The Search for a New Currency System
... Back in 1969, amid tension between the dollar's peg to gold and what was—by the standards of the day—a large budget deficit, an alternative to the dollar was created. Known as Special Drawing Rights, and overseen by the International Monetary Fund, this dollar substitute plays little role outside of ...
... Back in 1969, amid tension between the dollar's peg to gold and what was—by the standards of the day—a large budget deficit, an alternative to the dollar was created. Known as Special Drawing Rights, and overseen by the International Monetary Fund, this dollar substitute plays little role outside of ...
Business in the Global Economy
... Money passes from one country to another through investments and tourism Citizens may invest in foreign countries Businesses may invest in a factory in another country ...
... Money passes from one country to another through investments and tourism Citizens may invest in foreign countries Businesses may invest in a factory in another country ...
EXCHANGE RATE Chapter13 able
... How much can be exchanged for one dollar? ¥89.40/$ How much can be exchanged for one yen? $0.011185/¥ ...
... How much can be exchanged for one dollar? ¥89.40/$ How much can be exchanged for one yen? $0.011185/¥ ...
ECON 401 November 12, 2012 Export-led growth and the 1980s
... depended on the availability of foreign exchange Foreign exchange shortage emerged as one the most important barriers to the industrialization process during the last years of the 1970s. The shortage of foreign exchange also led to the shortages of key intermediate goods such as oil and electricity ...
... depended on the availability of foreign exchange Foreign exchange shortage emerged as one the most important barriers to the industrialization process during the last years of the 1970s. The shortage of foreign exchange also led to the shortages of key intermediate goods such as oil and electricity ...
A Foreign Exchange and Policy Perspective
... Good evening. It is a pleasure for me to be here to help mark the 25th Anniversary of the Foreign Exchange Committee. I thank David Puth for his kind introduction and Dino Kos for the invitation to speak. I have benefited greatly from the conversations I have had with both of them and others close t ...
... Good evening. It is a pleasure for me to be here to help mark the 25th Anniversary of the Foreign Exchange Committee. I thank David Puth for his kind introduction and Dino Kos for the invitation to speak. I have benefited greatly from the conversations I have had with both of them and others close t ...
CHAPTER 32. INTERNATIONAL CORPORATE FINANCE. I. The
... n The spot market and the forward market Size of FX market n Daily volume approximately $1 Trillion or $250 Trillion per year. n Daily trading volume on the NYSE is about $7 Billion [0.7%] Participants of FX markets n Typically larger commercial banks. n Stand ready to buy or sell currencies on a co ...
... n The spot market and the forward market Size of FX market n Daily volume approximately $1 Trillion or $250 Trillion per year. n Daily trading volume on the NYSE is about $7 Billion [0.7%] Participants of FX markets n Typically larger commercial banks. n Stand ready to buy or sell currencies on a co ...
REVIEWING CAPITAL CONTROLS
... US Fed’s policy of quantitative easing (QE), which has led to a decline in the dollar and sparked fears of global inflation. China has been vociferous in condemning QE2 since it rightly fears that this might be the first sign of its largest debtor taking the timehonoured route towards the euthanasia ...
... US Fed’s policy of quantitative easing (QE), which has led to a decline in the dollar and sparked fears of global inflation. China has been vociferous in condemning QE2 since it rightly fears that this might be the first sign of its largest debtor taking the timehonoured route towards the euthanasia ...
Module Exchange Rate Policy
... Module 43 Exchange Rate Policy KRUGMAN'S MACROECONOMICS for AP* Margaret Ray and David Anderson ...
... Module 43 Exchange Rate Policy KRUGMAN'S MACROECONOMICS for AP* Margaret Ray and David Anderson ...
US$ Depreciation
... 1. Increased demand as more foreign goods are demanded, more of the foreign currency is demand at each possible exchange rate 2. The price of the foreign currency in local currency ...
... 1. Increased demand as more foreign goods are demanded, more of the foreign currency is demand at each possible exchange rate 2. The price of the foreign currency in local currency ...
What is the Exchange Channel of monetary Policy Transmission
... and financial stability. Thus, changes in the exchange rate might induce changes in the relative prices of goods and services, and the level of spending by individuals and firms, especially if significant levels of their wealth are held in foreign currencies. An appreciation in the value of the exch ...
... and financial stability. Thus, changes in the exchange rate might induce changes in the relative prices of goods and services, and the level of spending by individuals and firms, especially if significant levels of their wealth are held in foreign currencies. An appreciation in the value of the exch ...
FREE Sample Here
... trade and financial transactions. London is still the world’s most important financial center. The British are also very proud of their long tradition in financial matters when “Britannia ruled the waves.” They are afraid that monetary and financial matters may eventually migrate to Frankfurt, where ...
... trade and financial transactions. London is still the world’s most important financial center. The British are also very proud of their long tradition in financial matters when “Britannia ruled the waves.” They are afraid that monetary and financial matters may eventually migrate to Frankfurt, where ...
Government Influence on Exchange Rates
... The international monetary system can be defined as the institutional framework within which international payments are made, movements of capital are accommodated, and exchange rates among currencies are determined. The exchange rate is a price, i.e., the price of one currency vis-à-vis another. Si ...
... The international monetary system can be defined as the institutional framework within which international payments are made, movements of capital are accommodated, and exchange rates among currencies are determined. The exchange rate is a price, i.e., the price of one currency vis-à-vis another. Si ...
solution
... interest rates perhaps too low for the UK, accelerating growth there and likely pushing inflation outside the 2% target range the UK prefers. At the same time, adding the UK to the euro area would have meant that the average growth rate and inflation rate in the euro area was higher. This may have l ...
... interest rates perhaps too low for the UK, accelerating growth there and likely pushing inflation outside the 2% target range the UK prefers. At the same time, adding the UK to the euro area would have meant that the average growth rate and inflation rate in the euro area was higher. This may have l ...
Exchange Rate Systems - Mays Business School
... The Bretton Woods System: 1944-1971 • After WWII, in 1944 representatives of 44 nations signed the Articles of Agreement of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) with European managing director and the U.S. having the largest quota/voting rights ...
... The Bretton Woods System: 1944-1971 • After WWII, in 1944 representatives of 44 nations signed the Articles of Agreement of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) with European managing director and the U.S. having the largest quota/voting rights ...
BOP Crisis and Economic Policy
... the foreign currency reserves gradually decline at the central bank, investors expect that the exchange rate will devalue in near future. Speculator swiftly buy large amount of foreign currency before domestic currency is devalued. The currency attack comes before the depletion of reserves. Lecture ...
... the foreign currency reserves gradually decline at the central bank, investors expect that the exchange rate will devalue in near future. Speculator swiftly buy large amount of foreign currency before domestic currency is devalued. The currency attack comes before the depletion of reserves. Lecture ...
Summary of IS-LM
... • Some countries operate fixed exchange rate regimes, where the Nominal Exchange rate is fixed: in that case the monetary authorities mop up and excess supply of foreign exchange by adding to reserves, and meet any excess demand by running down reserves • In a fixed exchange rate regime: Ms is endog ...
... • Some countries operate fixed exchange rate regimes, where the Nominal Exchange rate is fixed: in that case the monetary authorities mop up and excess supply of foreign exchange by adding to reserves, and meet any excess demand by running down reserves • In a fixed exchange rate regime: Ms is endog ...
MS34B-Week 5
... amount of products as a consumer in another country. In other words, it is the relative ability of two countries currencies to buy the same basket of goods in those two countries. MS34B, UWI Mona, Department of Management Studies ...
... amount of products as a consumer in another country. In other words, it is the relative ability of two countries currencies to buy the same basket of goods in those two countries. MS34B, UWI Mona, Department of Management Studies ...
International Monetary System
... Under the Bretton Woods system, the U.S. dollar was pegged to gold at $35 per ounce and other currencies were pegged to the U.S. dollar. Each country was responsible for maintaining its exchange rate within ±1% of the adopted par value by buying or selling foreign reserves as necessary. The Bretton ...
... Under the Bretton Woods system, the U.S. dollar was pegged to gold at $35 per ounce and other currencies were pegged to the U.S. dollar. Each country was responsible for maintaining its exchange rate within ±1% of the adopted par value by buying or selling foreign reserves as necessary. The Bretton ...
International Monetary System
... Under the Bretton Woods system, the U.S. dollar was pegged to gold at $35 per ounce and other currencies were pegged to the U.S. dollar. Each country was responsible for maintaining its exchange rate within ±1% of the adopted par value by buying or selling foreign reserves as necessary. The Bretton ...
... Under the Bretton Woods system, the U.S. dollar was pegged to gold at $35 per ounce and other currencies were pegged to the U.S. dollar. Each country was responsible for maintaining its exchange rate within ±1% of the adopted par value by buying or selling foreign reserves as necessary. The Bretton ...
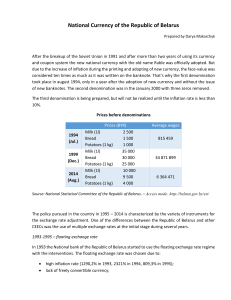
National Currency of the Republic of Belarus
... Government interventions in the functioning of financial markets resulted in the formation of parallel foreign-exchange market. At the end of 1996 the difference between the official and parallel market exchange rates was more than 40%. This led to the decrease of industrial efficiency, investments ...
... Government interventions in the functioning of financial markets resulted in the formation of parallel foreign-exchange market. At the end of 1996 the difference between the official and parallel market exchange rates was more than 40%. This led to the decrease of industrial efficiency, investments ...
The European Monetary System
... European Currency Unit (ECU), an The 1992 withdrawal of the UK from the European Exchange Rate artificial currency based on a basket of Mechanism, designed as a forerunner to a European political and member currencies. The fluctuations, currency union, sent shockwaves around the continent. which wer ...
... European Currency Unit (ECU), an The 1992 withdrawal of the UK from the European Exchange Rate artificial currency based on a basket of Mechanism, designed as a forerunner to a European political and member currencies. The fluctuations, currency union, sent shockwaves around the continent. which wer ...
Forex Systems 3 - IBECON
... This instability could reduce the volume of international trade as traders are unsure about the exchange rate that will prevail when their contracts are settled. The uncertainty could also reduce FDI as potential MNCs will not be able to make accurate profit projections. ...
... This instability could reduce the volume of international trade as traders are unsure about the exchange rate that will prevail when their contracts are settled. The uncertainty could also reduce FDI as potential MNCs will not be able to make accurate profit projections. ...