Noun Clauses - WordPress.com
... act as adjectives and adverbs. We can remove them ad still have a complete independent clause left. We can not do this with noun clauses. ...
... act as adjectives and adverbs. We can remove them ad still have a complete independent clause left. We can not do this with noun clauses. ...
Phrase Toolbox
... He wrote a poem about walking in the moonlight. (object of the preposition) Walking the dog is not my favorite task. (subject) Absolute phrase An absolute phrase (also called a nominative absolute) is a group of words consisting of a noun or pronoun, an “-ing” or “-ed” verb form, and any related mod ...
... He wrote a poem about walking in the moonlight. (object of the preposition) Walking the dog is not my favorite task. (subject) Absolute phrase An absolute phrase (also called a nominative absolute) is a group of words consisting of a noun or pronoun, an “-ing” or “-ed” verb form, and any related mod ...
is the noun - SchoolNotes
... Other linking verbs are words that can be used in place of a “to be” verb and yet mean the same. For example, rather than say “The child is happy” you could say: The child seems happy. The child remains happy. The child feels happy. The child looks happy. The child appears happy. ...
... Other linking verbs are words that can be used in place of a “to be” verb and yet mean the same. For example, rather than say “The child is happy” you could say: The child seems happy. The child remains happy. The child feels happy. The child looks happy. The child appears happy. ...
I, he, she - beverlyfrederick
... The PrA and PrN are also called Subject Complements. **** The linking verbs appear, feel, grow, look, remain, smell, sound, stay, taste, and turn can be either action or linking depending on their use in the sentence. If you can replace the verb with seem and not alter the meaning of your sentence, ...
... The PrA and PrN are also called Subject Complements. **** The linking verbs appear, feel, grow, look, remain, smell, sound, stay, taste, and turn can be either action or linking depending on their use in the sentence. If you can replace the verb with seem and not alter the meaning of your sentence, ...
A Remedial English Grammar
... The Articles 5. The names of profession and occupations take the indefinite article. E.g. My brother is a teacher. 6. The indefinite article always follows the word such when it is applied to countable forms. E.g. I have never seen such a wet summer. 7. If an adjective is preceded by so then indefi ...
... The Articles 5. The names of profession and occupations take the indefinite article. E.g. My brother is a teacher. 6. The indefinite article always follows the word such when it is applied to countable forms. E.g. I have never seen such a wet summer. 7. If an adjective is preceded by so then indefi ...
Los Mandatos Formales
... reflexive pronouns are still attached to the affirmative command Command + IDOP/DOP/reflexive Add YOUR accent mark! (Second to last syllable of verb by itself) Cómala (Eat it!) Escríbame (Write to me.) ...
... reflexive pronouns are still attached to the affirmative command Command + IDOP/DOP/reflexive Add YOUR accent mark! (Second to last syllable of verb by itself) Cómala (Eat it!) Escríbame (Write to me.) ...
Word Class Nouns Nouns are the names of things. • Proper nouns
... Collective nouns – are the names of groups of things. Abstract nouns – are the names of ideas such as friendship. Pronouns are used in place of nouns, mostly to avoid repetition. Personal pronouns – refer to particular people: I, you, us. Impersonal pronouns – refer to other people: she, the ...
... Collective nouns – are the names of groups of things. Abstract nouns – are the names of ideas such as friendship. Pronouns are used in place of nouns, mostly to avoid repetition. Personal pronouns – refer to particular people: I, you, us. Impersonal pronouns – refer to other people: she, the ...
here - St Martin`s School
... Expanding noun phrases to include an adjective and a prepositional phrase. − The red ball under the table Onomatopoeia: use pictures to create words and add an exclamation mark. − Ouch! Prepositional phrases – under the carpet…, above the whiteboard… Time connectives – next, last, later ...
... Expanding noun phrases to include an adjective and a prepositional phrase. − The red ball under the table Onomatopoeia: use pictures to create words and add an exclamation mark. − Ouch! Prepositional phrases – under the carpet…, above the whiteboard… Time connectives – next, last, later ...
Grammar Cheat Sheet
... Use a colon to introduce a list that appears after an independent clause. (Usually use introductory words such as following) ...
... Use a colon to introduce a list that appears after an independent clause. (Usually use introductory words such as following) ...
Ah depreciate other persons dinners you ministers give
... 1. When a sentence has two or more independent clauses, it is difficult to tell the purpose of the sentence if each clause has a different purpose. Therefore, try to determine THE OVERALL intent to decide the purpose of the sentence. ...
... 1. When a sentence has two or more independent clauses, it is difficult to tell the purpose of the sentence if each clause has a different purpose. Therefore, try to determine THE OVERALL intent to decide the purpose of the sentence. ...
on Phrases: prepositional, verbal and appositives
... A phrase is a group of related words that is used as a single part of speech and that does not contain both a verb and its subject. Example: for you and her (no subject or verb). Contrast with the definition of a clause: A group of words that has both a subject and a verb. There are three different ...
... A phrase is a group of related words that is used as a single part of speech and that does not contain both a verb and its subject. Example: for you and her (no subject or verb). Contrast with the definition of a clause: A group of words that has both a subject and a verb. There are three different ...
Grammar Glossary - Mossgate Primary school
... A collective noun is a word that refers to a group. For example, crowd, flock, team. Although these are singular in form, we often think of them as plural in meaning and use them with a plural verb. For example, if we say The team have won all their games so far, we think of ‘the team’ as ‘they’ (ra ...
... A collective noun is a word that refers to a group. For example, crowd, flock, team. Although these are singular in form, we often think of them as plural in meaning and use them with a plural verb. For example, if we say The team have won all their games so far, we think of ‘the team’ as ‘they’ (ra ...
(1) The Parts of Speech
... “both . . . and”; “whether . . . or”; “not only . . . but also”—and they work just like coordinating conjunctions: “Either Mary or Paul will go”; Either to sing well or to dance well is required”; “Either Mary will bake the cake, or John will bake the cake.” The subordinating conjunctions introduce ...
... “both . . . and”; “whether . . . or”; “not only . . . but also”—and they work just like coordinating conjunctions: “Either Mary or Paul will go”; Either to sing well or to dance well is required”; “Either Mary will bake the cake, or John will bake the cake.” The subordinating conjunctions introduce ...
EnglishGrammarCardVer19 File
... “We all make mistakes,” father said, “but you seem to specialise in them!” “There’s a place called ‘Stop’,” the judge told Flinty, “and you’re going there for two years.” Apostrophe ( ’ ) is used to show possession or ownership of nouns and contracted words. Jamilah’s birthday. Thomas’s bicycle. The ...
... “We all make mistakes,” father said, “but you seem to specialise in them!” “There’s a place called ‘Stop’,” the judge told Flinty, “and you’re going there for two years.” Apostrophe ( ’ ) is used to show possession or ownership of nouns and contracted words. Jamilah’s birthday. Thomas’s bicycle. The ...
Grammar Glossary
... A collective noun is a word that refers to a group. For example, crowd, flock, team. Although these are singular in form, we often think of them as plural in meaning and use them with a plural verb. For example, if we say The team have won all their games so far, we think of ‘the team’ as ‘they’ (ra ...
... A collective noun is a word that refers to a group. For example, crowd, flock, team. Although these are singular in form, we often think of them as plural in meaning and use them with a plural verb. For example, if we say The team have won all their games so far, we think of ‘the team’ as ‘they’ (ra ...
Parts of Speech I. NOUN
... 8. Solving the traffic problems taxes the imagination of those who have the responsibility of it. 9. He says anyone who enjoys driving under today’s traffic conditions must be crazy. 10. Some take up a hobby because it is fun. ...
... 8. Solving the traffic problems taxes the imagination of those who have the responsibility of it. 9. He says anyone who enjoys driving under today’s traffic conditions must be crazy. 10. Some take up a hobby because it is fun. ...
Parts of Speech - Garnet Valley School District
... Includes a __________________, a noun or pronoun called the __________________, and any modifiers of that object. Commonly Used Prepositions and Compound Prepositions ...
... Includes a __________________, a noun or pronoun called the __________________, and any modifiers of that object. Commonly Used Prepositions and Compound Prepositions ...
document
... A noun names a person, A noun names a thing A noun names a place, Lets hear you sing: A person named Mary, A thing could be a ball A place is your house, But Ideas are comin’ to call. Don’t forget courage, And don’t lose your pride, When it comes to nouns, You got nothin’ to hide. Nouns name people, ...
... A noun names a person, A noun names a thing A noun names a place, Lets hear you sing: A person named Mary, A thing could be a ball A place is your house, But Ideas are comin’ to call. Don’t forget courage, And don’t lose your pride, When it comes to nouns, You got nothin’ to hide. Nouns name people, ...
Spelling, punctuation and grammar in year 2
... • use sentences in different forms in their writing (statements, questions, exclamations and commands) • use some expanded noun phrases to describe and specify ...
... • use sentences in different forms in their writing (statements, questions, exclamations and commands) • use some expanded noun phrases to describe and specify ...
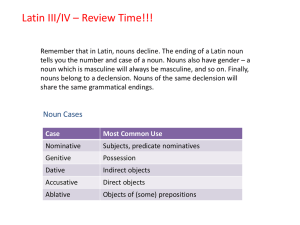
Latin II – Review Time!!!
... nominative form, but by the genitive. Third declension nouns may have different nominatives, but they all have a genitive ending in -is. ...
... nominative form, but by the genitive. Third declension nouns may have different nominatives, but they all have a genitive ending in -is. ...
English glossary - Rainford CE Primary School
... A distinct part of a sentence including a verb. A main clause makes sense on its own. A subordinate clause adds detail to the main clause but does not make sense on its own. A punctuation mark to introduce a list. A punctuation mark used to break up sentences so that they are easier to understand. T ...
... A distinct part of a sentence including a verb. A main clause makes sense on its own. A subordinate clause adds detail to the main clause but does not make sense on its own. A punctuation mark to introduce a list. A punctuation mark used to break up sentences so that they are easier to understand. T ...
PARTS OF SPEECH
... – Can be added to a verb to modify its meaning; can also modify adjectives and other adverbs – Tells you when, where, how, in what manner or to what extent an action is performed – Many end in “ly” , but not always! ...
... – Can be added to a verb to modify its meaning; can also modify adjectives and other adverbs – Tells you when, where, how, in what manner or to what extent an action is performed – Many end in “ly” , but not always! ...
Hierarchy of ESL Errors
... Depending on the kind of noun in a sentence, an article (i.e., “a,” “an,” or “the”) may need to precede it. Look at this sentence: “I told the teacher that I didn’t have a homework.” While “the” is used correctly before the definite noun of “teacher,” no “a” should precede “homework” since the latte ...
... Depending on the kind of noun in a sentence, an article (i.e., “a,” “an,” or “the”) may need to precede it. Look at this sentence: “I told the teacher that I didn’t have a homework.” While “the” is used correctly before the definite noun of “teacher,” no “a” should precede “homework” since the latte ...