Greek and Persia I. Persian Empire
... Realizing that his Greek army would soon be surrounded, Leonidas dismissed most of the troops. He and 300 Spartans remained and fought to the death. The Greek historian Herodotus (hair • RAH • deh • tuhs) gave this description of the battle: "They [the Spartans] defended themselves to the last, thos ...
... Realizing that his Greek army would soon be surrounded, Leonidas dismissed most of the troops. He and 300 Spartans remained and fought to the death. The Greek historian Herodotus (hair • RAH • deh • tuhs) gave this description of the battle: "They [the Spartans] defended themselves to the last, thos ...
Ancient Greece (3 of 4) - Bonner Social Studies
... Each side began to resent and mistrust the other. Athens thought Sparta was cold and heartless, Sparta thought Athens was soft and spoiled. Each side began to create alliances with other city-states to defend themselves in case the other attacked Delian League- Athenian lead alliance of city-states ...
... Each side began to resent and mistrust the other. Athens thought Sparta was cold and heartless, Sparta thought Athens was soft and spoiled. Each side began to create alliances with other city-states to defend themselves in case the other attacked Delian League- Athenian lead alliance of city-states ...
Persian War - Ms. Clancy`s Social Studies
... A. Their ships were fast and could maneuver in tight spaces B. They had more soldiers C. They wanted to win more D. They had a strong army on foot ...
... A. Their ships were fast and could maneuver in tight spaces B. They had more soldiers C. They wanted to win more D. They had a strong army on foot ...
Chapter 5: Section 4 The Expansion of Greece Greek city
... 546 B.C.- Cyrus of Persia conquered Lydia in Asia Minor acquiring Greek citystates on the western coast of the Aegean Sea ...
... 546 B.C.- Cyrus of Persia conquered Lydia in Asia Minor acquiring Greek citystates on the western coast of the Aegean Sea ...
The Design of the Circulation Euro Coins: Greece – 1 Cent – Trireme
... of its self-administration. It was just about paying reasonable tribute and sending soldiers. As a general rule, the wars the Greeks cities fought against each other witnesses much more cruel repercussions. Be that as it may, in autumn 481 B. C., roughly 30 Greek cities stroke a league against the P ...
... of its self-administration. It was just about paying reasonable tribute and sending soldiers. As a general rule, the wars the Greeks cities fought against each other witnesses much more cruel repercussions. Be that as it may, in autumn 481 B. C., roughly 30 Greek cities stroke a league against the P ...
Ch. 4 PP
... captured Eretria and attacked Athens (490 b.c.e.) The attack on Athens was foiled when Athenian forces defeated the Persians at Marathon. ...
... captured Eretria and attacked Athens (490 b.c.e.) The attack on Athens was foiled when Athenian forces defeated the Persians at Marathon. ...
Lesson I Democracy: The Meaning of Marathon Most great
... race to enlist help for her. In Sparta the next day he says: 'Spartans, the Athenians entreat you. Do not allow them to be enslaved to barbarians.' But there are some days yet to the full moon, and until the moon was full the Spartans would not march. 'We will come as soon after that as we can.' Ph ...
... race to enlist help for her. In Sparta the next day he says: 'Spartans, the Athenians entreat you. Do not allow them to be enslaved to barbarians.' But there are some days yet to the full moon, and until the moon was full the Spartans would not march. 'We will come as soon after that as we can.' Ph ...
Chapter 28 of History Alive!
... as allies. Allies are states that agree to help each other against a common enemy. Throughout history, soldiers Persian soldier have written home before battle. We can image the kind of letter an Athenian might have written to his family. "The Greek soldier Persians are fierce fighters. But I will s ...
... as allies. Allies are states that agree to help each other against a common enemy. Throughout history, soldiers Persian soldier have written home before battle. We can image the kind of letter an Athenian might have written to his family. "The Greek soldier Persians are fierce fighters. But I will s ...
Persian Invasions
... navy together in case the Persians came back again. At first everyone thought this was a good idea, except the Spartans, who refused. Then the Athenians said to the other cities, "Don't bother sending ships and men for the navy anymore; that is too hard. Just send money to Athens, and we will build ...
... navy together in case the Persians came back again. At first everyone thought this was a good idea, except the Spartans, who refused. Then the Athenians said to the other cities, "Don't bother sending ships and men for the navy anymore; that is too hard. Just send money to Athens, and we will build ...
THE GREEK WARS (499 BC * 404 BC)
... D. How did the Persian Wars affect the Greek city- states? 1. The Persian wars caused the Greek city-states (Sparta and Athens) to unite despite their rivalries. 2. The defeat of the great Persian Empire led to a Greek Golden Age. 3. Allowed Athens to preserve its independence and continue innovatio ...
... D. How did the Persian Wars affect the Greek city- states? 1. The Persian wars caused the Greek city-states (Sparta and Athens) to unite despite their rivalries. 2. The defeat of the great Persian Empire led to a Greek Golden Age. 3. Allowed Athens to preserve its independence and continue innovatio ...
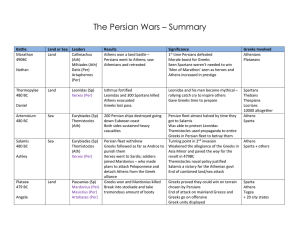
The Persian Wars – Summary Battle Land or Sea Leaders Results
... Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles naval policy justified Salamis a victory for the Athenian govt End of combined land/sea attack ...
... Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles naval policy justified Salamis a victory for the Athenian govt End of combined land/sea attack ...
Alexander the Great
... capture and burn Athens but are defeated by the Athenian navy at Salamis In 479, the Persians are defeated at Plataea and forced back to Anatolia ...
... capture and burn Athens but are defeated by the Athenian navy at Salamis In 479, the Persians are defeated at Plataea and forced back to Anatolia ...
lisarow high school senior ancient history
... 21) Persian Wars Revision -Match the person with his achievements: a) ...
... 21) Persian Wars Revision -Match the person with his achievements: a) ...
The Greeks at War!
... The Greek ruler Themistocles knew this was a temporary victory. He encouraged the Athenians to build up their fleet and prepare for battle with the Persians. In 480 B.C. Darius’ son Xerxes sent a larger force to conquer Greece. He sent 200,000 soldiers and nearly 1,000 ships. ...
... The Greek ruler Themistocles knew this was a temporary victory. He encouraged the Athenians to build up their fleet and prepare for battle with the Persians. In 480 B.C. Darius’ son Xerxes sent a larger force to conquer Greece. He sent 200,000 soldiers and nearly 1,000 ships. ...
persian Peloponnesian War facts1314
... and formed the Peloponnesian League War around Athens Athens believed that their Democracy was superior to the forms of government in other City-States Athens had a superior navy and Sparta had the superior Army Sparta Attacked Athens and surrounded the city-state. ...
... and formed the Peloponnesian League War around Athens Athens believed that their Democracy was superior to the forms of government in other City-States Athens had a superior navy and Sparta had the superior Army Sparta Attacked Athens and surrounded the city-state. ...
Marathon - Dominicana Journal
... their rise to power. To them, the present defeat was a surprise, to be sure, but they had been surprised and defeated before, only to return with a new an\cl. greater force. As the Persians sailed away from Marathon, there was little doubt in their minds that Darius would immediately begin preparati ...
... their rise to power. To them, the present defeat was a surprise, to be sure, but they had been surprised and defeated before, only to return with a new an\cl. greater force. As the Persians sailed away from Marathon, there was little doubt in their minds that Darius would immediately begin preparati ...
File
... 545 BC- Persians conquered Ionia 525 BC- Ionians revolted Ionians asked mainland Greece to help 520 BC- Persians put down Ionian Revolt Darius, Persian king, won and decided to punish mainland Greece for helping Ionians ...
... 545 BC- Persians conquered Ionia 525 BC- Ionians revolted Ionians asked mainland Greece to help 520 BC- Persians put down Ionian Revolt Darius, Persian king, won and decided to punish mainland Greece for helping Ionians ...
APWH Chapter 4 Lecture Outline Bulliet Ch. 4 Lecture
... Conflict between Athens and Sparta Sparta developed a navy paid for by the Persians Defeated Athens in 404 B.C.E. 2. Sparta’s arrogance inspired the opposition of the other Greek city-states Internal conflict among the Greeks Persia recovers lands in western Asia 3. Macedonia developed into a great ...
... Conflict between Athens and Sparta Sparta developed a navy paid for by the Persians Defeated Athens in 404 B.C.E. 2. Sparta’s arrogance inspired the opposition of the other Greek city-states Internal conflict among the Greeks Persia recovers lands in western Asia 3. Macedonia developed into a great ...
Persian responsibility - long essay
... inferior to that of his own troops. The Greek hoplites were equipped with bronze armour, bronze grieves and a bronze helmet. They also carried a sword, a spear and a bronze or wooden shield. The Persians, by contrast, had very little armour and only wicker shields. They relied instead on their arche ...
... inferior to that of his own troops. The Greek hoplites were equipped with bronze armour, bronze grieves and a bronze helmet. They also carried a sword, a spear and a bronze or wooden shield. The Persians, by contrast, had very little armour and only wicker shields. They relied instead on their arche ...
Persian Wars Power Point
... The Impact of the Persian Wars 1. Athens emerged as the most powerful city-state. 2. Athens organized the Delian League, an alliance with 150 Greek city-states and colonies in the Aegean region. 3. Athens used the Delian League to create an Athenian empire. 4. With Pericles as its leader, Athens en ...
... The Impact of the Persian Wars 1. Athens emerged as the most powerful city-state. 2. Athens organized the Delian League, an alliance with 150 Greek city-states and colonies in the Aegean region. 3. Athens used the Delian League to create an Athenian empire. 4. With Pericles as its leader, Athens en ...
File
... He was afraid that the Greeks would reach the Hellespont first and destroy the bridges he had built. As it turned out, the bridges had already been wrecked by a bad storm. Xerxes had to ferry his men across the water by boat. Xerxes left the rest of the Persian army in Greece, with orders to attack ...
... He was afraid that the Greeks would reach the Hellespont first and destroy the bridges he had built. As it turned out, the bridges had already been wrecked by a bad storm. Xerxes had to ferry his men across the water by boat. Xerxes left the rest of the Persian army in Greece, with orders to attack ...
What you looking at, punk?: The History of Greek Warfare
... the same about its army. After 10 years of fighting, neither army had made any real headway so they signed the Peace of Nicias which kept things as they were but stopped the fighting (Maybe it would work in that car with…no, probably not.) ...
... the same about its army. After 10 years of fighting, neither army had made any real headway so they signed the Peace of Nicias which kept things as they were but stopped the fighting (Maybe it would work in that car with…no, probably not.) ...
Xerxes` Invasion
... At this point I am forced to declare an opinion that most people will find offensive; yet, because I think it is true, I will not hold back. If the Athenians had taken fright at the approaching danger and had left their own country, or even if they had not left it but had remained and surrendered to ...
... At this point I am forced to declare an opinion that most people will find offensive; yet, because I think it is true, I will not hold back. If the Athenians had taken fright at the approaching danger and had left their own country, or even if they had not left it but had remained and surrendered to ...
Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with the individual actions of two Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus and Aristagoras. The cities of Ionia had been conquered by Persia around 540 BC, and thereafter were ruled by native tyrants, nominated by the Persian satrap in Sardis. In 499 BC, the then tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes to conquer Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position. The mission was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king Darius the Great.In 498 BC, supported by troops from Athens and Eretria, the Ionians marched on, captured, and burnt Sardis. However, on their return journey to Ionia, they were followed by Persian troops, and decisively beaten at the Battle of Ephesus. This campaign was the only offensive action by the Ionians, who subsequently went on the defensive. The Persians responded in 497 BC with a three pronged attack aimed at recapturing the outlying areas of the rebellion, but the spread of the revolt to Caria meant that the largest army, under Daurises, relocated there. While initially campaigning successfully in Caria, this army was annihilated in an ambush at the Battle of Pedasus. This resulted in a stalemate for the rest of 496 BC and 495 BC.By 494 BC the Persian army and navy had regrouped, and they made straight for the epicentre of the rebellion at Miletus. The Ionian fleet sought to defend Miletus by sea, but were decisively beaten at the Battle of Lade, after the defection of the Samians. Miletus was then besieged, captured, and its population was brought under Persian rule. This double defeat effectively ended the revolt, and the Carians surrendered to the Persians as a result. The Persians spent 493 BC reducing the cities along the west coast that still held out against them, before finally imposing a peace settlement on Ionia which was generally considered to be both just and fair.The Ionian Revolt constituted the first major conflict between Greece and the Persian Empire, and as such represents the first phase of the Greco-Persian Wars. Although Asia Minor had been brought back into the Persian fold, Darius vowed to punish Athens and Eretria for their support of the revolt. Moreover, seeing that the myriad city states of Greece posed a continued threat to the stability of his Empire, according to Herodotus, Darius decided to conquer the whole of Greece. In 492 BC, the first Persian invasion of Greece, the next phase of the Greco-Persian Wars, would begin as a direct consequence of the Ionian Revolt.