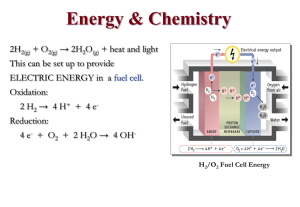
JCE0198 p0087 A Kinetics Experiment To Demonstrate the Role of
... Most general and physical chemistry texts explain that a catalyst significantly speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy of the reaction (typically by providing an alternate pathway from reactants to products) (1–3). Although this statement seems reasonable, students rarely ha ...
... Most general and physical chemistry texts explain that a catalyst significantly speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy of the reaction (typically by providing an alternate pathway from reactants to products) (1–3). Although this statement seems reasonable, students rarely ha ...
IB Definitions
... change (heat is evolved) An endothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall postive enthalpy change (heat is absorbed) The standard enthalpy change of a reaction is the enthalpy change when one mole of reactants is transformed into products at 298K and 101.3 KPa (1atm) Define the term avera ...
... change (heat is evolved) An endothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall postive enthalpy change (heat is absorbed) The standard enthalpy change of a reaction is the enthalpy change when one mole of reactants is transformed into products at 298K and 101.3 KPa (1atm) Define the term avera ...
Cellular Thermodynamics
... measurable. The complementary discipline of statistical mechanics applies the laws of physics to individual molecules, atoms and photons and, by considering the statistical behaviour of large numbers, deduces the behaviour of macroscopic systems. It thus relates thermodynamics to Newtonian or quantu ...
... measurable. The complementary discipline of statistical mechanics applies the laws of physics to individual molecules, atoms and photons and, by considering the statistical behaviour of large numbers, deduces the behaviour of macroscopic systems. It thus relates thermodynamics to Newtonian or quantu ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Notes File
... Standard enthalpy of formation ∆Hfº = change in enthalpy for the reaction that forms 1 mole of the compound from its elements, with all substance in their standard states. -- usually at 298 K and standard atmospheric pressure If an element exists in more than one form under standard conditions, the ...
... Standard enthalpy of formation ∆Hfº = change in enthalpy for the reaction that forms 1 mole of the compound from its elements, with all substance in their standard states. -- usually at 298 K and standard atmospheric pressure If an element exists in more than one form under standard conditions, the ...
Differential Equations of Gas-Phase Chemical Kinetics
... description. The information is collected in databases that are stored in files of the Microsoft Access type. The data are displayed in the tables and can be easily handled. Chemked has the multipledocument interface and can simultaneously process several reaction databases connected with a thermody ...
... description. The information is collected in databases that are stored in files of the Microsoft Access type. The data are displayed in the tables and can be easily handled. Chemked has the multipledocument interface and can simultaneously process several reaction databases connected with a thermody ...
Chapter 2. The First Law
... with Tgas = Tsurroundings and pgas = pexternal. If the external pressure is decreased infinitesimally at constant T, the gas will expand infinitesimally; if the external pressure is increased infinitesimally at constant T, the gas will be compressed by an infinitesimal amount. Strictly speaking, a r ...
... with Tgas = Tsurroundings and pgas = pexternal. If the external pressure is decreased infinitesimally at constant T, the gas will expand infinitesimally; if the external pressure is increased infinitesimally at constant T, the gas will be compressed by an infinitesimal amount. Strictly speaking, a r ...
Chapter 15
... In other words, an isolated system will naturally pursue a state of higher disorder. If you watch a magician throw a deck of cards into the air, you would expect the cards to fall to the floor around him in a very disorderly manner, since the system of cards would naturally tend toward a state of hi ...
... In other words, an isolated system will naturally pursue a state of higher disorder. If you watch a magician throw a deck of cards into the air, you would expect the cards to fall to the floor around him in a very disorderly manner, since the system of cards would naturally tend toward a state of hi ...
Test 8 Review
... Entropy. Entropy is randomness or disorder. In nature, high entropy is favored, yet many things that occur naturally are quite organized. This is because nature also favors low potential energy or enthalpy. Entropy and enthalpy sometimes conflict with each other. In order to determine if a reaction ...
... Entropy. Entropy is randomness or disorder. In nature, high entropy is favored, yet many things that occur naturally are quite organized. This is because nature also favors low potential energy or enthalpy. Entropy and enthalpy sometimes conflict with each other. In order to determine if a reaction ...
Final Exam Practice Problems Set 2
... When 50.0 mL of 0.400 M Ca(NO3)2 is added to 50.0 mL of 0.800 M NaF, CaF2 precipitates, as shown in the net ionic equation below. The initial temperature of both solutions is 21.0 ˚C. Assuming that the reaction goes to completion, and that the resulting solution has a mass of 100.00 g and a specific ...
... When 50.0 mL of 0.400 M Ca(NO3)2 is added to 50.0 mL of 0.800 M NaF, CaF2 precipitates, as shown in the net ionic equation below. The initial temperature of both solutions is 21.0 ˚C. Assuming that the reaction goes to completion, and that the resulting solution has a mass of 100.00 g and a specific ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY or Thermodynamics
... • Gay-Lussac showed that a plot of V versus T was a straight line that could be extrapolated to – 273.15ºC at zero volume, a theoretical state. • The slope of the plot of V versus T varies for the same gas at different pressures, but the intercept remains constant at –273.15ºC. • Significance of the ...
... • Gay-Lussac showed that a plot of V versus T was a straight line that could be extrapolated to – 273.15ºC at zero volume, a theoretical state. • The slope of the plot of V versus T varies for the same gas at different pressures, but the intercept remains constant at –273.15ºC. • Significance of the ...
Document
... Another form of the first law for DUsystem DU = q + w DU is the change in internal energy of a system q is the heat exchange between the system and the surroundings w is the work done on (or by) the system w = -PDV when a gas expands against a constant external pressure ...
... Another form of the first law for DUsystem DU = q + w DU is the change in internal energy of a system q is the heat exchange between the system and the surroundings w is the work done on (or by) the system w = -PDV when a gas expands against a constant external pressure ...
Thermochemistry1
... The enthalpy of a given chemical reaction is constant, regardless of the reaction happening in one step or many steps. If a chemical equation can be written as the sum of several other chemical equations (steps), the enthalpy change of the first chemical equation equals the sum of the enthalpy chang ...
... The enthalpy of a given chemical reaction is constant, regardless of the reaction happening in one step or many steps. If a chemical equation can be written as the sum of several other chemical equations (steps), the enthalpy change of the first chemical equation equals the sum of the enthalpy chang ...
4 - College of Arts and Sciences
... A sample of acetominophen (C8H9O2N) has 6.02 x 1023 atoms of Hydrogen. What is the mass in grams of the sample? How many atoms of H in one mole of C8H9O2N ? 9 x (6.02 x 1023) atoms of H Therefore have 1/9 of a mole of acetominophen What is the molecular weight of acetominophen ? ...
... A sample of acetominophen (C8H9O2N) has 6.02 x 1023 atoms of Hydrogen. What is the mass in grams of the sample? How many atoms of H in one mole of C8H9O2N ? 9 x (6.02 x 1023) atoms of H Therefore have 1/9 of a mole of acetominophen What is the molecular weight of acetominophen ? ...
Chemistry I
... 28. For a gas with temperature and number of moles are held constant, Boyle’s law describes a situation in which: a. volume and pressure have no relationship b. volume increases with increasing pressure c. volume decreases with decreasing speed d. volume decreases with increasing pressure 29. The le ...
... 28. For a gas with temperature and number of moles are held constant, Boyle’s law describes a situation in which: a. volume and pressure have no relationship b. volume increases with increasing pressure c. volume decreases with decreasing speed d. volume decreases with increasing pressure 29. The le ...
CH 5-7 Chapter 5-7 review wkey
... 35. Consider the thermal energy transfer during a chemical process. When heat is transferred to the system, the process is said to be _______ and the sign of H is ________. a) exothermic, positive b) endothermic, negative c) exothermic, negative d) endothermic, positive ...
... 35. Consider the thermal energy transfer during a chemical process. When heat is transferred to the system, the process is said to be _______ and the sign of H is ________. a) exothermic, positive b) endothermic, negative c) exothermic, negative d) endothermic, positive ...
APES Lesson 23B (2014-15) - Matter, Chemistry - science-b
... Define the terms law of conservation of matter, autotroph and heterotroph. Law of the Conservation of Matter: The principle that matter many be transformed for one type of substance into another s, but it cannot be created or destroyed. Autotroph: An organism that produces its own food from inorgan ...
... Define the terms law of conservation of matter, autotroph and heterotroph. Law of the Conservation of Matter: The principle that matter many be transformed for one type of substance into another s, but it cannot be created or destroyed. Autotroph: An organism that produces its own food from inorgan ...
CHAPTER 9
... (1) Replacement reactions and addition reactions are two terms which describe the same type of reaction. (2) Orientation relative to one another, at the moment of collision, is always a factor in determining whether a collision is effective. (3) An increase in temperature will always cause an endoth ...
... (1) Replacement reactions and addition reactions are two terms which describe the same type of reaction. (2) Orientation relative to one another, at the moment of collision, is always a factor in determining whether a collision is effective. (3) An increase in temperature will always cause an endoth ...
Chem 1202 - LSU Department of Chemistry
... However, most chemical reactions are not carried out at constant volume. They are usually carried out at constant pressure (in the open atmosphere). In some reactions, both heat and work are involved (e.g., explosions). So a new energy function was invented for contant pressure processes. Chemistry ...
... However, most chemical reactions are not carried out at constant volume. They are usually carried out at constant pressure (in the open atmosphere). In some reactions, both heat and work are involved (e.g., explosions). So a new energy function was invented for contant pressure processes. Chemistry ...
aspartic acid - West Liberty University
... Leak and Spill Procedure: Ventilate area. Eliminate ignition sources. Cleanup personnel should wear protective equipment and clothing sufficient to prevent inhalation of dust or mist, and contact with skin and eyes. Gather up in a manner that does not raise dust. Transfer into containers and arrange ...
... Leak and Spill Procedure: Ventilate area. Eliminate ignition sources. Cleanup personnel should wear protective equipment and clothing sufficient to prevent inhalation of dust or mist, and contact with skin and eyes. Gather up in a manner that does not raise dust. Transfer into containers and arrange ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... 6. Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions Electrons are transferred from one atom to another. Note that when one substance is oxidized, another compound must be reduced, and viceversa. Oxidation = - electrons from a substance Reduction = + electrons to a substance Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(g ...
... 6. Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions Electrons are transferred from one atom to another. Note that when one substance is oxidized, another compound must be reduced, and viceversa. Oxidation = - electrons from a substance Reduction = + electrons to a substance Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(g ...
File
... Therefore enzymes are catalysts because they speed up biochemical reactions • We need enzymes for every process that happens in our bodies! e.g. Digesting food, replicating DNA ...
... Therefore enzymes are catalysts because they speed up biochemical reactions • We need enzymes for every process that happens in our bodies! e.g. Digesting food, replicating DNA ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.