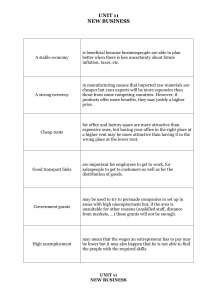
Brazil`s Currency Crisis
... • Brazil had been through 6 currencies since the 1960’s • In 1994 the Real Plan was adopted • Before it were a series of failed plans (the Cruzado Plan of 1986, Bresser plan of 1987, and more) • It worked well to tame inflation and maintain exchange rate stability for 5 years ...
... • Brazil had been through 6 currencies since the 1960’s • In 1994 the Real Plan was adopted • Before it were a series of failed plans (the Cruzado Plan of 1986, Bresser plan of 1987, and more) • It worked well to tame inflation and maintain exchange rate stability for 5 years ...
Vocabulary, Economic terms, page 99
... the difference in value between imports and exports of goods over a particular period: ...
... the difference in value between imports and exports of goods over a particular period: ...
The most visible roots of the crisis were the excess capital inflows
... general economic conditions in Russia. From 1995 to 1998, Russian borrowers (both government and non-governmental) had gone to the international capital markets for large quantities of capital. Servicing this debt soon became an increasing problem, as it was dollar denominated and required dolla ...
... general economic conditions in Russia. From 1995 to 1998, Russian borrowers (both government and non-governmental) had gone to the international capital markets for large quantities of capital. Servicing this debt soon became an increasing problem, as it was dollar denominated and required dolla ...
Lecture15-ForeignExchangeMarketB
... Exchange rate regimes • Exchange rate regimes in the international financial system are of two basic types: • Fixed and floating • In a fixed exchange rate regime, the value of currency are kept pegged relative to one currency called the anchor currency so that exchange rates are fixed • In a float ...
... Exchange rate regimes • Exchange rate regimes in the international financial system are of two basic types: • Fixed and floating • In a fixed exchange rate regime, the value of currency are kept pegged relative to one currency called the anchor currency so that exchange rates are fixed • In a float ...
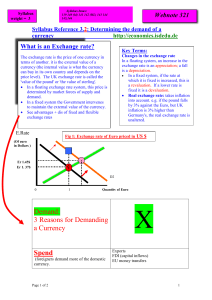
Demand for a currency - yELLOWSUBMARINER.COM
... The exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another. it is the external value of a currency (the internal value is what the currency can buy in its own country and depends on the price level). The UK exchange rate is called the 'value of the pound' or 'the value of sterling'. In a f ...
... The exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another. it is the external value of a currency (the internal value is what the currency can buy in its own country and depends on the price level). The UK exchange rate is called the 'value of the pound' or 'the value of sterling'. In a f ...
From Bretton Woods to the Euro
... Basically failed due to lack of harmonised macroeconomic policy (need similar IR, inflation and debt and deficit levels) ...
... Basically failed due to lack of harmonised macroeconomic policy (need similar IR, inflation and debt and deficit levels) ...
Fixed Rate System: Preview of Results
... aren’t hurt as badly as they would otherwise be – Your country’s terms of trade worsen ...
... aren’t hurt as badly as they would otherwise be – Your country’s terms of trade worsen ...
Exchange Rates - Continental Economics
... cost three times more than one beer One can also say: 3 beer exchange for 1 pack of cigarettes in a barter Thus exchange rates are prices and are linked to the exchange ratios of goods ...
... cost three times more than one beer One can also say: 3 beer exchange for 1 pack of cigarettes in a barter Thus exchange rates are prices and are linked to the exchange ratios of goods ...
exchange rates
... Another verb for fixing exchange rates against something else is to peg them. Increasing the value of an otherwise fixed exchange rate is called revaluation. A currency can appreciate if lots speculators buy it. In most western countries there is a system of floating exchange rates determined by sup ...
... Another verb for fixing exchange rates against something else is to peg them. Increasing the value of an otherwise fixed exchange rate is called revaluation. A currency can appreciate if lots speculators buy it. In most western countries there is a system of floating exchange rates determined by sup ...
4.6 B More on Exchange Rates
... occurs, this imbalance adjusts the exchange rate automatically to counteract that change. But – regardless of how the CA is changing, International flows of money in the capital account may affect the exchange rate, and thus worsen the current account unintentionally. 2. No need to employ monetary ...
... occurs, this imbalance adjusts the exchange rate automatically to counteract that change. But – regardless of how the CA is changing, International flows of money in the capital account may affect the exchange rate, and thus worsen the current account unintentionally. 2. No need to employ monetary ...
Chapter 3 Review
... C. North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) D. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) 16. ____ Maintains a system of world trade and exchange rates. 17. ____ Created after World War II to provide loans for rebuilding 18. ____Settles trade disputes and enforces free-trade agreements between member ...
... C. North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) D. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) 16. ____ Maintains a system of world trade and exchange rates. 17. ____ Created after World War II to provide loans for rebuilding 18. ____Settles trade disputes and enforces free-trade agreements between member ...
Slide 1
... political economy The transaction of money is at the heart of several current issues and debates important to the global system, including international development and the politics of multinational corporations ...
... political economy The transaction of money is at the heart of several current issues and debates important to the global system, including international development and the politics of multinational corporations ...
Balance of payments
... U.S. residents can hold U.S. assets OR assets in foreign countries As international investors shift their assets around the world, they link assets markets here and abroad affect income, exchange rates, and the ability of monetary policy to affect interest rates ...
... U.S. residents can hold U.S. assets OR assets in foreign countries As international investors shift their assets around the world, they link assets markets here and abroad affect income, exchange rates, and the ability of monetary policy to affect interest rates ...
AP Macroeconomics Study Guide for Unit 7, The
... What is purchasing power parity? What is an exchange rate regime? What is the difference between a fixed exchange rate system and floating exchange rate system? What are the advantages and disadvantages associated with each system? What are foreign exchange controls? What is the difference between d ...
... What is purchasing power parity? What is an exchange rate regime? What is the difference between a fixed exchange rate system and floating exchange rate system? What are the advantages and disadvantages associated with each system? What are foreign exchange controls? What is the difference between d ...
Chapter 3
... is that foreign holdings of actual currency are small relative to foreign holdings of dollardenominated interest-bearing securities and deposits. The United States earns no seigniorage return ...
... is that foreign holdings of actual currency are small relative to foreign holdings of dollardenominated interest-bearing securities and deposits. The United States earns no seigniorage return ...
Chapter 3 The International Monetary System
... banks or foreign branches of American banks. By locating outside of the United States Eurodollars escape regulation by the Federal ...
... banks or foreign branches of American banks. By locating outside of the United States Eurodollars escape regulation by the Federal ...
FM.2 Currency Exchange - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... (b) At the end of her trip, Andrea converts the money she has left back to Canadian dollars. At that time, the bank offers a buying rate of US$1=C$1.1283. Andrea has US$25 left. What is this worth in Canadian currency? ...
... (b) At the end of her trip, Andrea converts the money she has left back to Canadian dollars. At that time, the bank offers a buying rate of US$1=C$1.1283. Andrea has US$25 left. What is this worth in Canadian currency? ...
Monetary Intergration
... incidence of shocks and real wage rate flexibility as well as mobility of labor, an optimum currency area can be formed so as to gain better efficiency of transaction and welfare benefit than an exchange rate flexibility can offer ...
... incidence of shocks and real wage rate flexibility as well as mobility of labor, an optimum currency area can be formed so as to gain better efficiency of transaction and welfare benefit than an exchange rate flexibility can offer ...
students' powerpoint presentation sample 2
... • What was the gold-exchange standard in 1944 to 1973 and why is it important? • How globalization and world politics effected our economy? ...
... • What was the gold-exchange standard in 1944 to 1973 and why is it important? • How globalization and world politics effected our economy? ...
FIS 260 wk 5 CheckPoint: Development of the International
... trade, and direct the flow of financial capital b. Gold Standard - 1920 At fixed exchange rates, currencies of countries can be convertible into gold ...
... trade, and direct the flow of financial capital b. Gold Standard - 1920 At fixed exchange rates, currencies of countries can be convertible into gold ...