Briefing Session on 2012 HKDSE Examination (December 2012)
... One of the products in the alkaline hydrolysis of Y has a cleansing property. Explain the cleansing property of this product. • C17H35COO– ion has an ionic head (COO) and a hydrocarbon tail (C17H35). • The hydrocarbon tail dissolves in grease droplets / is hydrophobic, while the ionic head ...
... One of the products in the alkaline hydrolysis of Y has a cleansing property. Explain the cleansing property of this product. • C17H35COO– ion has an ionic head (COO) and a hydrocarbon tail (C17H35). • The hydrocarbon tail dissolves in grease droplets / is hydrophobic, while the ionic head ...
SAMPLE PAPER -2 Time Allowed: 3 Hrs
... (ii) A doctor advised a person suffering from high blood pressure to take less quantity of common salt. OR (a) Calculate the boiling point of a solution containing 0.61g of benzoic acid in 5 g of CS2 .Assuming 84% dimerisation of acid. The boiling point and Kb of CS2 are 46.2 0C and 2.3 K Kg mol-1 r ...
... (ii) A doctor advised a person suffering from high blood pressure to take less quantity of common salt. OR (a) Calculate the boiling point of a solution containing 0.61g of benzoic acid in 5 g of CS2 .Assuming 84% dimerisation of acid. The boiling point and Kb of CS2 are 46.2 0C and 2.3 K Kg mol-1 r ...
Syllabus of the International Chemistry Olympiad
... by-product of Dutch cheese making, how whales manage to stay under water for a considerable length of time, how the color of Delft blue pottery can be understood, how a bio-compatible polymer can be made from lactic acid, how modern spectroscopy is applied, how the structure of the natural product c ...
... by-product of Dutch cheese making, how whales manage to stay under water for a considerable length of time, how the color of Delft blue pottery can be understood, how a bio-compatible polymer can be made from lactic acid, how modern spectroscopy is applied, how the structure of the natural product c ...
No Slide Title
... 2. Large beds of rocks are used in some solar-heated homes to store heat. Calculate the quantity of heat absorbed by 50.0 kg of rocks if their temperature increases by 12 C. Assume that the specific heat of the rocks is 0.821 J/ g K. What temperature change would these rocks undergo if they absorbe ...
... 2. Large beds of rocks are used in some solar-heated homes to store heat. Calculate the quantity of heat absorbed by 50.0 kg of rocks if their temperature increases by 12 C. Assume that the specific heat of the rocks is 0.821 J/ g K. What temperature change would these rocks undergo if they absorbe ...
Problem Set 2
... a) The oxidation step: ----------------------------------------------------b) The reduction step: ------------------------------------------------------c) The oxidizing agent: ------------------------------------------------------d) The reducing agent: ----------------------------------------------- ...
... a) The oxidation step: ----------------------------------------------------b) The reduction step: ------------------------------------------------------c) The oxidizing agent: ------------------------------------------------------d) The reducing agent: ----------------------------------------------- ...
Thermochemistry and calorimetry
... Since the process takes place at constant volume, the reaction vessel must be constructed to withstand the high pressure resulting from the combustion process, which amounts to a confined explosion. The vessel is usually called a “bomb”, and the technique is known as bomb calorimetry. The reaction i ...
... Since the process takes place at constant volume, the reaction vessel must be constructed to withstand the high pressure resulting from the combustion process, which amounts to a confined explosion. The vessel is usually called a “bomb”, and the technique is known as bomb calorimetry. The reaction i ...
IGCSE Revision Guide (Double Award) | PDF
... Chemical formulae Write balanced chemical equations including, where specified, state symbols. It is worth noting that 2 and chemical ...
... Chemical formulae Write balanced chemical equations including, where specified, state symbols. It is worth noting that 2 and chemical ...
Chapter 13 Energy, Heat, and Chemical Change
... The neon atoms, more massive than helium, develop a lower speed given the same amount of kinetic energy ($mv2). 10. Total thermal energy is an extensive property, scaling with the number of molecules. The average thermal energy per molecule, an intensive property, is independent of total amount and ...
... The neon atoms, more massive than helium, develop a lower speed given the same amount of kinetic energy ($mv2). 10. Total thermal energy is an extensive property, scaling with the number of molecules. The average thermal energy per molecule, an intensive property, is independent of total amount and ...
06_00 AP PPT Thermochemistry
... EU 5.B – Energy is neither created nor destroyed, but only transformed from one form to another. EK 5.B.1 – Energy is transferred between systems either through heat transfer or through one system doing work on the other system. EK 5.B.2 – When two systems are in contact with each other and are othe ...
... EU 5.B – Energy is neither created nor destroyed, but only transformed from one form to another. EK 5.B.1 – Energy is transferred between systems either through heat transfer or through one system doing work on the other system. EK 5.B.2 – When two systems are in contact with each other and are othe ...
chemistry-c7-what-you-should
... I can recall that the feedstocks of nitrogen and hydrogen for the Haber process are made from air, natural gas and steam I in the context of the Haber process: a. I understand that the reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen to form ammonia is a reversible reaction b. I understand how the yield of am ...
... I can recall that the feedstocks of nitrogen and hydrogen for the Haber process are made from air, natural gas and steam I in the context of the Haber process: a. I understand that the reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen to form ammonia is a reversible reaction b. I understand how the yield of am ...
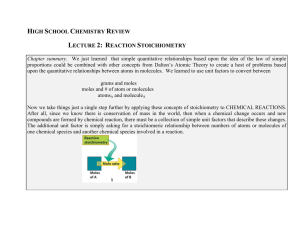
HIGH SCHOOL CHEMISTRY REVIEW LECTURE 2: REACTION
... Now we take things just a single step further by applying these concepts of stoichiometry to CHEMICAL REACTIONS. After all, since we know there is conservation of mass in the world, then when a chemical change occurs and new compounds are formed by chemical reaction, there must be a collection of si ...
... Now we take things just a single step further by applying these concepts of stoichiometry to CHEMICAL REACTIONS. After all, since we know there is conservation of mass in the world, then when a chemical change occurs and new compounds are formed by chemical reaction, there must be a collection of si ...
2. Laws of thermodynamics
... a. Students should understand the kinetic theory model of an ideal gas so they can: 1.) State the assumptions of the model. 2.) State the connection between temperature and mean translational kinetic energy and apply it to determine the mean speed of gas molecules as a function of their mass and the ...
... a. Students should understand the kinetic theory model of an ideal gas so they can: 1.) State the assumptions of the model. 2.) State the connection between temperature and mean translational kinetic energy and apply it to determine the mean speed of gas molecules as a function of their mass and the ...
Atkins/ de Paula
... becomes a gas. Hence, all liquids can be expected to have similar standard entropies of vaporization. Liquids that show significant deviations from Trouton’s rule do so on account of strong molecular interactions that restrict molecular motion. As a result, there is a greater dispersal of energy and ...
... becomes a gas. Hence, all liquids can be expected to have similar standard entropies of vaporization. Liquids that show significant deviations from Trouton’s rule do so on account of strong molecular interactions that restrict molecular motion. As a result, there is a greater dispersal of energy and ...
Unit 2 Chemical Reactions
... Note: i) Treat hydrogen as a metal ii) Treat acids (e.g HCl) as ionic compounds ( H+, Cl-) iii) Treat water as ionic (H+ , OH-) iv) Use The Activity Series of the Elements Table : any element will displace another element below it on the series. This is used to predict if a reaction will occur or no ...
... Note: i) Treat hydrogen as a metal ii) Treat acids (e.g HCl) as ionic compounds ( H+, Cl-) iii) Treat water as ionic (H+ , OH-) iv) Use The Activity Series of the Elements Table : any element will displace another element below it on the series. This is used to predict if a reaction will occur or no ...
Chapter 2
... • ___________ –between two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other. • Example- sodium (one valence electron) in its third shell transfers this electron to chlorine with 7 valence electrons in its third shell. • Now, s ...
... • ___________ –between two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other. • Example- sodium (one valence electron) in its third shell transfers this electron to chlorine with 7 valence electrons in its third shell. • Now, s ...
ch6_f08
... from one form of energy to another • Also known as the first law of thermodynamics • How does water falling over a waterfall demonstrate this law? 6.1 An object has energy if it is capable of doing work ...
... from one form of energy to another • Also known as the first law of thermodynamics • How does water falling over a waterfall demonstrate this law? 6.1 An object has energy if it is capable of doing work ...
Scientific Measurement
... the time. _____40. I can state the conditions under which real gases behave most like ideal ...
... the time. _____40. I can state the conditions under which real gases behave most like ideal ...
Revision Y12 Chemistry PLC
... AS/A Level Module 3 – Periodic Table & Energy Unit 2 – Physical Chemistry Learners should be able to demonstrate and apply their knowledge and understanding of: Part 1 – Enthalpy Changes Enthalpy changes: ΔH of reaction, formation, combustion and neutralisation (a) explanation that some chemical re ...
... AS/A Level Module 3 – Periodic Table & Energy Unit 2 – Physical Chemistry Learners should be able to demonstrate and apply their knowledge and understanding of: Part 1 – Enthalpy Changes Enthalpy changes: ΔH of reaction, formation, combustion and neutralisation (a) explanation that some chemical re ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.