4. Water (2)
... remains constant in any process (First law of thermodynamics). Energy is generally defined as the capacity to do work. 6.2 A process (e.g., a chemical reaction) can occur spontaneously only if the sum of the entropies (randomness) of the system (open) and its surrounding (the universe) increases (Se ...
... remains constant in any process (First law of thermodynamics). Energy is generally defined as the capacity to do work. 6.2 A process (e.g., a chemical reaction) can occur spontaneously only if the sum of the entropies (randomness) of the system (open) and its surrounding (the universe) increases (Se ...
Lab1_Lab2-1 - chem
... 2. Now use the syringes at your lab station For each substance that is sealed in a syringe, test the compressibility by pushing on the plunger and observing the decrease in volume for the substance. Record your findings. (Press syringes according to directions!) 3. Using words and pictures, develop ...
... 2. Now use the syringes at your lab station For each substance that is sealed in a syringe, test the compressibility by pushing on the plunger and observing the decrease in volume for the substance. Record your findings. (Press syringes according to directions!) 3. Using words and pictures, develop ...
6-1 Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
... The amount of heat in Joules can be calculated as follows: q = specific heat of water x grams of water x change in temperature specific heat of water = 4.18 J /(g oC) grams of water = 50. change in temperature = final temperature - initial temperature There are 4.184 Joules in one calorie. Clean Up: ...
... The amount of heat in Joules can be calculated as follows: q = specific heat of water x grams of water x change in temperature specific heat of water = 4.18 J /(g oC) grams of water = 50. change in temperature = final temperature - initial temperature There are 4.184 Joules in one calorie. Clean Up: ...
Chapter Five
... The substance(s) which we begin with are called the reactant(s) The substance(s) which we end with are called the product(s) We will examine chemical reactions in greater depth in Chapter Eight Writing Chemical Equations Chemical equations are written with the reactants to the left, the prod ...
... The substance(s) which we begin with are called the reactant(s) The substance(s) which we end with are called the product(s) We will examine chemical reactions in greater depth in Chapter Eight Writing Chemical Equations Chemical equations are written with the reactants to the left, the prod ...
Document
... adjusts itself such that, after some time, the reaction rates of the direct and inverse reactions are equal, i.e., the number of moles of CO2 that dissociate, according to the direct reaction, is equal to the number of moles that are formed, according to the inverse reaction, per unit of time. A che ...
... adjusts itself such that, after some time, the reaction rates of the direct and inverse reactions are equal, i.e., the number of moles of CO2 that dissociate, according to the direct reaction, is equal to the number of moles that are formed, according to the inverse reaction, per unit of time. A che ...
Measuring Rates
... The analysis of kinetic data demands a basic understanding of the mathematical relationships between concentration and time for chemical reactions with different rate orders. It also requires that we understand how experimental data can be represented in different ways to elicit underlying trends. D ...
... The analysis of kinetic data demands a basic understanding of the mathematical relationships between concentration and time for chemical reactions with different rate orders. It also requires that we understand how experimental data can be represented in different ways to elicit underlying trends. D ...
Chapter 3. Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and
... •Mass percent is the number of grams of each element in 100 g of sample •From these masses, number of moles can be calculated (use atomic weights on the periodic table) •The lowest whole-number ratio of moles is the empirical formula • Finding the empirical mass percent of elements from the empirica ...
... •Mass percent is the number of grams of each element in 100 g of sample •From these masses, number of moles can be calculated (use atomic weights on the periodic table) •The lowest whole-number ratio of moles is the empirical formula • Finding the empirical mass percent of elements from the empirica ...
Ch 1 notes
... 1-12 Heat and Temperature A) Temperature is: A measure of the kinetic energy of a substance B) Conversion formulas: 1. Between T (in K) and T (in °C): _______________________________ 2. Between T (in °C) and T (in °F): _________________________________ ...
... 1-12 Heat and Temperature A) Temperature is: A measure of the kinetic energy of a substance B) Conversion formulas: 1. Between T (in K) and T (in °C): _______________________________ 2. Between T (in °C) and T (in °F): _________________________________ ...
CHEMISTRY
... Some atoms achieve a ______________ electron structure by sharing electrons with another element. The mutual attraction that each atom has for the shared electrons is called a ___________________. One covalent bond consists of 2 shared electrons. Generally, covalent bonds exist between _____________ ...
... Some atoms achieve a ______________ electron structure by sharing electrons with another element. The mutual attraction that each atom has for the shared electrons is called a ___________________. One covalent bond consists of 2 shared electrons. Generally, covalent bonds exist between _____________ ...
Equivalence of Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements
... • The vacuum pump will evacuate chamber B and restore the gas to chamber A. The vacuum pump is then removed. • But the vacuum pump has increased the internal energy of the gas by an amount equal to the electrical work consumed by it. • Therefore, only after an equal amount of heat has to be rejected ...
... • The vacuum pump will evacuate chamber B and restore the gas to chamber A. The vacuum pump is then removed. • But the vacuum pump has increased the internal energy of the gas by an amount equal to the electrical work consumed by it. • Therefore, only after an equal amount of heat has to be rejected ...
Ductility-the ability to be stretched into wires
... identity) and form a new substance with different properties? Is the ability to be torn a physical or chemical property? Physical Property: Property that can be tested/observed without changing chemical identity of the substance; can be undone ...
... identity) and form a new substance with different properties? Is the ability to be torn a physical or chemical property? Physical Property: Property that can be tested/observed without changing chemical identity of the substance; can be undone ...
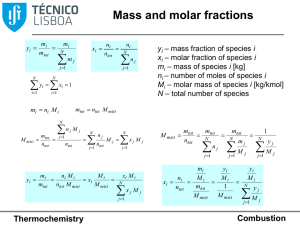
Combustion thermodynamics
... A detailed description of fuels, oxidisers, their mixing, the ignition process and the kinetics of its propagation, can be found elsewhere. A succinct description of the process in Fig. 1 may be as follows. As it will be shown below, at least 9.5 m3 of air are required for the complete combustion of ...
... A detailed description of fuels, oxidisers, their mixing, the ignition process and the kinetics of its propagation, can be found elsewhere. A succinct description of the process in Fig. 1 may be as follows. As it will be shown below, at least 9.5 m3 of air are required for the complete combustion of ...
practice test2(Answers)
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
Mole Ratio and Mass IP
... How to use mole: mole ratios to determine how much of a chemical is needed for a reaction: ...
... How to use mole: mole ratios to determine how much of a chemical is needed for a reaction: ...
lec38 - UConn Physics
... PV diagram This allows us to visualize the process through which the gas is progressing ...
... PV diagram This allows us to visualize the process through which the gas is progressing ...
No Slide Title
... Determining Direction of Reaction • Q < Kc:ratio of products to reactants is too small, reaction will proceed in forward direction to reach equilibrium. • Q = Kc:the system is at equilibrium. • Q > Kc:ratio of products to reactants is too large, reaction will proceed in reverse direction to reach e ...
... Determining Direction of Reaction • Q < Kc:ratio of products to reactants is too small, reaction will proceed in forward direction to reach equilibrium. • Q = Kc:the system is at equilibrium. • Q > Kc:ratio of products to reactants is too large, reaction will proceed in reverse direction to reach e ...
Empirical Formula
... • Hydrogen gas (____) is explosive • Oxygen gas (_____) is not explosive but must be present for combustion (fire) to occur • When these two gases come together to react, they form water – A molecule now with completely different properties!!! ...
... • Hydrogen gas (____) is explosive • Oxygen gas (_____) is not explosive but must be present for combustion (fire) to occur • When these two gases come together to react, they form water – A molecule now with completely different properties!!! ...
1. All matter is made up of
... 17. Sand and iron particles that are similar in size and color are mixed together in a beaker. What would be the best method of separating the particles? 1. Use tweezers to separate them. 2. Add water to the mixture. 3. Use a magnet to separate them. 4. Pour the mixture into a filter. ...
... 17. Sand and iron particles that are similar in size and color are mixed together in a beaker. What would be the best method of separating the particles? 1. Use tweezers to separate them. 2. Add water to the mixture. 3. Use a magnet to separate them. 4. Pour the mixture into a filter. ...
Some general information about thermodynamics
... Important thermodynamic cycles are created by heat engines. A heat engine is a device that takes heat (Q) and converts some of this heat into mechanical work (W) that can be used to power machines or biological processes. A heat engine takes heat from a high temperature reservoir, converts some of t ...
... Important thermodynamic cycles are created by heat engines. A heat engine is a device that takes heat (Q) and converts some of this heat into mechanical work (W) that can be used to power machines or biological processes. A heat engine takes heat from a high temperature reservoir, converts some of t ...
Chapter 7 - Chemical Quantities
... we need two molecules of hydrogen to react with one molecule of oxygen to give two molecules of water. From the mole concept, we can interpret the equation in terms of moles. Thus, 2 moles of hydrogen react with 1 mole of oxygen to give 2 moles of water. The coefficients in the above equation are ca ...
... we need two molecules of hydrogen to react with one molecule of oxygen to give two molecules of water. From the mole concept, we can interpret the equation in terms of moles. Thus, 2 moles of hydrogen react with 1 mole of oxygen to give 2 moles of water. The coefficients in the above equation are ca ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.