First Law of Thermodynamics
... liquid are loosely bound and may mix with one another freely. (While a liquid has a definite volume, it still takes the shape of its container. The molecules of a gas interact with each other slightly, but usually move at higher speeds than that of solid of liquid. In all three states of matter the ...
... liquid are loosely bound and may mix with one another freely. (While a liquid has a definite volume, it still takes the shape of its container. The molecules of a gas interact with each other slightly, but usually move at higher speeds than that of solid of liquid. In all three states of matter the ...
Accepted Manuscript
... et al (1995), is that there are implicit relations among the interest variables calculated by the simulator and both continuous decision (independent variables) and binary topological variables. ...
... et al (1995), is that there are implicit relations among the interest variables calculated by the simulator and both continuous decision (independent variables) and binary topological variables. ...
HOCl wt/wt 0.06 x mL 90 one cy
... Refer to your tables (makes a good starting point). What was observed during the reaction? Any colour change, any precipitate (why?), is it a homogeneous mixture, bubbling of gas? Was there any odour? What was the appearance of the product after recrystallization. Can you explain why these changes a ...
... Refer to your tables (makes a good starting point). What was observed during the reaction? Any colour change, any precipitate (why?), is it a homogeneous mixture, bubbling of gas? Was there any odour? What was the appearance of the product after recrystallization. Can you explain why these changes a ...
Atomic Mass - HCC Learning Web
... 25.0 g of NH3 are reacted with 150. g of F2, (a) What is the limiting reactant? (b) Calculate the theoretical yield of N2F4 in grams. (c) Calculate the percent yield if 56.8 g of N2F4 are actually obtained. (d) Calculate the actual yield of N2F4 in grams if the percent yield is 90%. (b) Calculate th ...
... 25.0 g of NH3 are reacted with 150. g of F2, (a) What is the limiting reactant? (b) Calculate the theoretical yield of N2F4 in grams. (c) Calculate the percent yield if 56.8 g of N2F4 are actually obtained. (d) Calculate the actual yield of N2F4 in grams if the percent yield is 90%. (b) Calculate th ...
Balancing Oxidation-Reduction Equations
... LO 1.17: The student is able to express the law of conservation of mass quantitatively and qualitatively using symbolic representations and particulate drawings. LO 1.18: The student is able to apply conservation of atoms to the rearrangement of atoms in various processes. LO 3.1: Students can trans ...
... LO 1.17: The student is able to express the law of conservation of mass quantitatively and qualitatively using symbolic representations and particulate drawings. LO 1.18: The student is able to apply conservation of atoms to the rearrangement of atoms in various processes. LO 3.1: Students can trans ...
Computational Study of protonation of ozone
... Optimization of geometrical parameters of molecular structures was carried out using a threeparameter exchange-correlation functional B3LYP and the basis set 6-311 ++ G (d, p). To confirm that the structures are minima on the potential energy surface, and to determine the zeropoint energy at the sam ...
... Optimization of geometrical parameters of molecular structures was carried out using a threeparameter exchange-correlation functional B3LYP and the basis set 6-311 ++ G (d, p). To confirm that the structures are minima on the potential energy surface, and to determine the zeropoint energy at the sam ...
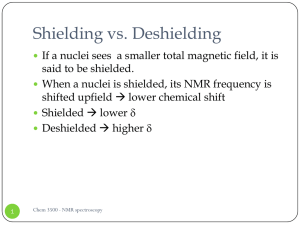
Shielding vs. Deshielding
... functional groups in a chemical compound. The effect is used in a qualitative way and describes the electron withdrawing or releasing properties of the substituents based on relevant resonance structures and is symbolized by the letter M. The mesomeric effect is negative (-M) when the substituent is ...
... functional groups in a chemical compound. The effect is used in a qualitative way and describes the electron withdrawing or releasing properties of the substituents based on relevant resonance structures and is symbolized by the letter M. The mesomeric effect is negative (-M) when the substituent is ...
1st-Year-ch-wise-test
... (6)Paschen, Brackette and Pfund series fall which region (a) ultraviolet region (b) I.R region (c) visible region (d) X-rays region (7) The volume of 1 mole of a gas at STP (a) 22.414 dm3 (b) 22414 dm3 ...
... (6)Paschen, Brackette and Pfund series fall which region (a) ultraviolet region (b) I.R region (c) visible region (d) X-rays region (7) The volume of 1 mole of a gas at STP (a) 22.414 dm3 (b) 22414 dm3 ...
Practice Problem Set #6
... (in milliliters) of H2 gas is produced when the gas is measured at 735 mm Hg and 22.5 °C? 6. Use a table of thermodynamic data to calculate the enthalpy and free energy change for the reaction: 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2(g) Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? Is the reaction product- or reacta ...
... (in milliliters) of H2 gas is produced when the gas is measured at 735 mm Hg and 22.5 °C? 6. Use a table of thermodynamic data to calculate the enthalpy and free energy change for the reaction: 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2(g) Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? Is the reaction product- or reacta ...
OSHA Material Safety Data Sheet
... Carcinogenicity: This mixture contains ingredients identified as carcinogens, at 0.1% or greater, by the following : None [X] ACGIH [ ] IARC [ ] NTP [ ] OSHA [ ] ...
... Carcinogenicity: This mixture contains ingredients identified as carcinogens, at 0.1% or greater, by the following : None [X] ACGIH [ ] IARC [ ] NTP [ ] OSHA [ ] ...
Ch 3 Chemical Reactions 2013-Sept-08
... in water so they form a black mass in the deep ocean floor cracks. Chemical Reactions are the heart of Chemistry. This chapter is an introduction to symbols and chemical reactions. 3.1 Intro to Chemical Equations In the late 1770’s Oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley coming from heating mercur ...
... in water so they form a black mass in the deep ocean floor cracks. Chemical Reactions are the heart of Chemistry. This chapter is an introduction to symbols and chemical reactions. 3.1 Intro to Chemical Equations In the late 1770’s Oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley coming from heating mercur ...
13 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM W MODULE - 5
... reactants and products. The numerator of the law of equilibrium is the product of equilibrium molar concentrations of products, each term being raised to the power equal to its stoichiometric coefficient in the chemical equation and the denominator contains products of similar concentration terms of ...
... reactants and products. The numerator of the law of equilibrium is the product of equilibrium molar concentrations of products, each term being raised to the power equal to its stoichiometric coefficient in the chemical equation and the denominator contains products of similar concentration terms of ...
Chapter 19
... The latent heat of vaporization is relevant for evaporation as well as boiling. The heat of vaporization of water rises slightly as the temperature decreases. On a molecular level, the heat added during a change of state does not go to increasing the kinetic energy of individual molecules, but rathe ...
... The latent heat of vaporization is relevant for evaporation as well as boiling. The heat of vaporization of water rises slightly as the temperature decreases. On a molecular level, the heat added during a change of state does not go to increasing the kinetic energy of individual molecules, but rathe ...
Thermochemistry - Xavier High School
... form of heat and light than the amount of energy it absorbs to start. Yes, but only indirectly. If the reaction were confined, then any temperature changes in the surroundings could be attributed to heat transfer from the reaction. ...
... form of heat and light than the amount of energy it absorbs to start. Yes, but only indirectly. If the reaction were confined, then any temperature changes in the surroundings could be attributed to heat transfer from the reaction. ...
Physical Chemistry 2.pdf
... nuclear chemistry. In solutions, we examine essentially the behaviour of homogenous mixtures involving pure substances. We shall also look at colloids, which differ from solutions only in terms of sizes of the solute. The topic of phase equilibrium looks at the physical transformation of pure substa ...
... nuclear chemistry. In solutions, we examine essentially the behaviour of homogenous mixtures involving pure substances. We shall also look at colloids, which differ from solutions only in terms of sizes of the solute. The topic of phase equilibrium looks at the physical transformation of pure substa ...
Department of Chemistry Second Year Syllabus
... The second year of the degree in Chemistry aims to provide the students with an expanded and deeper understanding of the fundamental concepts required to rationalise and predict chemical reactivity. To achieve this goal the students study the behaviour of a wide range of chemicals (both organic and ...
... The second year of the degree in Chemistry aims to provide the students with an expanded and deeper understanding of the fundamental concepts required to rationalise and predict chemical reactivity. To achieve this goal the students study the behaviour of a wide range of chemicals (both organic and ...
genius 13.1 Introduction. (1) Thermodynamics : It is a branch of
... It is a statement of conservation of energy in thermodynamical process. According to it heat given to a system (Q) is equal to the sum of increase in its internal energy (U) and the work done (W) by the system against the surroundings. Q U W ...
... It is a statement of conservation of energy in thermodynamical process. According to it heat given to a system (Q) is equal to the sum of increase in its internal energy (U) and the work done (W) by the system against the surroundings. Q U W ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.