Economy: Undo Jonathan`s Sealed Failure (2)
... a budget surplus of N671.7 billion or 2.3 per cent of GDP. In that scenario, the proportion of the budget devoted to recurrent expenditure and capital expenditure respectively, that is, the recurrent to capital expenditure ratio would have remained 74:26 as in the report. But there would have been n ...
... a budget surplus of N671.7 billion or 2.3 per cent of GDP. In that scenario, the proportion of the budget devoted to recurrent expenditure and capital expenditure respectively, that is, the recurrent to capital expenditure ratio would have remained 74:26 as in the report. But there would have been n ...
Chapter 7_Problem set
... Name: __________________________ Date: _____________ 1. Open-economy macroeconomics is the branch of economics that deals with: A) reducing regulations on business. B) the relationships between economies of different nations. C) reducing employment discrimination. D) the provision of financial infor ...
... Name: __________________________ Date: _____________ 1. Open-economy macroeconomics is the branch of economics that deals with: A) reducing regulations on business. B) the relationships between economies of different nations. C) reducing employment discrimination. D) the provision of financial infor ...
operating_exposure
... The less price elastic the demand for the company’s products, the more price flexibility the company has. Price elasticity depends on the degree of competition and the location of key competitors. The more differentiated a company’s products are, the less competition it will face. (e.g. Merced ...
... The less price elastic the demand for the company’s products, the more price flexibility the company has. Price elasticity depends on the degree of competition and the location of key competitors. The more differentiated a company’s products are, the less competition it will face. (e.g. Merced ...
Details
... in Korean Won. • If the Hong Kong company does not have sufficient Korean Won, it has to buy KRW by converting HKD to KRW in order to settle the payment. ...
... in Korean Won. • If the Hong Kong company does not have sufficient Korean Won, it has to buy KRW by converting HKD to KRW in order to settle the payment. ...
Comments on “Income and Price Elasticities of Croatian Trade
... As a result of these factors, exchange rate policies lose much of their effectiveness, demand from developed countries is again a major determinant of TC export performance. Devaluation is an effective tool in this respect when used by one TC, if employed by a group the effects are wiped out! Devalu ...
... As a result of these factors, exchange rate policies lose much of their effectiveness, demand from developed countries is again a major determinant of TC export performance. Devaluation is an effective tool in this respect when used by one TC, if employed by a group the effects are wiped out! Devalu ...
Kaminisky, Graciela L
... Contagion effects: if it is present, a crisis in a neighboring country may be an indicator of a future domestic crisis through channels of trade or finance. ...
... Contagion effects: if it is present, a crisis in a neighboring country may be an indicator of a future domestic crisis through channels of trade or finance. ...
Document
... 6. Suppose the U.S. dollar appreciates relative to the Japanese yen. How will exports and imports of the two countries be affected. If the U.S. dollar appreciates relative to the Japanese yen, Japanese goods and services will be less expensive to Americans. Americans can now purchase more Japanese g ...
... 6. Suppose the U.S. dollar appreciates relative to the Japanese yen. How will exports and imports of the two countries be affected. If the U.S. dollar appreciates relative to the Japanese yen, Japanese goods and services will be less expensive to Americans. Americans can now purchase more Japanese g ...
Chapter 13
... increase imports, which also creates demand for the foreign currency, lowering the exchange rate However, the resulting interest rate increase causes the exchange rate to rise. So we are left with an ambiguous overall implication for the exchange rate NX declines because of the rise in the interest ...
... increase imports, which also creates demand for the foreign currency, lowering the exchange rate However, the resulting interest rate increase causes the exchange rate to rise. So we are left with an ambiguous overall implication for the exchange rate NX declines because of the rise in the interest ...
E719_No13_Chapter13
... increase imports, which also creates demand for the foreign currency, lowering the exchange rate However, the resulting interest rate increase causes the exchange rate to rise. So we are left with an ambiguous overall implication for the exchange rate NX declines because of the rise in the interest ...
... increase imports, which also creates demand for the foreign currency, lowering the exchange rate However, the resulting interest rate increase causes the exchange rate to rise. So we are left with an ambiguous overall implication for the exchange rate NX declines because of the rise in the interest ...
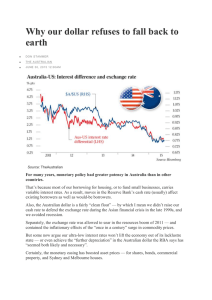
Why our dollar refuses to fall back to earth
... early 2013, relative to the difference in interest rates between the US and Australia. But that discrepancy was corrected in the June quarter of 2013 and has not reappeared. The Australian dollar seems to be about where relative interest rates suggest it should be. For our dollar to decline usefully ...
... early 2013, relative to the difference in interest rates between the US and Australia. But that discrepancy was corrected in the June quarter of 2013 and has not reappeared. The Australian dollar seems to be about where relative interest rates suggest it should be. For our dollar to decline usefully ...
Exchange Rate Regimes and Policies
... 1. Real versus nominal exchange rates 2. Exchange rate policy and welfare 3. The scourge of overvaluation 4. From exchange rate policy to economic growth 5. Exchange rate regimes To float or not to float ...
... 1. Real versus nominal exchange rates 2. Exchange rate policy and welfare 3. The scourge of overvaluation 4. From exchange rate policy to economic growth 5. Exchange rate regimes To float or not to float ...
Unit 8 PPT
... the same effect as devaluation—it increases exports and reduces imports, increasing aggregate demand even more than the intended monetary policy! ...
... the same effect as devaluation—it increases exports and reduces imports, increasing aggregate demand even more than the intended monetary policy! ...
Devalvācijas efekts uz ārējo tirdzniecību un tekošo kontu
... • Fixed exchange rate regime provides a clear nominal anchor • Changes in regime will lead to a loss in Central Bank credibility • Latvian business cycles are converging towards euro area business cycles • Exchange rate stability stimulates exports • Foreign debt is mostly denominated in euros • Inf ...
... • Fixed exchange rate regime provides a clear nominal anchor • Changes in regime will lead to a loss in Central Bank credibility • Latvian business cycles are converging towards euro area business cycles • Exchange rate stability stimulates exports • Foreign debt is mostly denominated in euros • Inf ...
Determination of exchange rates
... when imports and exports are sufficiently inelastic in the short run, both unstable exchange rates and a temporary worsening of the balance of trade after currency depreciation – but in the long run the imports and exports are more elastic the trade balance turns around and stability returns to fore ...
... when imports and exports are sufficiently inelastic in the short run, both unstable exchange rates and a temporary worsening of the balance of trade after currency depreciation – but in the long run the imports and exports are more elastic the trade balance turns around and stability returns to fore ...
Exhange Rate Project
... reintroduction of the gold standard required a massive creation of dollars and a deflationary policy in the UK, policies which ultimately led to the crash in 1929. As the depression wore on, the UK parted from the gold standard in 1931, leaving the Dutch official pound reserves in shambles. The Dutc ...
... reintroduction of the gold standard required a massive creation of dollars and a deflationary policy in the UK, policies which ultimately led to the crash in 1929. As the depression wore on, the UK parted from the gold standard in 1931, leaving the Dutch official pound reserves in shambles. The Dutc ...
III. Determinants of Exchange Rate
... as discussed previously, encourages the government to decide on a political economy base. • The relative importance of the tradable producers, represented by the tradable sector, and the consumer voters are crucial to the argument of the political economy of exchange rate commitments. • The tradable ...
... as discussed previously, encourages the government to decide on a political economy base. • The relative importance of the tradable producers, represented by the tradable sector, and the consumer voters are crucial to the argument of the political economy of exchange rate commitments. • The tradable ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from... Economic Research Volume Title: The Great Contraction, 1929–33
... to gold with the smallest actual gold reserves, and whose financial struc- ...
... to gold with the smallest actual gold reserves, and whose financial struc- ...
Backed by Gold Fiat Money - Saint Joseph High School
... – South Africa and Klondike region of Canada ...
... – South Africa and Klondike region of Canada ...
Comment - Lars E.O. Svensson
... ative effects. IMF (2011b) examined international capital flows over the last 30 years and found that net capital flows to emerging markets have been strongly correlated with changes in global financing conditions, rising sharply during periods with relatively low global interest rates. Based on the ...
... ative effects. IMF (2011b) examined international capital flows over the last 30 years and found that net capital flows to emerging markets have been strongly correlated with changes in global financing conditions, rising sharply during periods with relatively low global interest rates. Based on the ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES COMPETITIVENESS, REALIGNMENT, AND SPECULATION: Maurice Obstfeld
... here is part of the NBERS research program in International Studies. Any opinions expressed are those of the author and not those of the National Bureau of Economic ...
... here is part of the NBERS research program in International Studies. Any opinions expressed are those of the author and not those of the National Bureau of Economic ...
FREE Sample Here
... A. The Gold Standard: An international monetary system in which nations fix their exchange rates in terms of gold. Thus, all currencies are fixed in terms of each other. Any balance of payment problems could be made up by shipments of gold. There is a relationship between the balance of payments and ...
... A. The Gold Standard: An international monetary system in which nations fix their exchange rates in terms of gold. Thus, all currencies are fixed in terms of each other. Any balance of payment problems could be made up by shipments of gold. There is a relationship between the balance of payments and ...
A Theory of Optimum Currency Areas1
... need cause neither inflation nor unemployment in either region. The Western dollar appreciates relative to the Eastern dollar, thus assuring balance-of-payments equilibrium, while the Eastern and Western central banks adopt monetary policies to ensure constancy of effective demand in terms of the re ...
... need cause neither inflation nor unemployment in either region. The Western dollar appreciates relative to the Eastern dollar, thus assuring balance-of-payments equilibrium, while the Eastern and Western central banks adopt monetary policies to ensure constancy of effective demand in terms of the re ...
DOC
... and 4 percent per annum in the United States; (2) today's spot price of the pound is $1.50 while the 6-month forward price of the pound is $1.485. Consider Interest Rates. If U.S. investors cover their exchange-rate risk, the extra return for the 6 months on the U.K. treasury bills is: a) 1.0 perce ...
... and 4 percent per annum in the United States; (2) today's spot price of the pound is $1.50 while the 6-month forward price of the pound is $1.485. Consider Interest Rates. If U.S. investors cover their exchange-rate risk, the extra return for the 6 months on the U.K. treasury bills is: a) 1.0 perce ...