expected output
... SYLLABUS:The concept of development and underdevelopment; socio-economic indicators of growth and development; group dynamics, organising people and activities, e.g. Harambee, e.t.c. division of labour; fundamentals of project management technology and society; role and responsibility project manage ...
... SYLLABUS:The concept of development and underdevelopment; socio-economic indicators of growth and development; group dynamics, organising people and activities, e.g. Harambee, e.t.c. division of labour; fundamentals of project management technology and society; role and responsibility project manage ...
expected output
... SYLLABUS:The concept of development and underdevelopment; socio-economic indicators of growth and development; group dynamics, organising people and activities, e.g. Harambee, e.t.c. division of labour; fundamentals of project management technology and society; role and responsibility project manage ...
... SYLLABUS:The concept of development and underdevelopment; socio-economic indicators of growth and development; group dynamics, organising people and activities, e.g. Harambee, e.t.c. division of labour; fundamentals of project management technology and society; role and responsibility project manage ...
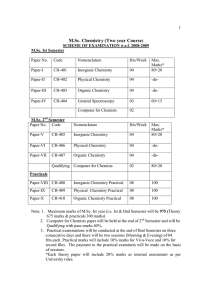
M.Sc. Chemistry (Two year Course)
... Thermodynamics: Brief resume of first and second Law of thermodynamics. Entropy changes in reversible and irreversible processes; variation of entropy with temperature , pressure and volume, entropy concept as a measure of unavailable energy and criteria for the spontaneity of reaction; free energy ...
... Thermodynamics: Brief resume of first and second Law of thermodynamics. Entropy changes in reversible and irreversible processes; variation of entropy with temperature , pressure and volume, entropy concept as a measure of unavailable energy and criteria for the spontaneity of reaction; free energy ...
G - Senger Science
... We will be forming 2 lines…Stand across from your class BFF. Be prepared to share your research topic choice(s). When you share your choice, your friend will tell you a comment that will help you with your project. Acceptable comment examples: “What one variable are you isolating” or “Where will you ...
... We will be forming 2 lines…Stand across from your class BFF. Be prepared to share your research topic choice(s). When you share your choice, your friend will tell you a comment that will help you with your project. Acceptable comment examples: “What one variable are you isolating” or “Where will you ...
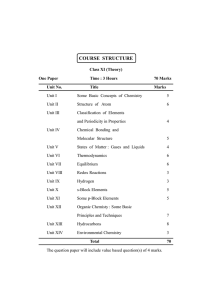
COURSE STRUCTURE
... for n, l and ml provided their spins are opposite (ms is different). Therefore an orbital can have at the most two electrons if they have opposite spins. Hund’s Rule of maximum Multiplicity : ‘‘The electrons start pairing only when all the degenerate orbitals of a subshell are singly occupied with p ...
... for n, l and ml provided their spins are opposite (ms is different). Therefore an orbital can have at the most two electrons if they have opposite spins. Hund’s Rule of maximum Multiplicity : ‘‘The electrons start pairing only when all the degenerate orbitals of a subshell are singly occupied with p ...
Chemical fractionation at environmental interfaces
... acoustic cavitational threshold, the bubbles would overgrow and eventually collapse.36 The transient collapse of bubbles leads to almost adiabatic compression of gas and vapor inside the bubbles, thus creating extremely high temperatures and pressures. The average vapor temperatures within the bubbl ...
... acoustic cavitational threshold, the bubbles would overgrow and eventually collapse.36 The transient collapse of bubbles leads to almost adiabatic compression of gas and vapor inside the bubbles, thus creating extremely high temperatures and pressures. The average vapor temperatures within the bubbl ...
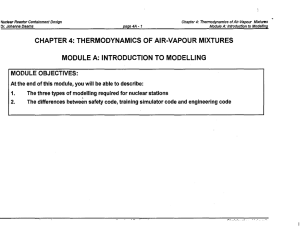
CHAPTER 4: THERMODYNAMICS OF AIR
... what happens to a perfect gas in a control volume when mass leaves, mass enters, the volume changes, or heat is transferred. • Textbooks of thermodynamics rarely consider the first two scenarios, which are critical for our modelling work. Focus is on getting an expanding gas to do work by enlarging ...
... what happens to a perfect gas in a control volume when mass leaves, mass enters, the volume changes, or heat is transferred. • Textbooks of thermodynamics rarely consider the first two scenarios, which are critical for our modelling work. Focus is on getting an expanding gas to do work by enlarging ...
Exam - Vcaa
... Answer all questions in the spaces provided. Write using black or blue pen. To obtain full marks for your responses you should • give simplified answers with an appropriate number of significant figures to all numerical questions; unsimplified answers will not be given full marks. • show all working ...
... Answer all questions in the spaces provided. Write using black or blue pen. To obtain full marks for your responses you should • give simplified answers with an appropriate number of significant figures to all numerical questions; unsimplified answers will not be given full marks. • show all working ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions - An Introduction to Chemistry
... accompanied by reduction (gain of electrons). In the reaction that forms ZnO from Zn and O2, the uncharged zinc atoms cannot easily lose electrons and be oxidized unless something such as oxygen is there to gain the electrons and be reduced. In the reaction that converts NaCl to Na and Cl2, the chlo ...
... accompanied by reduction (gain of electrons). In the reaction that forms ZnO from Zn and O2, the uncharged zinc atoms cannot easily lose electrons and be oxidized unless something such as oxygen is there to gain the electrons and be reduced. In the reaction that converts NaCl to Na and Cl2, the chlo ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced. – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced. – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined. Stoichiometry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced. – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced. – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined. Stoichiometry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
syntheses, structures, and their interconversion
... The products were hand-selected under a light microscope unless stated otherwise. The product mixture for the synthesis of thallate and plumbate compounds always contained amorphous (side-)products that were not further investigated, and K2Ch2 and K2Ch3 that were identified via single crystal diffrac ...
... The products were hand-selected under a light microscope unless stated otherwise. The product mixture for the synthesis of thallate and plumbate compounds always contained amorphous (side-)products that were not further investigated, and K2Ch2 and K2Ch3 that were identified via single crystal diffrac ...
THE USE OF THE FIRST PRINCIPLE APPROACH TO ENABLE
... students, some of which are referred to in this section, have included the limiting reagent concept as part of the studies. A study by Gauchon and Méheut (2007) investigated the effect of Grade 10 students’ preconceptions about the concept of limiting reagent on their understanding of stoichiometry. ...
... students, some of which are referred to in this section, have included the limiting reagent concept as part of the studies. A study by Gauchon and Méheut (2007) investigated the effect of Grade 10 students’ preconceptions about the concept of limiting reagent on their understanding of stoichiometry. ...
Medical Emergency Dial 911 or x52111
... Use a full-face respirator with multi-purpose combination (US) respirator cartridges as a backup to engineering controls. Respirators should be used only under any of the following circumstances: As a last line of defense (i.e., after engineering and administrative controls have been exhausted). ...
... Use a full-face respirator with multi-purpose combination (US) respirator cartridges as a backup to engineering controls. Respirators should be used only under any of the following circumstances: As a last line of defense (i.e., after engineering and administrative controls have been exhausted). ...
Chapter 4-5
... Aqueous reactions Aqueous reactions can be grouped into three general categories; a. precipitation, b. acid-base and c. Oxidation reactions – Reactions are driven from reactants to products by some energetic force that pushes them along. 1. Precipitation Reactions • Driving force = removal of mater ...
... Aqueous reactions Aqueous reactions can be grouped into three general categories; a. precipitation, b. acid-base and c. Oxidation reactions – Reactions are driven from reactants to products by some energetic force that pushes them along. 1. Precipitation Reactions • Driving force = removal of mater ...
An experimentally validated numerical model of interface advance of
... hardener was used to encapsulate crystals at room temperature. After solidification of the resin containing the crystal as shown in Fig. 2, samples were polished using abrasive papers of grit 600–4000 to increase their transparency and then an end surface in the direction [010] was ground to remove ...
... hardener was used to encapsulate crystals at room temperature. After solidification of the resin containing the crystal as shown in Fig. 2, samples were polished using abrasive papers of grit 600–4000 to increase their transparency and then an end surface in the direction [010] was ground to remove ...
Chapter 5: Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... Therefore, we need a conversion factor to convert atoms and molecules to grams. Mole is the connection or the conversion factor between atoms and grams. Avogadro's number The name "Avogadro's Number" is just an honorary name attached to the calculated value of the number of atoms, molecules, etc. in ...
... Therefore, we need a conversion factor to convert atoms and molecules to grams. Mole is the connection or the conversion factor between atoms and grams. Avogadro's number The name "Avogadro's Number" is just an honorary name attached to the calculated value of the number of atoms, molecules, etc. in ...
Engineering Thermodynamics
... Subscripts and Superscripts ............................................................................................................... 7 Basic Terminology and Selected Concepts ........................................................................................... 7 Energy and Work (2) .... ...
... Subscripts and Superscripts ............................................................................................................... 7 Basic Terminology and Selected Concepts ........................................................................................... 7 Energy and Work (2) .... ...
Section 4.9 Oxidation–Reduction Reactions
... • Limiting Reactant – reactant that is completely consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product ...
... • Limiting Reactant – reactant that is completely consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.