independently during meiosis; applies in most cases Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. ...
5. To determine the genotype of your offspring for the traits
... with predictable outcomes. In this stimulation, you will illustrate the genetic concepts of dominance, segregation, independent assortment, genotype, phenotype, dominant-recessive inheritance, incomplete dominance, and polygenic inheritance when you are your lab partner “produce” a baby. Most of the ...
... with predictable outcomes. In this stimulation, you will illustrate the genetic concepts of dominance, segregation, independent assortment, genotype, phenotype, dominant-recessive inheritance, incomplete dominance, and polygenic inheritance when you are your lab partner “produce” a baby. Most of the ...
Genetics Unit Test Review
... You have the same alleles for a gene b. What are the genotypes that represent a purebred trait? Needs to be the same letter BB (purebred dominant) or bb (purebred recessive) c. What is another term that means the same thing as purebred? ...
... You have the same alleles for a gene b. What are the genotypes that represent a purebred trait? Needs to be the same letter BB (purebred dominant) or bb (purebred recessive) c. What is another term that means the same thing as purebred? ...
Complementation
... • Genetic screens designed to identify phenotypes association with disruption of a particular gene or DNA sequence of interest. GENE ...
... • Genetic screens designed to identify phenotypes association with disruption of a particular gene or DNA sequence of interest. GENE ...