Unity - long essay
... How important was unity to the Greek states in their victory over the Persians? Unity was crucial to the Greek victory in the two Persian Wars – particularly the Second, which was a two year campaign. Without it they would never have been able to muster sufficient forces to take on the might of Pers ...
... How important was unity to the Greek states in their victory over the Persians? Unity was crucial to the Greek victory in the two Persian Wars – particularly the Second, which was a two year campaign. Without it they would never have been able to muster sufficient forces to take on the might of Pers ...
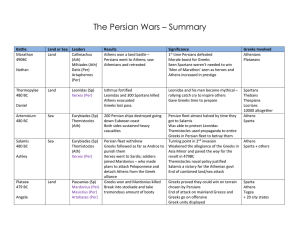
The Persian Wars – Summary Battle Land or Sea Leaders Results
... Persian fleet almost halved by time they got to Salamis Was able to protect Leonidas Themistocles used propaganda to entire Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles ...
... Persian fleet almost halved by time they got to Salamis Was able to protect Leonidas Themistocles used propaganda to entire Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles ...
Chapter 6: Greek Civilization 2000 BC to 323 BC
... Around 1100 BC, Spartans enslaved native farmers and ...
... Around 1100 BC, Spartans enslaved native farmers and ...
to Unit 3 - Ancient Greece Notes
... C. The Greek city-states ________________ & ________________ represented the differences among polis 1. Athenian society focused on ________________ & ________________: a. Athens had a direct democracy in which both rich & poor citizens could ______________ & hold public office b. Architects built ...
... C. The Greek city-states ________________ & ________________ represented the differences among polis 1. Athenian society focused on ________________ & ________________: a. Athens had a direct democracy in which both rich & poor citizens could ______________ & hold public office b. Architects built ...
Archaic Age - Way of living – polis revolved around market place
... Leaders are from nobles (archonts) Council of elders (rada starších)– aeropag Democracy – rule by people, decisions are made by all citizens Tyranny – run by a master, power in hands of tyran Citizens had civil’s rights for a election, own land, have life and property protected, their also h ...
... Leaders are from nobles (archonts) Council of elders (rada starších)– aeropag Democracy – rule by people, decisions are made by all citizens Tyranny – run by a master, power in hands of tyran Citizens had civil’s rights for a election, own land, have life and property protected, their also h ...
Greek Review Answers
... Persian Kings 9.b) Analyze; How did the Greeks use strategy to defeat a larger fighng force? The Greeks led the larger Persian navy into narrow straits of Salamis, in which the Persian navy could not fit. As a result, the smaller Athenian boats easily sank many Persian ships. 9.c) Elaborate; What we ...
... Persian Kings 9.b) Analyze; How did the Greeks use strategy to defeat a larger fighng force? The Greeks led the larger Persian navy into narrow straits of Salamis, in which the Persian navy could not fit. As a result, the smaller Athenian boats easily sank many Persian ships. 9.c) Elaborate; What we ...
Background to Lysistrata
... – Xerxes left some guys behind with his second in command. – Greeks win—small contingent of Persians run away. – Greek naval victory at Mykale in Asia Minor ends the Persian threat. – Later Alexander will take it all away from Persia and then succumb to Persia ...
... – Xerxes left some guys behind with his second in command. – Greeks win—small contingent of Persians run away. – Greek naval victory at Mykale in Asia Minor ends the Persian threat. – Later Alexander will take it all away from Persia and then succumb to Persia ...
The ETRUSCAN
... T he Ionian Revolt of 499 BC by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule is the starting point of Mika Waltari’s The Etruscan. The cities of Ionia had been conquered earlier by Persia around 540 BC. The revolt was finally ended in 493 BC by the Persian king, Darius. Because the revol ...
... T he Ionian Revolt of 499 BC by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule is the starting point of Mika Waltari’s The Etruscan. The cities of Ionia had been conquered earlier by Persia around 540 BC. The revolt was finally ended in 493 BC by the Persian king, Darius. Because the revol ...
Ancient Greece
... • When Ancient Greece began, there were 4 different governments: Monarchy, Oligarchy, Tyranny, democracy. • Although Greece was small, it was broken up into small city–states with individual governments. • Alexander the Great was part of a powerful monarchy. ...
... • When Ancient Greece began, there were 4 different governments: Monarchy, Oligarchy, Tyranny, democracy. • Although Greece was small, it was broken up into small city–states with individual governments. • Alexander the Great was part of a powerful monarchy. ...
Ancient Greece - Calaveras Unified School District
... 1. They were educated to think and act as 2. They were eager to 3. Two leaders reformed the government into a democracy 4. Solon (594 BC) reforms the economy and politics. a. Canceled all debts, freed indebted slaves, made farming profitable and required sons to get a trade. b. Allowed all males to ...
... 1. They were educated to think and act as 2. They were eager to 3. Two leaders reformed the government into a democracy 4. Solon (594 BC) reforms the economy and politics. a. Canceled all debts, freed indebted slaves, made farming profitable and required sons to get a trade. b. Allowed all males to ...
Delian Confederacy Worksheet
... Athens considering her own interests in encouraging money payment instead of................. ...
... Athens considering her own interests in encouraging money payment instead of................. ...
LastStandOfThe300Video
... 28. What would the Greeks eventually do years later to the Persian threat? 29. In the end, what were the main accomplishments of the 300 Spartans? 30. What idea might have been destroyed if the Persians had conquered the Greeks? ...
... 28. What would the Greeks eventually do years later to the Persian threat? 29. In the end, what were the main accomplishments of the 300 Spartans? 30. What idea might have been destroyed if the Persians had conquered the Greeks? ...
File
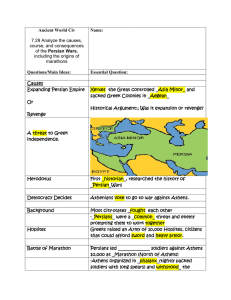
... Most city-states _fought each other -_Persians_ were a _common_ threat and enemy prompting them to work together Greeks raised an Army of 10,000 Hoplites, citizens that could afford sword and heavy armor. ...
... Most city-states _fought each other -_Persians_ were a _common_ threat and enemy prompting them to work together Greeks raised an Army of 10,000 Hoplites, citizens that could afford sword and heavy armor. ...
CHRONOLOGICAL OUTLINE OF ANCIENT GREEK HISTORY
... Expansion of the Persian Empire Cyrus (559-530) vs. Croesus of Lydia, ca. 544 Cambyses (530-522) in Egypt Darius I, "the Great" (522-486): imperial ambitions in Europe; operations in Thrace and beyond the Danube. Phoenician sea-power plus Persian land power; mercantile competition in the west. Collu ...
... Expansion of the Persian Empire Cyrus (559-530) vs. Croesus of Lydia, ca. 544 Cambyses (530-522) in Egypt Darius I, "the Great" (522-486): imperial ambitions in Europe; operations in Thrace and beyond the Danube. Phoenician sea-power plus Persian land power; mercantile competition in the west. Collu ...
Greeces last stand of 300
... • A Persian-sympathizer & traitor named Ephialtes led the Persians around the pass showing them where to attack from behind. • Expecting defeat, Leonidas sent away most of his troops. • The remaining 300 Spartan warriors fought the Persians & blocked the pass long enough so the rest of the Greek arm ...
... • A Persian-sympathizer & traitor named Ephialtes led the Persians around the pass showing them where to attack from behind. • Expecting defeat, Leonidas sent away most of his troops. • The remaining 300 Spartan warriors fought the Persians & blocked the pass long enough so the rest of the Greek arm ...
Classical Greece
... Assembly – voted on issues decided by the council of elders Rejected outside world’s ideas ...
... Assembly – voted on issues decided by the council of elders Rejected outside world’s ideas ...
Honors LastStandOfThe300Video
... 27. Why wasn’t there a great loss of life? 28. What would the Greeks eventually do years later to the Persian threat? 29. In the end, what were the main accomplishments of the 300 Spartans? 30. What idea might have been destroyed if the Persians had conquered the Greeks? ...
... 27. Why wasn’t there a great loss of life? 28. What would the Greeks eventually do years later to the Persian threat? 29. In the end, what were the main accomplishments of the 300 Spartans? 30. What idea might have been destroyed if the Persians had conquered the Greeks? ...
The Persian Wars
... 6. Who did Leonidus consult for advice on whether to join with the other Greeks against Persia? How many Spartan warriors was he allowed to choose to go into battle with him? ...
... 6. Who did Leonidus consult for advice on whether to join with the other Greeks against Persia? How many Spartan warriors was he allowed to choose to go into battle with him? ...
Persian Wars - Taylored teaching
... • After the defeat of the Greeks at Thermopylae, the Persians marched south and stormed the city of Athens, destroying it almost entirely. • Despite their victories at Thermopylae and Athens, the Persians had lost their naval support and so Xerxes returned to Persia with a large part of his army. • ...
... • After the defeat of the Greeks at Thermopylae, the Persians marched south and stormed the city of Athens, destroying it almost entirely. • Despite their victories at Thermopylae and Athens, the Persians had lost their naval support and so Xerxes returned to Persia with a large part of his army. • ...
the persian wars
... Athens, under the leadership of Themistocles, abandoned Athens and retreated to the small island of Salamis. The Greek navy, made up of smaller and quicker boats called Triremes, easily defeated the larger and awkward Persian warships. Xerxes, with the remainder of his army, then retreated back acro ...
... Athens, under the leadership of Themistocles, abandoned Athens and retreated to the small island of Salamis. The Greek navy, made up of smaller and quicker boats called Triremes, easily defeated the larger and awkward Persian warships. Xerxes, with the remainder of his army, then retreated back acro ...
Victory and Defeat in the Greek World: Quiz
... Write the letter of the correct answer in the blank provided. 6. Why did Persia go to war against Athens in 490 B.C.? a. Athenian traders attacked Persian ships. b. Athens interfered in Persian affairs. ...
... Write the letter of the correct answer in the blank provided. 6. Why did Persia go to war against Athens in 490 B.C.? a. Athenian traders attacked Persian ships. b. Athens interfered in Persian affairs. ...
Miss Farrell Welcomes you to South Pointe MS 6th
... 1. How were the Spartans able to hold the Persians off? ...
... 1. How were the Spartans able to hold the Persians off? ...
The Greco-Persian Wars, The Peloponnesian Wars, and Alexander
... from its little tiny peninsula to the entirety of the known world. Moreover, he culturally blended Greek culture with the culture of the people he conquered through cultural borrowing. Alexander’s conquests opened the door to a new world order, which EuropeanMediterranean culture would dominate ...
... from its little tiny peninsula to the entirety of the known world. Moreover, he culturally blended Greek culture with the culture of the people he conquered through cultural borrowing. Alexander’s conquests opened the door to a new world order, which EuropeanMediterranean culture would dominate ...
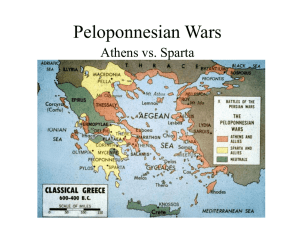
Athens and Sparta
... • Big Idea: War of Opposing Ideologies “This day will be the beginning of great evils for the Greeks.” ...
... • Big Idea: War of Opposing Ideologies “This day will be the beginning of great evils for the Greeks.” ...
Corinthian War

The Corinthian War was an ancient Greek conflict lasting from 395 BC until 387 BC, pitting Sparta against a coalition of four allied states, Thebes, Athens, Corinth, and Argos, who were initially backed by Persia. The immediate cause of the war was a local conflict in northwest Greece in which both Thebes and Sparta intervened. The deeper cause was hostility towards Sparta provoked by that city's ""expansionism in Asia Minor, central and northern Greece and even the west"".The war was fought on two fronts, on land near Corinth (hence the name) and Thebes and at sea in the Aegean. On land, the Spartans achieved several early successes in major battles, but were unable to capitalize on their advantage, and the fighting soon became stalemated. At sea, the Spartan fleet was decisively defeated by a Persian fleet early in the war, an event that effectively ended Sparta's attempts to become a naval power. Taking advantage of this fact, Athens launched several naval campaigns in the later years of the war, recapturing a number of islands that had been part of the original Athenian Empire during the 5th century BC.Alarmed by these Athenian successes, the Persians stopped backing the allies and began supporting Sparta. This defection forced the allies to seek peace. The Peace of Antalcidas, commonly known as the King's Peace, was signed in 387 BC, ending the war. This treaty declared that Persia would control all of Ionia, and that all other Greek cities would be independent. Sparta was to be the guardian of the peace, with the power to enforce its clauses. The effects of the war, therefore, were to establish Persia's ability to interfere successfully in Greek politics and to affirm Sparta's hegemonic position in the Greek political system.