
Ch 6 LAN 7th Intro Chem Chemical Reactions
... dioxide and water as indicated in the following reaction 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) When 26.0 g of acetylene is burned in sufficient oxygen for complete reaction, the theoretical yield of CO2 is 88.0 g Calculate the percent yield for this reaction if the actual yield is only 72.4 ...
... dioxide and water as indicated in the following reaction 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) When 26.0 g of acetylene is burned in sufficient oxygen for complete reaction, the theoretical yield of CO2 is 88.0 g Calculate the percent yield for this reaction if the actual yield is only 72.4 ...
Changes of State
... Explain the relationship between equilibrium and changes of state. Predict changes in equilibrium using Le Chatelier's Principle. Explain what is meant by equilibrium vapor pressure. Describe the processes of boiling, freezing, melting, and sublimation. Interpret phase diagrams. ...
... Explain the relationship between equilibrium and changes of state. Predict changes in equilibrium using Le Chatelier's Principle. Explain what is meant by equilibrium vapor pressure. Describe the processes of boiling, freezing, melting, and sublimation. Interpret phase diagrams. ...
B.Sc. Physical Sciences - Department of Computer Science
... diagonal form upto matrices of order 3. Computation of matrix inverses using elementary row operations. Rank of matrix. Solutions of a system of linear equations using matrices. Illustrative examples of above concepts from Geometry, Physics, Chemistry, Combinatorics and Statistics. Unit II. Calculus ...
... diagonal form upto matrices of order 3. Computation of matrix inverses using elementary row operations. Rank of matrix. Solutions of a system of linear equations using matrices. Illustrative examples of above concepts from Geometry, Physics, Chemistry, Combinatorics and Statistics. Unit II. Calculus ...
MC_16_mac
... Enthalpy of Formation, continued • Some standard enthalpies of formation are given in the appendix of your book. • Each entry in the table is the enthalpy of formation for the synthesis of one mole of the compound from its elements in their standard states. • The thermochemical equation to accompany ...
... Enthalpy of Formation, continued • Some standard enthalpies of formation are given in the appendix of your book. • Each entry in the table is the enthalpy of formation for the synthesis of one mole of the compound from its elements in their standard states. • The thermochemical equation to accompany ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Formulas and Equations Stoichiometry ...
... Formulas and Equations Stoichiometry ...
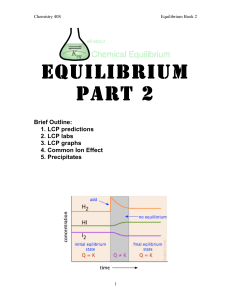
Equilibrium Part 2
... a system at equilibrium. The system attempts to remove added heat by using it up in the forward reaction (endothermic reaction). The equilibrium position shifts towards the right (products). The concentration of NO2 increases and the concentration of N2O4 decreases. We can also think of adding heat ...
... a system at equilibrium. The system attempts to remove added heat by using it up in the forward reaction (endothermic reaction). The equilibrium position shifts towards the right (products). The concentration of NO2 increases and the concentration of N2O4 decreases. We can also think of adding heat ...
Calculations on the equations reaction
... Determine the degree of oxidation of elements. Write the oxidant and reductant. 20.To equalize the oxidation-reduction reaction by electron balance method KMnO4 + HCl → MnCl2 + H2O +Cl2 + KCl . Determine the degree of oxidation of elements. Write the oxidant and reductant. Calculations based on the ...
... Determine the degree of oxidation of elements. Write the oxidant and reductant. 20.To equalize the oxidation-reduction reaction by electron balance method KMnO4 + HCl → MnCl2 + H2O +Cl2 + KCl . Determine the degree of oxidation of elements. Write the oxidant and reductant. Calculations based on the ...
Stoichiometry PP
... 2C2H2 + 5 O2 4CO2 + 2 H2O If 3.84 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of O2 are needed? (9.60 mol) How many moles of C2H2 are needed to produce 8.95 mole of H2O? (8.95 mol) If 2.47 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of CO2 are formed? (4.94 ...
... 2C2H2 + 5 O2 4CO2 + 2 H2O If 3.84 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of O2 are needed? (9.60 mol) How many moles of C2H2 are needed to produce 8.95 mole of H2O? (8.95 mol) If 2.47 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of CO2 are formed? (4.94 ...
B.Sc. Physical Sciences - Educational Multimedia Research Centre
... diagonal form upto matrices of order 3. Computation of matrix inverses using elementary row operations. Rank of matrix. Solutions of a system of linear equations using matrices. Illustrative examples of above concepts from Geometry, Physics, Chemistry, Combinatorics and Statistics. Unit II. Calculus ...
... diagonal form upto matrices of order 3. Computation of matrix inverses using elementary row operations. Rank of matrix. Solutions of a system of linear equations using matrices. Illustrative examples of above concepts from Geometry, Physics, Chemistry, Combinatorics and Statistics. Unit II. Calculus ...
Time allotted: 3hours Maximum Marks: 70
... b) Fluorine is strongest oxidant among all halogen. c) Among all the noble gases only xenon is known to form true chemical compound d) PbO2 is strongest oxidizing agent than SnO2. e) All the bonds in PCl5 are not equivalent. ...
... b) Fluorine is strongest oxidant among all halogen. c) Among all the noble gases only xenon is known to form true chemical compound d) PbO2 is strongest oxidizing agent than SnO2. e) All the bonds in PCl5 are not equivalent. ...
MSc Applied Chemistry Syllabus
... Kinetic aspects – reactive intermediates – their formation and stability – . Nucleophilic substitution at a saturated carbon atom – SN 1, SN 2 and SN i reactions. Elimination reactions E1, E2 and E1 c B- Elimination versus substitution. AROMATIC NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION : The SN Ar , benzyne and SR ...
... Kinetic aspects – reactive intermediates – their formation and stability – . Nucleophilic substitution at a saturated carbon atom – SN 1, SN 2 and SN i reactions. Elimination reactions E1, E2 and E1 c B- Elimination versus substitution. AROMATIC NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION : The SN Ar , benzyne and SR ...
Knowledge Check (Answer Key)
... No heat can flow into or out of the system because the cylinder is perfectly insulated from the surroundings (adiabatic enclosure). An adiabatic process will be described since there will be no external source or sink of heat energy. A weight is removed from the piston's platform and placed on an ad ...
... No heat can flow into or out of the system because the cylinder is perfectly insulated from the surroundings (adiabatic enclosure). An adiabatic process will be described since there will be no external source or sink of heat energy. A weight is removed from the piston's platform and placed on an ad ...
PDF File
... constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the pH (38). The affinity of S or P for the ribozyme is very high (see Figure 2B and Results), such that nonspecific losses to the tube walls are observed at the low ribozym ...
... constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the pH (38). The affinity of S or P for the ribozyme is very high (see Figure 2B and Results), such that nonspecific losses to the tube walls are observed at the low ribozym ...
Chapter 6 Rates of Chemical Reactions
... Check the values of m and n by inspection. When [ICl] doubles (when [H2 ] is constant), the rate also doubles. When [H2 ] quadruples (when [ICl] is constant), the rate also quadruples. To check the value for k, substitute data from experiments 2 or 3 into the equation and solve for k. Check that the ...
... Check the values of m and n by inspection. When [ICl] doubles (when [H2 ] is constant), the rate also doubles. When [H2 ] quadruples (when [ICl] is constant), the rate also quadruples. To check the value for k, substitute data from experiments 2 or 3 into the equation and solve for k. Check that the ...
Unit_1_Introduction_to_Chemistry_Student[1]
... the lab, so make sure you understand each rule! 1. Safety goggles must be worn at all times during a lab. This rule must be followed not matter what you are doing during the lab period. 2. Contact lenses are not allowed. Even when worn under safety goggles, since fumes from the chemicals can get und ...
... the lab, so make sure you understand each rule! 1. Safety goggles must be worn at all times during a lab. This rule must be followed not matter what you are doing during the lab period. 2. Contact lenses are not allowed. Even when worn under safety goggles, since fumes from the chemicals can get und ...
The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions
... the amazing variety of chemical reactions. Rapid chemical changes occur among gas molecules as sunlight bathes the atmosphere or lightning rips through a stormy sky (see margin). Oceans are gigantic containers in which aqueous reaction chemistry goes on unceasingly. In every cell of your body, thous ...
... the amazing variety of chemical reactions. Rapid chemical changes occur among gas molecules as sunlight bathes the atmosphere or lightning rips through a stormy sky (see margin). Oceans are gigantic containers in which aqueous reaction chemistry goes on unceasingly. In every cell of your body, thous ...
1984 Advanced Placement Exam
... (A) temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the external pressure. (B) temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to 760 mm Hg. (C) temperature at which the solid, liquid, and vapor phases are all in equilibrium. (D) temperature at which liquid and vapor ...
... (A) temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the external pressure. (B) temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to 760 mm Hg. (C) temperature at which the solid, liquid, and vapor phases are all in equilibrium. (D) temperature at which liquid and vapor ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.


















![Unit_1_Introduction_to_Chemistry_Student[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022016930_1-98bbde1835e65f7e36a50862854faaef-300x300.png)


