Thermodynamic course year 99-00
... can prevent flow of heat (adiabatic) material (a closed system) or changes in the volume or pressure. A thermodynamic state is specified by a set of thermodynamic parameters (or coordinates) necessary for the description of the system. These parameters are measurable quantities associated with the s ...
... can prevent flow of heat (adiabatic) material (a closed system) or changes in the volume or pressure. A thermodynamic state is specified by a set of thermodynamic parameters (or coordinates) necessary for the description of the system. These parameters are measurable quantities associated with the s ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
... • Before discussing isothermal or adiabatic processes, a new term is needed to make the calculations easier. • Heat Capacity, C is equal to the ratio of the heat absorbed or withdrawn from the system to the resultant change in temperature. q C T • Note: This is only true when phase change does not ...
... • Before discussing isothermal or adiabatic processes, a new term is needed to make the calculations easier. • Heat Capacity, C is equal to the ratio of the heat absorbed or withdrawn from the system to the resultant change in temperature. q C T • Note: This is only true when phase change does not ...
Chapter 7: Thermochemistry
... A system does not contain heat, the energy content of a system is a quantity called internal energy. Heat is simply a form in which a quantity of energy may be transferred across a boundary between a system and its surroundings. When heat, (i. e., energy), goes into a substance one of two things can ...
... A system does not contain heat, the energy content of a system is a quantity called internal energy. Heat is simply a form in which a quantity of energy may be transferred across a boundary between a system and its surroundings. When heat, (i. e., energy), goes into a substance one of two things can ...
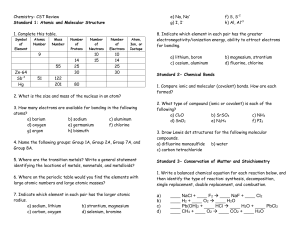
CP Chemistry Midterm Study Guide
... 20. What is the solution concentration of 25 g of NaCl mixed in 50 g of H2O? 21. How many grams of MgCl2 are in 500 mL of a 3.2 M solution? 22. How many atoms of sulfur do you have if you have 4 moles? 23. Convert 500 grams of magnesium to moles. 24. If we have 6.02x1023 molecules of oxygen, how man ...
... 20. What is the solution concentration of 25 g of NaCl mixed in 50 g of H2O? 21. How many grams of MgCl2 are in 500 mL of a 3.2 M solution? 22. How many atoms of sulfur do you have if you have 4 moles? 23. Convert 500 grams of magnesium to moles. 24. If we have 6.02x1023 molecules of oxygen, how man ...
Lecture 3: 09.14.05 The first law of thermodynamics
... Work and heat are not state functions; they are path dependent- what does this mean? In most physical situations, we are concerned with a quantity of heat or work transferred into or out of a material, which causes a change from one state of the material to another. Path dependence implies that the ...
... Work and heat are not state functions; they are path dependent- what does this mean? In most physical situations, we are concerned with a quantity of heat or work transferred into or out of a material, which causes a change from one state of the material to another. Path dependence implies that the ...
P - School of Chemical Sciences
... angular momentum, etc. There are “thermodynamic” variables in addition to the standard “mechanical” variables. ...
... angular momentum, etc. There are “thermodynamic” variables in addition to the standard “mechanical” variables. ...
Chapter 8 Chemical Equations and Reactions
... iv) List four kinds of single-displacement reactions and three kinds of double-displacement reactions. v) Predict the products of simple reactions given the reactants. ...
... iv) List four kinds of single-displacement reactions and three kinds of double-displacement reactions. v) Predict the products of simple reactions given the reactants. ...
introduction to matter
... A mixture is composed of two or more substances and may be heterogeneous or homogeneous. Its composition may be varied, i.e. you can form salt-water mixture (NaCl in H2O) with varying relative amounts of salt and water. Heterogeneous mixtures have properties that vary within the sample while homogen ...
... A mixture is composed of two or more substances and may be heterogeneous or homogeneous. Its composition may be varied, i.e. you can form salt-water mixture (NaCl in H2O) with varying relative amounts of salt and water. Heterogeneous mixtures have properties that vary within the sample while homogen ...
Lecture 5. Entropy and the Second Law (Ch. 2 )
... certain macropartition has a multiplicity of 6101024, while the total number of microstates available to the system in all macropartitions is 3101034. What is the probability to find the system in this macropartition? Imagine that the system is initially in the macropartition with a multiplicity o ...
... certain macropartition has a multiplicity of 6101024, while the total number of microstates available to the system in all macropartitions is 3101034. What is the probability to find the system in this macropartition? Imagine that the system is initially in the macropartition with a multiplicity o ...
Homework Exercises
... 2. What happens to the rate of a reaction if the concentration of the reactants is decreased? ...
... 2. What happens to the rate of a reaction if the concentration of the reactants is decreased? ...
KINETICS AND EQUILIBRIUM
... 1. In general for a closed system there will exist an equilibrium between phases where the rate of escape (from the phase) = the rate of return (to that phase) 2. Equilibrium existing between a solid and liquid phase at a substances melting point. At the melting point the rate at which a solid melts ...
... 1. In general for a closed system there will exist an equilibrium between phases where the rate of escape (from the phase) = the rate of return (to that phase) 2. Equilibrium existing between a solid and liquid phase at a substances melting point. At the melting point the rate at which a solid melts ...
Original powerpoint (~1.9 MB)
... reversible process without making an infinite number of infinitesimally small changes. ...
... reversible process without making an infinite number of infinitesimally small changes. ...
Name
... 7. A chemical reaction involving substances A and B stops when B is completely used. B is the a. excess reactant. b. limiting reactant. c. primary reactant. d. primary product. 8. The substance not completely used up in a chemical reaction is known as the a. limiting reactant. b. limiting product. ...
... 7. A chemical reaction involving substances A and B stops when B is completely used. B is the a. excess reactant. b. limiting reactant. c. primary reactant. d. primary product. 8. The substance not completely used up in a chemical reaction is known as the a. limiting reactant. b. limiting product. ...
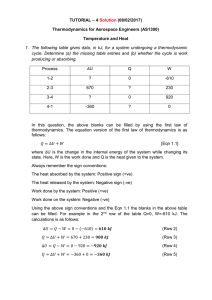
Solution Tutorial 4 - Aerospace Engineering, IIT Madras
... Thermodynamics for Aerospace Engineers (AS1300) Temperature and Heat 1. The following table gives data, in kJ, for a system undergoing a thermodynamic cycle. Determine (a) the missing table entries and (b) whether the cycle is work producing or absorbing. Process ...
... Thermodynamics for Aerospace Engineers (AS1300) Temperature and Heat 1. The following table gives data, in kJ, for a system undergoing a thermodynamic cycle. Determine (a) the missing table entries and (b) whether the cycle is work producing or absorbing. Process ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.