Inflation, Exchange Rates and Interest Rates
... and the International Fisher Effect (IFE) scenarios. The study admits that several factors cause inflation in Ghana besides exchange rate movement and the nominal interest rates but the study will focus on these two factors in addition to the assessment of the FE and IFE. The FE theory postulates that ...
... and the International Fisher Effect (IFE) scenarios. The study admits that several factors cause inflation in Ghana besides exchange rate movement and the nominal interest rates but the study will focus on these two factors in addition to the assessment of the FE and IFE. The FE theory postulates that ...
Chapter 9
... • Increase base price by one-half of any real depreciation of the dollar relative to the euro • Decrease base price by one-half of any real appreciation of the dollar relative to the euro ...
... • Increase base price by one-half of any real depreciation of the dollar relative to the euro • Decrease base price by one-half of any real appreciation of the dollar relative to the euro ...
La Follette School of Public Affairs Dollar Real Exchange Rate
... nominal exchange rate by adding actual inflation to changes in the model-based real exchange rate. We find that the model-based exchange rates display two well known properties of actual exchange rates. First, for both nominal and real model based rates, autocorrelations of the growth rates are qui ...
... nominal exchange rate by adding actual inflation to changes in the model-based real exchange rate. We find that the model-based exchange rates display two well known properties of actual exchange rates. First, for both nominal and real model based rates, autocorrelations of the growth rates are qui ...
Chapter 8 Monetarism the British Monetarist Experiment Paul Devereux
... forced to raise interest rates to prevent a sterling free fall which would have had large inflationary consequences. This policy made sense but it was not monetarism in that money targets were considered to be less important than the value of the pound. If sterling falls threatened inflation, sterli ...
... forced to raise interest rates to prevent a sterling free fall which would have had large inflationary consequences. This policy made sense but it was not monetarism in that money targets were considered to be less important than the value of the pound. If sterling falls threatened inflation, sterli ...
1 9 9 8 - 03, July The International Role of the Euro Agnès Bénassy
... At the beginning of Stage III, the euro/dollar exchange rate may prove quite unstable, due to portfolio reallocations, as well as various uncertainties which will favour high sensitivity to policy announcements and possible herd behaviour in financial markets. In the long run, the trans-Atlantic exc ...
... At the beginning of Stage III, the euro/dollar exchange rate may prove quite unstable, due to portfolio reallocations, as well as various uncertainties which will favour high sensitivity to policy announcements and possible herd behaviour in financial markets. In the long run, the trans-Atlantic exc ...
Reconciling Switzerland`s minimum exchange rate and current
... Over the last few years, exchange rate tensions between the major economies have flared up. In this context, some observers have criticized central banks for influencing exchange rates, either directly through foreign currency purchases, or indirectly through additional monetary easing measures such ...
... Over the last few years, exchange rate tensions between the major economies have flared up. In this context, some observers have criticized central banks for influencing exchange rates, either directly through foreign currency purchases, or indirectly through additional monetary easing measures such ...
Chinese Silver Standard Economy and the 1929 Great Depression
... “The gold standard of the 1920s set the stage for the Depression of the 1930s by heightening the fragility of the international financial system. The gold standard was the mechanism transmitting the destabilizing impulse from the United States to the rest of the world. The gold standard magnified th ...
... “The gold standard of the 1920s set the stage for the Depression of the 1930s by heightening the fragility of the international financial system. The gold standard was the mechanism transmitting the destabilizing impulse from the United States to the rest of the world. The gold standard magnified th ...
Chap 15
... • A temporary increase in a country’s money supply causes its currency to depreciate in the foreign exchange market in short run; in long run, temporary increase in money supply has no impact on both exchange rate and interest rate. • A temporary decrease in a country’s money supply causes its curre ...
... • A temporary increase in a country’s money supply causes its currency to depreciate in the foreign exchange market in short run; in long run, temporary increase in money supply has no impact on both exchange rate and interest rate. • A temporary decrease in a country’s money supply causes its curre ...
CH 17: Tools of Monetary policy
... in a financial trouble and with sever liquidity problems(0.5% above discount rate) ...
... in a financial trouble and with sever liquidity problems(0.5% above discount rate) ...
Stock prices and the East Asian Financial Crisis
... their capital out of the respective domestic markets. This resulted in a subsequent depreciation of the exchange rate as the domestic currency was sold. However the degree of severity of the crisis varied across East Asia, as did the extent of the decline in the domestic stock markets. ...
... their capital out of the respective domestic markets. This resulted in a subsequent depreciation of the exchange rate as the domestic currency was sold. However the degree of severity of the crisis varied across East Asia, as did the extent of the decline in the domestic stock markets. ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES
... The new open economy macro literature also probably has not paid enough attention to another possibility: that the low degree of pass-through of exchange rates to prices may not primarily reflect price stickiness, but instead optimal price discrimination. Bergin and Feenstra (2001) and Bergin (2001) ...
... The new open economy macro literature also probably has not paid enough attention to another possibility: that the low degree of pass-through of exchange rates to prices may not primarily reflect price stickiness, but instead optimal price discrimination. Bergin and Feenstra (2001) and Bergin (2001) ...
International Finance
... sum of the balance of payments should be zero. When a country buys more goods and services than it sells (a deficit on the combined current and capital accounts), it must finance the difference by borrowing or selling more assets than it buys (a surplus on the financial account). When a country sell ...
... sum of the balance of payments should be zero. When a country buys more goods and services than it sells (a deficit on the combined current and capital accounts), it must finance the difference by borrowing or selling more assets than it buys (a surplus on the financial account). When a country sell ...
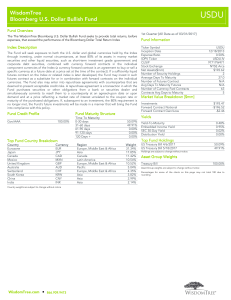
WisdomTree Bloomberg U.S. Dollar Bullish Fund
... Investments in currency involve additional special risks, such as credit risk and interest rate fluctuations. Derivative investments can be volatile and these investments may be less liquid than other securities, and more sensitive to the effect of varied economic conditions. While the Fund attempts ...
... Investments in currency involve additional special risks, such as credit risk and interest rate fluctuations. Derivative investments can be volatile and these investments may be less liquid than other securities, and more sensitive to the effect of varied economic conditions. While the Fund attempts ...
English title
... heavily regulated economies in the East bloc • Level of macroeconomic stability, private savings and credibility of the currency relatively high • Nominal inflation low, hidden inflation high (demand overhang on market with state controlled prices) • Field for the monetary policy ...
... heavily regulated economies in the East bloc • Level of macroeconomic stability, private savings and credibility of the currency relatively high • Nominal inflation low, hidden inflation high (demand overhang on market with state controlled prices) • Field for the monetary policy ...
Document
... • A permanent fiscal expansion changes the long-run expected exchange rate. – If the economy starts at long-run equilibrium, a permanent change in fiscal policy has no effect on output. – It causes an immediate and permanent exchange rate jump that offsets exactly the fiscal policy’s direct effect o ...
... • A permanent fiscal expansion changes the long-run expected exchange rate. – If the economy starts at long-run equilibrium, a permanent change in fiscal policy has no effect on output. – It causes an immediate and permanent exchange rate jump that offsets exactly the fiscal policy’s direct effect o ...
The Persistence of the `Peso Problem` when Policy is Noisy
... early 1980s when the dollar exchange rate systematically traded at a forward discount as the dollar followed a basic appreciating path. Second, the exchange rate may appear to be too strong relative to the levels implied by observing the correct set of fundamental forcing variables. Third, the condi ...
... early 1980s when the dollar exchange rate systematically traded at a forward discount as the dollar followed a basic appreciating path. Second, the exchange rate may appear to be too strong relative to the levels implied by observing the correct set of fundamental forcing variables. Third, the condi ...
The Relationship between Exchange Rates and Stock Prices
... currencies. Analysts kept trying to predict when this downward trend would come to an end based on the U.S. trade deficit. Was not the exchange rate affected by the stock market instead? In this paper, I study if there is a link between the stock market and exchange rates that might explain fluctuat ...
... currencies. Analysts kept trying to predict when this downward trend would come to an end based on the U.S. trade deficit. Was not the exchange rate affected by the stock market instead? In this paper, I study if there is a link between the stock market and exchange rates that might explain fluctuat ...
Tilburg University Theories on the scope for foreign exchange
... 'The exact implications of an operation in foreign currency by the domestic central bank depend on who is the counterparry in the transaction. An earlier version of this paper which was circulated as a Research Memorandum of the Department of Economics, Tilburg University and which is available from ...
... 'The exact implications of an operation in foreign currency by the domestic central bank depend on who is the counterparry in the transaction. An earlier version of this paper which was circulated as a Research Memorandum of the Department of Economics, Tilburg University and which is available from ...
$doc.title
... optimal domestic policy does not react to policy shocks and cyclical conditions in the world economy. This may be the case, for instance, when goods are produced with domestic inputs only and are priced in the producers’ currency, or when exporters are fully insured against currency volatility. Othe ...
... optimal domestic policy does not react to policy shocks and cyclical conditions in the world economy. This may be the case, for instance, when goods are produced with domestic inputs only and are priced in the producers’ currency, or when exporters are fully insured against currency volatility. Othe ...
Open economy models of distribution and growth
... claims of workers and firms are said to be ‘conflicting’ if what each group wants for itself would imply the other group getting less than its target. This conflict generates inflation if both groups raise nominal wages and prices in an effort (which in general can only be partially successful for e ...
... claims of workers and firms are said to be ‘conflicting’ if what each group wants for itself would imply the other group getting less than its target. This conflict generates inflation if both groups raise nominal wages and prices in an effort (which in general can only be partially successful for e ...
The global economic system
... establishment or acquisition of local banks. On both the assets and liabilities sides, banking is now international, its loans and borrowings denominated in various currencies, its scope and reach covering the whole globe. Perhaps just as telling, but more atypical, is the increased convergence of ...
... establishment or acquisition of local banks. On both the assets and liabilities sides, banking is now international, its loans and borrowings denominated in various currencies, its scope and reach covering the whole globe. Perhaps just as telling, but more atypical, is the increased convergence of ...
Five Questions About Current Monetary Policy
... the lowest possible unemployment rate consistent with price stability. So we refer to a “dual mandate,” meaning both maximum employment and stable prices. Members of the Federal Open Market Committee or FOMC – the presidents of the Reserve Banks and the members of the Board of Governors in Washingto ...
... the lowest possible unemployment rate consistent with price stability. So we refer to a “dual mandate,” meaning both maximum employment and stable prices. Members of the Federal Open Market Committee or FOMC – the presidents of the Reserve Banks and the members of the Board of Governors in Washingto ...
a stable money demand function for zimbabwe as a pre
... proxied for the opportunity cost of holding either money balances or other assets. The researcher also introduced into the estimating equations an exchange rate variable (exe) which took account of the openness of the economy and capital mobility as residents of Zimbabweans may choose to hold their ...
... proxied for the opportunity cost of holding either money balances or other assets. The researcher also introduced into the estimating equations an exchange rate variable (exe) which took account of the openness of the economy and capital mobility as residents of Zimbabweans may choose to hold their ...
Appendix The Theory of Credit and Macro-economic
... 0: An increase in the money supply leads to a lowering of the interest rate, and this should increase nominal and real income. But our naïve regressions show that an increase in money lowers real income (β ‘ is negative, though not significantly different from zero), though it increases nominal inco ...
... 0: An increase in the money supply leads to a lowering of the interest rate, and this should increase nominal and real income. But our naïve regressions show that an increase in money lowers real income (β ‘ is negative, though not significantly different from zero), though it increases nominal inco ...
Chapter 13. Open Economy Macroeconomics
... required to combat unemployment or inflation do not consider the rest of the world. Clearly, this is no longer an acceptable approach in an increasingly integrated world. In the open economy, we can summarize the desirable economic goals as being the attainment of internal and external balance. Inte ...
... required to combat unemployment or inflation do not consider the rest of the world. Clearly, this is no longer an acceptable approach in an increasingly integrated world. In the open economy, we can summarize the desirable economic goals as being the attainment of internal and external balance. Inte ...