to view
... (ii) In the crystal of FeO, some of the Fe2+ cations are replaced by Fe3+ ions. Three Fe2+ ions are replaced by two Fe3+ ions to make up for the loss of positive charge. Thus there would be less amount of metal as compared to stoichiometric ...
... (ii) In the crystal of FeO, some of the Fe2+ cations are replaced by Fe3+ ions. Three Fe2+ ions are replaced by two Fe3+ ions to make up for the loss of positive charge. Thus there would be less amount of metal as compared to stoichiometric ...
Chemical Reaction
... Metals are usually solid, shiny and strong. They are also good conductors of heat and electricity. Metals can be changed into new substances when they are involved in a chemical reaction. Some metals can react with acids. This type of chemical reaction is called corrosion. ...
... Metals are usually solid, shiny and strong. They are also good conductors of heat and electricity. Metals can be changed into new substances when they are involved in a chemical reaction. Some metals can react with acids. This type of chemical reaction is called corrosion. ...
Chemistry basics powerpoint Chapter 2
... electron equally In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule ...
... electron equally In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule ...
KS4-Rates - Free Exam Papers
... bonds between atoms often before new given but out as energy bonds can be formed ones have to be new old bonds needed to broken. form break existing • This means that there has to be enough energy bonds (activation energy)to start breaking the old bonds before a reaction can occur. ...
... bonds between atoms often before new given but out as energy bonds can be formed ones have to be new old bonds needed to broken. form break existing • This means that there has to be enough energy bonds (activation energy)to start breaking the old bonds before a reaction can occur. ...
4 Expressing and Measuring Chemical Change
... time, most equations can eventually be balanced this way. However, the job can be made much easier if you follow a good plan of attack. Keep the following hints in mind when attempting to balance an equation: • Begin by balancing atoms that appear in only one place on each side of the equation. Atom ...
... time, most equations can eventually be balanced this way. However, the job can be made much easier if you follow a good plan of attack. Keep the following hints in mind when attempting to balance an equation: • Begin by balancing atoms that appear in only one place on each side of the equation. Atom ...
Chapter 7 Review
... For the reaction CO(g) + 2 H2(g) <---> CH3OH(g) + heat; [CO(g)] = 0.025 mol/L, [H2(g) ] = 0.050 mol/L and [CH3OH(g)] = 0.0063 mol/L a) b) ...
... For the reaction CO(g) + 2 H2(g) <---> CH3OH(g) + heat; [CO(g)] = 0.025 mol/L, [H2(g) ] = 0.050 mol/L and [CH3OH(g)] = 0.0063 mol/L a) b) ...
Physical Setting/Chemistry Examination
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
PREPARATORY PROBLEMS (Theoretical)
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, DG. This is the universal principle. If DG < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, DG. This is the universal principle. If DG < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
Solution of the 1st Major Exam, Term 061, Version 000, all correct
... E) Elements of the first vertical column of the periodic table are called alkaline earth metals ...
... E) Elements of the first vertical column of the periodic table are called alkaline earth metals ...
Kinetics of Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol with Dilute Nitric Acid
... oxidation of benzyl alcohol using molecular oxygen requires a heterogeneous catalyst, high temperature (210 °C), and longer reaction times (>5 h). Although the reported selectivity is quite good (75%-95%), the conversion levels are too low (maximum of 40%).14 Practically, in all the previously cited ...
... oxidation of benzyl alcohol using molecular oxygen requires a heterogeneous catalyst, high temperature (210 °C), and longer reaction times (>5 h). Although the reported selectivity is quite good (75%-95%), the conversion levels are too low (maximum of 40%).14 Practically, in all the previously cited ...
Section 4.6: Double Displacement Reactions
... 7. Silver ions are the only metal ions that can be precipitated from a solution containing the C2H3O2− ions. Therefore, a solution such as NaC2H3O2(aq) can be used to precipitate silver ions from a mixture of dissolved metal ions. 8. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Most of the limescale that forms ...
... 7. Silver ions are the only metal ions that can be precipitated from a solution containing the C2H3O2− ions. Therefore, a solution such as NaC2H3O2(aq) can be used to precipitate silver ions from a mixture of dissolved metal ions. 8. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Most of the limescale that forms ...
Chemistry General v. 2016
... Utilize Lewis dot Structures to predict the structure and bonding in simple compounds and draw the Lewis dot structure for simple molecules and ionic compounds. Compare and contrast different bond types that result in the formation of molecules and compounds and explain how atoms combine to form com ...
... Utilize Lewis dot Structures to predict the structure and bonding in simple compounds and draw the Lewis dot structure for simple molecules and ionic compounds. Compare and contrast different bond types that result in the formation of molecules and compounds and explain how atoms combine to form com ...
answers to part a of the national high school
... The more general form of the fire traingle is needed because there are all sorts of other oxidants apart from oxygen that substances can burn in, e.g. chlorine or nitrogen dioxide. Solid substances such as nitrates or chlorates are also considered to be oxidising substances because they can release ...
... The more general form of the fire traingle is needed because there are all sorts of other oxidants apart from oxygen that substances can burn in, e.g. chlorine or nitrogen dioxide. Solid substances such as nitrates or chlorates are also considered to be oxidising substances because they can release ...
Name: Per: Date: Unit 1. Materials: Formulating Matter B. Periodic
... 37. Polyatomic Ions. A polyatomic ion is a group of atoms that, as a group, carries an electrical charge. There are many negatively-charged polyatomic ions, but the only polyatomic ion with a positive charge is NH4+. When a polyatomic ion occurs two or more times in a formula, its formula is placed ...
... 37. Polyatomic Ions. A polyatomic ion is a group of atoms that, as a group, carries an electrical charge. There are many negatively-charged polyatomic ions, but the only polyatomic ion with a positive charge is NH4+. When a polyatomic ion occurs two or more times in a formula, its formula is placed ...
acid
... Why Ionic Compounds Dissolve in Water The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is ...
... Why Ionic Compounds Dissolve in Water The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is ...
Chapter 1.1 –Chemistry is a Physical Science Chemistry is one of
... Magnesium reacts with oxygen from the air producing an extremely bright flame. This is a chemical change since magnesium oxide has completely different properties than magnesium metal shown on the left. ...
... Magnesium reacts with oxygen from the air producing an extremely bright flame. This is a chemical change since magnesium oxide has completely different properties than magnesium metal shown on the left. ...
Chemistry Notes - The Bored of Studies Community
... condensed out, left-over reactants can be recycled through the process (with some fresh reactant mixture added) without any build-up of one reactant over the other. An important factor in designing an industrial process is energy management. In the Haber process we would like to use the head release ...
... condensed out, left-over reactants can be recycled through the process (with some fresh reactant mixture added) without any build-up of one reactant over the other. An important factor in designing an industrial process is energy management. In the Haber process we would like to use the head release ...
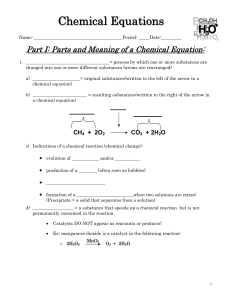
Chemical Equations
... 1. _____________________________________= process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances (atoms are rearranged) a) _____________________= original substances(written to the left of the arrow in a chemical equation) b) ________________________ = resulting su ...
... 1. _____________________________________= process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances (atoms are rearranged) a) _____________________= original substances(written to the left of the arrow in a chemical equation) b) ________________________ = resulting su ...
Stoichiometry intro
... 2) Every time 4 moles of Al atoms react with 3 moles of O2 molecules, 2 moles of Al2O3 molecules form. ...
... 2) Every time 4 moles of Al atoms react with 3 moles of O2 molecules, 2 moles of Al2O3 molecules form. ...
H2-rich fluids from serpentinization: Geochemical and biotic
... represent a water-dominated part of fluid circulation, like a vein. We assume a fluid pressure of 500 bars, which is appropriate for high-level crustal rocks during the early Earth when much of its water had not yet entered the mantle and was either in the ocean or the atmosphere, and for modern rea ...
... represent a water-dominated part of fluid circulation, like a vein. We assume a fluid pressure of 500 bars, which is appropriate for high-level crustal rocks during the early Earth when much of its water had not yet entered the mantle and was either in the ocean or the atmosphere, and for modern rea ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Curriculum
... ended. Sometimes, EQs can be debated. A student’s answer to an EQ will help teachers determine if he/she truly understands. Consider having only one or two EQs per Enduring Understanding.) ...
... ended. Sometimes, EQs can be debated. A student’s answer to an EQ will help teachers determine if he/she truly understands. Consider having only one or two EQs per Enduring Understanding.) ...
prs-A3
... The following diagram represents the collection of carbon dioxide and water formed by the decomposition of a hydrocarbon. What was the empirical formula of the original hydrocarbon? • C4H16 • C 2H 8 • CH4 • While the diagram indicates 4 carbons, and you might think there could have been 1 C4H16, 2 ...
... The following diagram represents the collection of carbon dioxide and water formed by the decomposition of a hydrocarbon. What was the empirical formula of the original hydrocarbon? • C4H16 • C 2H 8 • CH4 • While the diagram indicates 4 carbons, and you might think there could have been 1 C4H16, 2 ...
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding
... octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if all of its single electrons are used in a covalent bond, and there are sur ...
... octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if all of its single electrons are used in a covalent bond, and there are sur ...
CHEM 101 Final (Term 141)
... a liquid that does not dissolve in another liquid. a solid substance that does not dissolve at a given temperature. a solid substance which does not dissolve in water. a substance containing a solid, liquid, or gas. ...
... a liquid that does not dissolve in another liquid. a solid substance that does not dissolve at a given temperature. a solid substance which does not dissolve in water. a substance containing a solid, liquid, or gas. ...
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... A few other groups are given family names. These include the alkali metals (Group 1), such as sodium and potassium, which are soft and white and extremely reactive chemically. Alkaline earth metals (Group 2), such as magnesium and calcium, are found in the second column of the periodic table. The tr ...
... A few other groups are given family names. These include the alkali metals (Group 1), such as sodium and potassium, which are soft and white and extremely reactive chemically. Alkaline earth metals (Group 2), such as magnesium and calcium, are found in the second column of the periodic table. The tr ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.