Temperature and Thermal Energy
... thermometer in your mouth and wait for a few minutes before checking the thermometer for your temperature reading. The atomic level process involved in measuring temperature involves collisions and energy transfers between the thermometer and your body. ...
... thermometer in your mouth and wait for a few minutes before checking the thermometer for your temperature reading. The atomic level process involved in measuring temperature involves collisions and energy transfers between the thermometer and your body. ...
Document
... new thermodynamic function, the Gibbs energy, is introduced. G A + pV At constant temperature and pressure, a chemical system changes spontaneously to the states of lower Gibbs energy, i.e., dG 0, if possible. Therefore, the Gibbs free energy can be employed to access whether a chemical reaction ...
... new thermodynamic function, the Gibbs energy, is introduced. G A + pV At constant temperature and pressure, a chemical system changes spontaneously to the states of lower Gibbs energy, i.e., dG 0, if possible. Therefore, the Gibbs free energy can be employed to access whether a chemical reaction ...
Chapter 14 Review
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
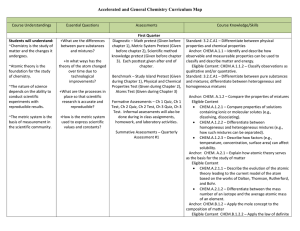
Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Standard: 3.2.C.A2 – Draw Lewis dot structures for simple molecules and ionic compounds. Anchor: CHEM.A.2.2 – Describe the behavior of electrons in atoms. Eligible Content: CHEM.A.2.2.3 – Explain the relationship between the electron configurations and the atomic structure of a given atom or ion (e. ...
... Standard: 3.2.C.A2 – Draw Lewis dot structures for simple molecules and ionic compounds. Anchor: CHEM.A.2.2 – Describe the behavior of electrons in atoms. Eligible Content: CHEM.A.2.2.3 – Explain the relationship between the electron configurations and the atomic structure of a given atom or ion (e. ...
Modeling the Rate of Heterogeneous Reactions
... surface diffusion, chemical transformations of adsorbed species, and desorption, and it is the basis for deriving the kinetics of the reaction. In the macroscopic regime, the rate of a catalytic reaction is modeled by fitting empirical equations, such as power laws, to experimental data to describe ...
... surface diffusion, chemical transformations of adsorbed species, and desorption, and it is the basis for deriving the kinetics of the reaction. In the macroscopic regime, the rate of a catalytic reaction is modeled by fitting empirical equations, such as power laws, to experimental data to describe ...
2 - Gordon State College
... CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR Carefully examine the following reaction sequence for the catalytic formation of ozone, O3, from molecular oxygen, O2. Which chemical compound is behaving as the catalyst? O2 + 2 NO 2 NO2 2 NO2 2 NO + 2 O 2 O + 2 O 2 2 O3 A. Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 B. Nitrogen monoxide, NO C. ...
... CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR Carefully examine the following reaction sequence for the catalytic formation of ozone, O3, from molecular oxygen, O2. Which chemical compound is behaving as the catalyst? O2 + 2 NO 2 NO2 2 NO2 2 NO + 2 O 2 O + 2 O 2 2 O3 A. Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 B. Nitrogen monoxide, NO C. ...
Sec 6.2 Enthalpy - Okemos Public Schools
... When 55.0g of water at 67.0°C is added to a beaker of water at 44.0°C the final temperature ends up being 58.0°C. What was the mass of water in the beaker? ...
... When 55.0g of water at 67.0°C is added to a beaker of water at 44.0°C the final temperature ends up being 58.0°C. What was the mass of water in the beaker? ...
10. Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
... Again, the collision theory of reactions explains this phenomenon: the average kinetic energy of molecules (energy of motion) is a direct function of temperature. When the temperature is increased, molecules move more rapidly, which means that they collide more frequently, but more importantly, that ...
... Again, the collision theory of reactions explains this phenomenon: the average kinetic energy of molecules (energy of motion) is a direct function of temperature. When the temperature is increased, molecules move more rapidly, which means that they collide more frequently, but more importantly, that ...
Subject Materials for Chemistry
... Glycerol decreases the rate of reaction. So glycerol is –ve catalyst. No, Catalyst doesn’t undergo any change chemically. A Catalyst may be recovered in mass and composition at the end of the chemical reaction. 6. What is the effect of temperature on the following? i) Dissociation of an electrolyte ...
... Glycerol decreases the rate of reaction. So glycerol is –ve catalyst. No, Catalyst doesn’t undergo any change chemically. A Catalyst may be recovered in mass and composition at the end of the chemical reaction. 6. What is the effect of temperature on the following? i) Dissociation of an electrolyte ...
H2 Chemistry Syllabus (9729)
... structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O Level, students have been introduced to the fundamental idea that matter is made up of particles and the simple atomic model (electrons in discrete shells around a positively charged nucleus). This allows students to apply the key ideas ...
... structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O Level, students have been introduced to the fundamental idea that matter is made up of particles and the simple atomic model (electrons in discrete shells around a positively charged nucleus). This allows students to apply the key ideas ...
Practical Exercises in Physical Chemistry
... In this work you are requested to obtain values of the dissociation rate constants of Mn(III) trisoxalate at three different temperatures and estimate values of the activation energy of the dissociation and the frequency factor of the Arrhenius equation. To do that you should experimentally measure: ...
... In this work you are requested to obtain values of the dissociation rate constants of Mn(III) trisoxalate at three different temperatures and estimate values of the activation energy of the dissociation and the frequency factor of the Arrhenius equation. To do that you should experimentally measure: ...
print
... reaction will also begin to be important. This condition makes determining the order of a reaction challenging, because the instantaneous rate is always changing. ...
... reaction will also begin to be important. This condition makes determining the order of a reaction challenging, because the instantaneous rate is always changing. ...
9647 H2 Chemistry
... discuss the effects on the entropy of a chemical system by the following: (i) change in temperature (ii) change in phase (iii) change in the number of particles (especially for gaseous systems) (iv) mixing of particles ...
... discuss the effects on the entropy of a chemical system by the following: (i) change in temperature (ii) change in phase (iii) change in the number of particles (especially for gaseous systems) (iv) mixing of particles ...
30 Scientific American, November 2010
... —will feel as though he is sitting inside a microwave oven set at a particular temperature proportional to his acceleration. (See Turning Up the Heat). This effect is real in the sense that such an accelerating observer can use this temperature he notices to heat up, say, a glass of water. In additi ...
... —will feel as though he is sitting inside a microwave oven set at a particular temperature proportional to his acceleration. (See Turning Up the Heat). This effect is real in the sense that such an accelerating observer can use this temperature he notices to heat up, say, a glass of water. In additi ...
Objective (Local, State, National – College Board)
... 1.a. Introduce acid-base behavior in terms of ionization. Use light bulb tester to show acids and bases contain conduct electricity because they contain ions. Good conductors are strong acids and bases, weak conductors are weak acids and bases. Arrhenius definitions are based on these observations. ...
... 1.a. Introduce acid-base behavior in terms of ionization. Use light bulb tester to show acids and bases contain conduct electricity because they contain ions. Good conductors are strong acids and bases, weak conductors are weak acids and bases. Arrhenius definitions are based on these observations. ...
Electron - HCC Learning Web
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Dipole Moment
... Polarities of X-H bonds increase upon hydrogen-bond formation, often leading to complexes whose dipole moments are larger than those expected from vectorial addition. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance (NMR) chemical shifts of protons in hydrogen bonds are substantially smaller than those observed in the co ...
... Polarities of X-H bonds increase upon hydrogen-bond formation, often leading to complexes whose dipole moments are larger than those expected from vectorial addition. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance (NMR) chemical shifts of protons in hydrogen bonds are substantially smaller than those observed in the co ...
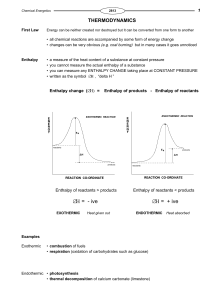
unit-4-notes-1_enthalpy-and-entropy
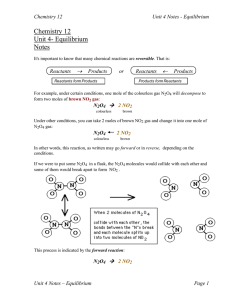
... and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at the start, but the reverse reaction rate eventually "caught up", the rates became equal and equilibrium was established. Can you guess what would happen if we had started with pure NO2 instead (no N2O4 )? The reverse rate would start out high and the ...
... and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at the start, but the reverse reaction rate eventually "caught up", the rates became equal and equilibrium was established. Can you guess what would happen if we had started with pure NO2 instead (no N2O4 )? The reverse rate would start out high and the ...
The Free High School Science Texts: A Textbook for High School
... Aside: Probabilities describe the chance of something happening or of being true. They usually have a value between 0 and 1 or 0% and 100% where 0 means no chance at all and 1 means definite. Probabilities are used when the state of something is uncertain. For example, probabilities are often used ...
... Aside: Probabilities describe the chance of something happening or of being true. They usually have a value between 0 and 1 or 0% and 100% where 0 means no chance at all and 1 means definite. Probabilities are used when the state of something is uncertain. For example, probabilities are often used ...
4_ Chemical reactions
... Consider the reaction in which magnesium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form magnesium carbonate. We can represent the above “word description” by a “chemical equation”. Chemical equation: MgO + CO2 → MgCO3 Reactants Product We often indicate the physical state of reactants and products using t ...
... Consider the reaction in which magnesium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form magnesium carbonate. We can represent the above “word description” by a “chemical equation”. Chemical equation: MgO + CO2 → MgCO3 Reactants Product We often indicate the physical state of reactants and products using t ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.