word - University of Guelph
... Typical reaction set-ups involve the heating and stirring of (complex) mixtures of various chemicals and organic solvents in glas apparatus, often under reflux conditions with continous water cooling and under inert gas atmosphere or vacuum on a scale of 10 to 1000 mL total volume. Typical maximum h ...
... Typical reaction set-ups involve the heating and stirring of (complex) mixtures of various chemicals and organic solvents in glas apparatus, often under reflux conditions with continous water cooling and under inert gas atmosphere or vacuum on a scale of 10 to 1000 mL total volume. Typical maximum h ...
2nd Semester Exam 1 Review Key
... 4) Benzene (C6H6) combusts with oxygen gas to yield carbon dioxide and water. 2C6H6 + 15O2 → 6H2O + 12CO2 combustion ...
... 4) Benzene (C6H6) combusts with oxygen gas to yield carbon dioxide and water. 2C6H6 + 15O2 → 6H2O + 12CO2 combustion ...
Study Guide for Exam 2_Sp12
... Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show h ...
... Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show h ...
2.4 Revision 1: There were two atoms. One got hit by an extremely
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
Q1) Discuss the following briefly: (a) The effect of hydrogen bond on
... (c) Solutes are often precipitated from solutions by the addition of an electrolyte. solutes are often liberated from solutions in which they are dissolved by the introduction of an electrolyte such as sodium chloride and sometimes by a nonelectrolyte such as sucrose. This phenomenon is known as sal ...
... (c) Solutes are often precipitated from solutions by the addition of an electrolyte. solutes are often liberated from solutions in which they are dissolved by the introduction of an electrolyte such as sodium chloride and sometimes by a nonelectrolyte such as sucrose. This phenomenon is known as sal ...
TYPES OF REACTIONS
... Atoms other than H and O O atoms (add H2O) H atoms (adding H+) Balance charge with electrons Combine half-reactions Add number of OH- ion equal to number of H+ ions on both sides of overall reaction and combine hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions to form water when they appear on the same side of ...
... Atoms other than H and O O atoms (add H2O) H atoms (adding H+) Balance charge with electrons Combine half-reactions Add number of OH- ion equal to number of H+ ions on both sides of overall reaction and combine hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions to form water when they appear on the same side of ...
Chapter 2
... If the cation is monoatomic- Name the metal (cation) just write the name. If the cation is polyatomic- name it. If the anion is monoatomic- name it but change the ending to –ide. If the anion is poly atomic- just name it ...
... If the cation is monoatomic- Name the metal (cation) just write the name. If the cation is polyatomic- name it. If the anion is monoatomic- name it but change the ending to –ide. If the anion is poly atomic- just name it ...
The s-Block Elements - GCG-42
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
Chemical Bonds
... • Bonds form as a result of lowering of the total energy (energy of separated species is higher than that of bonded species) • Bond formation is accompanied by rearrangement of valence electrons – complete transfer of electrons – formation of ions (ionic bonding) – sharing of electrons – formation o ...
... • Bonds form as a result of lowering of the total energy (energy of separated species is higher than that of bonded species) • Bond formation is accompanied by rearrangement of valence electrons – complete transfer of electrons – formation of ions (ionic bonding) – sharing of electrons – formation o ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... There are many types of chemical reactions. Five of the most common are: synthesis: two or more reactants combine to form a single product. A+BC decomposition: one reactant disintegrates (decomposes) to form two or more products: AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atom ...
... There are many types of chemical reactions. Five of the most common are: synthesis: two or more reactants combine to form a single product. A+BC decomposition: one reactant disintegrates (decomposes) to form two or more products: AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atom ...
Pre-AP Chemistry Kinetic Theory and Heat Quiz
... predictable pattern of boiling point temperatures? (i.e. ionic higher than polar covalent, which is higher than nonpolar covalent) because of the intermolecular forces that hold them together - the stronger the intermolecular force the more energy it takes to separate the molecules to form a gas How ...
... predictable pattern of boiling point temperatures? (i.e. ionic higher than polar covalent, which is higher than nonpolar covalent) because of the intermolecular forces that hold them together - the stronger the intermolecular force the more energy it takes to separate the molecules to form a gas How ...
Intermolecular Forces
... Intermolecular Forces The strength of the intermolecular forces determines the physical properties of the substance: ...
... Intermolecular Forces The strength of the intermolecular forces determines the physical properties of the substance: ...
Unit 4 Compounds, Naming, Formula Writing
... masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. ...
CHEM104 Examlette 1 – ANSWERS TOTAL POINTS = 94 Multiple
... c) Pick one type of solid from (a) and explain what energies and forces are involved when the solid dissolves in a liquid to make a solution. (4 pts): The strong ionic bonding in ionic alts must be broken—this is the negative of the lattice enthalpy— and is very endothermic. This is compensated by t ...
... c) Pick one type of solid from (a) and explain what energies and forces are involved when the solid dissolves in a liquid to make a solution. (4 pts): The strong ionic bonding in ionic alts must be broken—this is the negative of the lattice enthalpy— and is very endothermic. This is compensated by t ...
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... 1. Name the cation first and the anion second 2. Monoatomic cations use the element. 3. Monoatomic anions take their name from the root of the element name plus the suffix -ide. 4. Group 1A and 2A metals have only one oxidation number. Transition metals and metals on the right side of the periodic t ...
... 1. Name the cation first and the anion second 2. Monoatomic cations use the element. 3. Monoatomic anions take their name from the root of the element name plus the suffix -ide. 4. Group 1A and 2A metals have only one oxidation number. Transition metals and metals on the right side of the periodic t ...
Dielectric properties of critical conducting mixtures
... non-linear dielectric effect will be presented in pure binary mixtures and in mixtures doped by small amounts of ionic ingredients. Interesting properties related to the existence of ions capable to migrating in microscopically inhomogeneous systems are expected and were found. It will be presented ...
... non-linear dielectric effect will be presented in pure binary mixtures and in mixtures doped by small amounts of ionic ingredients. Interesting properties related to the existence of ions capable to migrating in microscopically inhomogeneous systems are expected and were found. It will be presented ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... Evidence of a chemical change Driving forces Molecular, ionic & net ionic equations Stoichiometry Classification of reactions Exothermic & endothermic reactions Electrochemistry ...
... Evidence of a chemical change Driving forces Molecular, ionic & net ionic equations Stoichiometry Classification of reactions Exothermic & endothermic reactions Electrochemistry ...
Chemistry Honors Lesson Plans—K Dean Lake Minneola High
... Extensions of content. Work in small groups. Priority seating. Additional time if necessary. Cue students as needed. Group students for maximum success. Any other accommodations as listed on individual student plans. ...
... Extensions of content. Work in small groups. Priority seating. Additional time if necessary. Cue students as needed. Group students for maximum success. Any other accommodations as listed on individual student plans. ...
Lecture 2 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... If a complete chemical reaction has occurred, all of the reactant atoms must be present in the product(s) ...
... If a complete chemical reaction has occurred, all of the reactant atoms must be present in the product(s) ...
Ang. bindningstyper och elektronegativitet
... electronegativity [difference] of [atoms in] these bonds is 0.3 to 1.7. Ionic bonding is a type of electrostatic interaction between atoms which have a large electronegativity difference. There is no precise value that distinguishes ionic from covalent bonding, but a difference of electronegativity ...
... electronegativity [difference] of [atoms in] these bonds is 0.3 to 1.7. Ionic bonding is a type of electrostatic interaction between atoms which have a large electronegativity difference. There is no precise value that distinguishes ionic from covalent bonding, but a difference of electronegativity ...
Chapter 8 Notes
... Consider a sample of a metal. Although the atoms that make up that sample have valence electrons, they do not share these electrons (as is the case in molecular compounds) or lose electrons (as in the case of ions). Instead, the valence electrons enter a “sea” of electrons. The positively charged me ...
... Consider a sample of a metal. Although the atoms that make up that sample have valence electrons, they do not share these electrons (as is the case in molecular compounds) or lose electrons (as in the case of ions). Instead, the valence electrons enter a “sea” of electrons. The positively charged me ...
Zumdahl Chapter
... First Year Chemistry Podcast DVD Featuring Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams from Peak Educational Consulting LLC All Rights Reserved © This is an interactive page that allows you to get to all of the content on this DVD. Click to each unit packet or podcast. The podcasts require Quicktime and the pa ...
... First Year Chemistry Podcast DVD Featuring Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams from Peak Educational Consulting LLC All Rights Reserved © This is an interactive page that allows you to get to all of the content on this DVD. Click to each unit packet or podcast. The podcasts require Quicktime and the pa ...
CHEMISTRY VOCABULARY
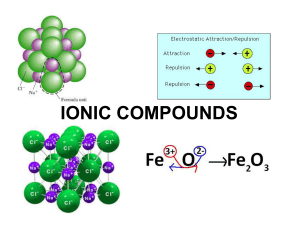
... COVALENT COMPOUNDS are formed between non metals, bonds contain shared pairs of electrons. If you know something about SALT (sodium chloride) you know something about IONIC COMPOUNDS IONIC COMPOUNDS are like salt, crystalline solids, with high melting and boiling points, they are usually soluble in ...
... COVALENT COMPOUNDS are formed between non metals, bonds contain shared pairs of electrons. If you know something about SALT (sodium chloride) you know something about IONIC COMPOUNDS IONIC COMPOUNDS are like salt, crystalline solids, with high melting and boiling points, they are usually soluble in ...
Ionic liquid
An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt in the liquid state. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below some arbitrary temperature, such as 100 °C (212 °F). While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of electrically neutral molecules, ionic liquids are largely made of ions and short-lived ion pairs. These substances are variously called liquid electrolytes, ionic melts, ionic fluids, fused salts, liquid salts, or ionic glasses. Ionic liquids have many applications, such as powerful solvents and electrically conducting fluids (electrolytes). Salts that are liquid at near-ambient temperature are important for electric battery applications, and have been used as sealants due to their very low vapor pressure.Any salt that melts without decomposing or vaporizing usually yields an ionic liquid. Sodium chloride (NaCl), for example, melts at 801 °C (1,474 °F) into a liquid that consists largely of sodium cations (Na+) and chloride anions (Cl−). Conversely, when an ionic liquid is cooled, it often forms an ionic solid—which may be either crystalline or glassy.The ionic bond is usually stronger than the Van der Waals forces between the molecules of ordinary liquids. For that reason, common salts tend to melt at higher temperatures than other solid molecules. Some salts are liquid at or below room temperature. Examples include compounds based on the 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium (EMIM) cation and include: EMIM:Cl, EMIM dicyanamide, (C2H5)(CH3)C3H3N+2·N(CN)−2, that melts at −21 °C (−6 °F); and 1-butyl-3,5-dimethylpyridinium bromide which becomes a glass below −24 °C (−11 °F).Low-temperature ionic liquids can be compared to ionic solutions, liquids that contain both ions and neutral molecules, and in particular to the so-called deep eutectic solvents, mixtures of ionic and non-ionic solid substances which have much lower melting points than the pure compounds. Certain mixtures of nitrate salts can have melting points below 100 °C.The term ""ionic liquid"" in the general sense was used as early as 1943.