Phy 211: General Physics I
... – Solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) – Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
... – Solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) – Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
Answers to practice questions
... _____ 99. What does the ideal gas law allow a scientist to calculate that the other laws do not? A) number of moles B) pressure C) volume D) temperature _____ 100. Under laboratory conditions of 25.0oC and 99.5 kPa, what is the maximum number of liters of ammonia that could be produced from 1.50 L o ...
... _____ 99. What does the ideal gas law allow a scientist to calculate that the other laws do not? A) number of moles B) pressure C) volume D) temperature _____ 100. Under laboratory conditions of 25.0oC and 99.5 kPa, what is the maximum number of liters of ammonia that could be produced from 1.50 L o ...
Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the Atom • Early Models of the Atom atom
... - He didn't: - Explain chemical behavior - have experimental support • Dalton's Atomic Theory(1766-1844) 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms ...
... - He didn't: - Explain chemical behavior - have experimental support • Dalton's Atomic Theory(1766-1844) 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms ...
Final Exam Study Guide Page 1 Quiz
... a. Is completely used up in the reaction b. Will have some amount unchanged, or leftover, after the reaction c. Cannot be calculated without performing the reaction d. Has no effect in the amount of product formed ...
... a. Is completely used up in the reaction b. Will have some amount unchanged, or leftover, after the reaction c. Cannot be calculated without performing the reaction d. Has no effect in the amount of product formed ...
L1 - Internal Energy..
... Remember, a chemical system is described by P, V, n, T, and reactivity based on the properties of species reacting. Notice P and V are the variables of work. Also, notice that T, n (in terms of mass) and reactivity (in terms of specific heat) are the variables of heat transferred. ...
... Remember, a chemical system is described by P, V, n, T, and reactivity based on the properties of species reacting. Notice P and V are the variables of work. Also, notice that T, n (in terms of mass) and reactivity (in terms of specific heat) are the variables of heat transferred. ...
So where did all the matter on Earth come from - Bennatti
... letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnesium is Mg. Note the letter g is lower case. This is important as Co is the element cobalt but CO is the compound carbon monoxide ...
... letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnesium is Mg. Note the letter g is lower case. This is important as Co is the element cobalt but CO is the compound carbon monoxide ...
Energy
... standard enthalpy changes for many reactions. In an application of Hess’s Law, it is as if the reactants are decomposed into their elements, and then the elements are recombined into the desired products. Since enthalpies of reaction are independent of pathway, this provides an accurate way to calcu ...
... standard enthalpy changes for many reactions. In an application of Hess’s Law, it is as if the reactants are decomposed into their elements, and then the elements are recombined into the desired products. Since enthalpies of reaction are independent of pathway, this provides an accurate way to calcu ...
Combined quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM
... An ensemble is the assembly of all possible configurations that are consistent with the constraints that we impose on the system. A number of different ensemble averages are possible depending on the conditions of measurement (or simulation). The microcanonical ensemble (NVE) is the assembly of all ...
... An ensemble is the assembly of all possible configurations that are consistent with the constraints that we impose on the system. A number of different ensemble averages are possible depending on the conditions of measurement (or simulation). The microcanonical ensemble (NVE) is the assembly of all ...
2. Essential Chemistry
... o Cells constantly rearrange molecules by breaking existing chemical bonds and forming new ones o Such changes in the chemical composition of matter are called chemical reactions o Chemical reactions enable atoms to give up or acquire electrons in order to complete their outer shells These interac ...
... o Cells constantly rearrange molecules by breaking existing chemical bonds and forming new ones o Such changes in the chemical composition of matter are called chemical reactions o Chemical reactions enable atoms to give up or acquire electrons in order to complete their outer shells These interac ...
Barnard Castle School Chemistry Department
... hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide sodium chloride + water sulphuric acid + copper oxide copper sulphate + water Metals and Acids can also react Some metals also react with acids to produce salts. Reaction with metals produce hydrogen gas as another product. This can be identified by holding a ...
... hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide sodium chloride + water sulphuric acid + copper oxide copper sulphate + water Metals and Acids can also react Some metals also react with acids to produce salts. Reaction with metals produce hydrogen gas as another product. This can be identified by holding a ...
Laws of thermodynamics
... The gas constant for 1 kg of moist air is larger than that for 1 kg of dry air. But the exact value of the gas constant of moist air would depend on the amount of water vapor contained in the air. It is inconvenient to calculate the gas constant for moist air. It is more convenient to retain the gas ...
... The gas constant for 1 kg of moist air is larger than that for 1 kg of dry air. But the exact value of the gas constant of moist air would depend on the amount of water vapor contained in the air. It is inconvenient to calculate the gas constant for moist air. It is more convenient to retain the gas ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Normally, a compound composed of only C, H, (and maybe O) is reacted with oxygen – usually called “burning” If the combustion is complete, the products will be CO2 and H2O. If the combustion is incomplete, the products will be CO (or possibly just C) and H2O. ...
... Normally, a compound composed of only C, H, (and maybe O) is reacted with oxygen – usually called “burning” If the combustion is complete, the products will be CO2 and H2O. If the combustion is incomplete, the products will be CO (or possibly just C) and H2O. ...
the powerpoint
... • A coefficient is the number that comes before the chemical formula and indicates the number of particles that participate in the reaction. • In order to determine whether an equation is balanced, multiply the number in front of the chemical formula in the equation (coefficient) by the number writt ...
... • A coefficient is the number that comes before the chemical formula and indicates the number of particles that participate in the reaction. • In order to determine whether an equation is balanced, multiply the number in front of the chemical formula in the equation (coefficient) by the number writt ...
objectives chm 1025 - Miami Dade College
... f. Predicting when an acid or a base is leveled by a solvent and by recognizing pairs of acids or bases which can be differentiated by a solvent. [OPTIONAL] Competency 14: The student will demonstrate knowledge of thermodynamics by: a. Distinguishing among state functions, system, surroundings, and ...
... f. Predicting when an acid or a base is leveled by a solvent and by recognizing pairs of acids or bases which can be differentiated by a solvent. [OPTIONAL] Competency 14: The student will demonstrate knowledge of thermodynamics by: a. Distinguishing among state functions, system, surroundings, and ...
Name________________________ Midterm Review Date
... 43. Which set of procedures and observations indicates a chemical change? A) Ethanol is added to an empty beaker and the ethanol eventually disappears. B) Large crystals are crushed with a mortar and pestle and become powder. C) A solid is gently heated in a crucible and the solid slowly turns to li ...
... 43. Which set of procedures and observations indicates a chemical change? A) Ethanol is added to an empty beaker and the ethanol eventually disappears. B) Large crystals are crushed with a mortar and pestle and become powder. C) A solid is gently heated in a crucible and the solid slowly turns to li ...
Lecture #5
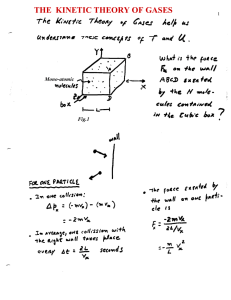
... Molecularity: The number of molecules in the activated complex. Thermodynamics tells only that Ea > H. III D. KINETIC THEORY OF GASES When molecules in the gas phase collide they sometimes rearrange their chemical bonds to form new molecules. The rate of formation of the new molecules is determined ...
... Molecularity: The number of molecules in the activated complex. Thermodynamics tells only that Ea > H. III D. KINETIC THEORY OF GASES When molecules in the gas phase collide they sometimes rearrange their chemical bonds to form new molecules. The rate of formation of the new molecules is determined ...
Chemical Reactions Practice Test
... b) the same number of atoms c) half the number of atoms _____2. What unit allows chemists to compare one chemical to another? a) amu b) kilograms c) atomic weights d) moles ______3. The coefficients from the balanced equation represent a) mole ratios b) masses c) molar masses _______4. In a chemical ...
... b) the same number of atoms c) half the number of atoms _____2. What unit allows chemists to compare one chemical to another? a) amu b) kilograms c) atomic weights d) moles ______3. The coefficients from the balanced equation represent a) mole ratios b) masses c) molar masses _______4. In a chemical ...
Mechanical Engineering
... Examples of intensive properties are pressure, temperature, density, volume per mass, molar volume (which is volume per mole), and average molecular weight (or molecular mass). These properties are the same regardless of how you vary the amount of mass of the substance. Properties are like the varia ...
... Examples of intensive properties are pressure, temperature, density, volume per mass, molar volume (which is volume per mole), and average molecular weight (or molecular mass). These properties are the same regardless of how you vary the amount of mass of the substance. Properties are like the varia ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.