Atomic Structure
... information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. Describe a method for making pure crystals of magnesium chloride from magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. In your method you should name the apparatus you will use. You do not need to mention safety. ...
... information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. Describe a method for making pure crystals of magnesium chloride from magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. In your method you should name the apparatus you will use. You do not need to mention safety. ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... 1. Count: H2O is the chemical formula for water. In order to produce a single molecule of water, how many hydrogen atoms are needed? _______ Oxygen atoms? _______ 2. Predict: Set the number of O2 molecules to five and the number of H2 molecules to eight. A. How many oxygen atoms are present? _______ ...
... 1. Count: H2O is the chemical formula for water. In order to produce a single molecule of water, how many hydrogen atoms are needed? _______ Oxygen atoms? _______ 2. Predict: Set the number of O2 molecules to five and the number of H2 molecules to eight. A. How many oxygen atoms are present? _______ ...
Document
... An electron dot diagram or Lewis structure is created for atoms involved in the chemical bonding process. A chemical symbol is used to represent the atoms that are being bonded. The appropriate number of dots is drawn on the four sides of the chemical symbol to represent the number of valence electr ...
... An electron dot diagram or Lewis structure is created for atoms involved in the chemical bonding process. A chemical symbol is used to represent the atoms that are being bonded. The appropriate number of dots is drawn on the four sides of the chemical symbol to represent the number of valence electr ...
Unit 6: Reactions and Stoichiometry
... 7.When 10.0 g of copper was reacted with 60.0 g of silver nitrate solution. How many grams of silver are produced? How much of each reactant is left over?( Calculate the amount in grams) ...
... 7.When 10.0 g of copper was reacted with 60.0 g of silver nitrate solution. How many grams of silver are produced? How much of each reactant is left over?( Calculate the amount in grams) ...
Regents Review Questions
... A substance known as heavy water can be obtained from ordinary water and could be a significant source of energy in the future. Heavy water contains deuterium, H-2. Instead of the two hydrogen atoms in a typical water molecule, a heavy water molecule has two deuterium atoms. In 3.78 kilograms of ord ...
... A substance known as heavy water can be obtained from ordinary water and could be a significant source of energy in the future. Heavy water contains deuterium, H-2. Instead of the two hydrogen atoms in a typical water molecule, a heavy water molecule has two deuterium atoms. In 3.78 kilograms of ord ...
2.5 THE NAMES AND FORMULAS OF COMPOUNDS
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
Properties and Changes Reading Assignment Name: Chemistry 2
... examples of substances, which are also referred to as pure substances. Gold and copper have some properties in common, but there are differences besides their distinctive colors. Pure copper can scratch the surface of pure gold because copper is harder than gold. Copper is better than gold as a cond ...
... examples of substances, which are also referred to as pure substances. Gold and copper have some properties in common, but there are differences besides their distinctive colors. Pure copper can scratch the surface of pure gold because copper is harder than gold. Copper is better than gold as a cond ...
PAGE PROOFS
... Hydrochloric acid is found in our stomachs, where it is used to help break down food. It is also used in industry, where it is sometimes called ‘spirit of salts’, to clean bricks and to clean off the coating of oxide on corroded iron or steel before plating the metal with a protective layer of zinc ...
... Hydrochloric acid is found in our stomachs, where it is used to help break down food. It is also used in industry, where it is sometimes called ‘spirit of salts’, to clean bricks and to clean off the coating of oxide on corroded iron or steel before plating the metal with a protective layer of zinc ...
Toluenediamine
... The reduction of dinitrotoluene is characterized by its strong exotherm of >1100 kJ/mol. Due to this fact combined with the thermal instability of the dinitro compound certain processing requirements must be considered. Gas-phase reaction of dinitrotoluene can merely be realized and particular preca ...
... The reduction of dinitrotoluene is characterized by its strong exotherm of >1100 kJ/mol. Due to this fact combined with the thermal instability of the dinitro compound certain processing requirements must be considered. Gas-phase reaction of dinitrotoluene can merely be realized and particular preca ...
Nikolai N. Semenov - Nobel Lecture
... propagations, a phenomenon so important to safety techniques, was also forthcoming. We explained this phenomenon by describing how the heat losses on the walls of the pipes in which the flame is propagated reduce the flame temperature and the rate of propagation; the lessening in the propagation rat ...
... propagations, a phenomenon so important to safety techniques, was also forthcoming. We explained this phenomenon by describing how the heat losses on the walls of the pipes in which the flame is propagated reduce the flame temperature and the rate of propagation; the lessening in the propagation rat ...
Covalent Bonding
... Carbon is usually in the middle Group 1 and 17 elements are always at ends Atoms that are less numerous are usually in the middle Hydrogen always forms one single bond Oxygen has two bonding electrons and two lone pairs Nitrogen has three bonding electron and one lone pair Group 13 elements h ...
... Carbon is usually in the middle Group 1 and 17 elements are always at ends Atoms that are less numerous are usually in the middle Hydrogen always forms one single bond Oxygen has two bonding electrons and two lone pairs Nitrogen has three bonding electron and one lone pair Group 13 elements h ...
ap chemistry unit two notes
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. 3. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from atoms of any other element. 4. Compounds result from the chemical combination of a specific ratio of atoms of different elements. ...
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. 3. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from atoms of any other element. 4. Compounds result from the chemical combination of a specific ratio of atoms of different elements. ...
Question, hints, and answers. Look at hints if you need help. Look at
... Molecules in a sample of NH3(l) are held closely together by intermolecular forces *hint In the NH3 molecule, there is a covalent bond between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge ...
... Molecules in a sample of NH3(l) are held closely together by intermolecular forces *hint In the NH3 molecule, there is a covalent bond between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge ...
(H) +
... • Generally do not contain C • Usually smaller than organic molecules • Usually dissociate in water, forming ions • Water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and inorganic salts ...
... • Generally do not contain C • Usually smaller than organic molecules • Usually dissociate in water, forming ions • Water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and inorganic salts ...
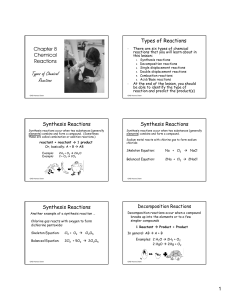
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Fluorine reacts with Hydrochloric Acid to form Chlorine and Hydrogen fluoride Skeleton Equation: ...
... Fluorine reacts with Hydrochloric Acid to form Chlorine and Hydrogen fluoride Skeleton Equation: ...
21:3 Classifying Chemical Reactions
... respire as other living things. They consume sugars and give off carbon dioxide gas into their environment. ...
... respire as other living things. They consume sugars and give off carbon dioxide gas into their environment. ...
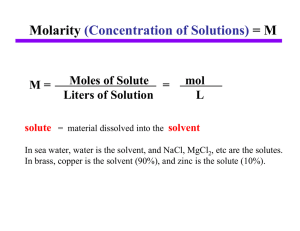
Molarity = M (Concentration of Solutions)
... are allowed to mix and react. The first container with a volume of 2.79 L contains Ammonia gas at a pressure of 0.776 atm and a temperature of 18.7 oC. The second with a volume of 1.16 L contains HCl gas at a pressure of 0.932 atm and a temperature of 18.7 oC. What mass of solid ammonium chloride wi ...
... are allowed to mix and react. The first container with a volume of 2.79 L contains Ammonia gas at a pressure of 0.776 atm and a temperature of 18.7 oC. The second with a volume of 1.16 L contains HCl gas at a pressure of 0.932 atm and a temperature of 18.7 oC. What mass of solid ammonium chloride wi ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry
... Computational chemists are hired by academic institutions, government agencies, and all types of industries. The pharmaceutical industry in particular has embraced computational chemistry as an effective tool in the design of new drugs. Computational chemists are employed to study all types of chemi ...
... Computational chemists are hired by academic institutions, government agencies, and all types of industries. The pharmaceutical industry in particular has embraced computational chemistry as an effective tool in the design of new drugs. Computational chemists are employed to study all types of chemi ...
Chemistry 11th
... (ii) The oxides of alkali and alkaline earth metal dissolve in water to form their respective hydroxides. These oxides are strong bases. However, the oxides of alkali metals are more basic than those of alkaline earth metals. This is because the ionization enthalpy of alkali metals is lower. The e ...
... (ii) The oxides of alkali and alkaline earth metal dissolve in water to form their respective hydroxides. These oxides are strong bases. However, the oxides of alkali metals are more basic than those of alkaline earth metals. This is because the ionization enthalpy of alkali metals is lower. The e ...
practice test 4 CHM 112
... 6. The equilibrium 3Fe(s) + C(s) Fe3C(s) is established in a solid solution. For such a solution, one can write an equilibrium constant in the usual way except that here one has concentrations that refer to solids in the solid solution. Determine the equilibrium constant for the formation of cementi ...
... 6. The equilibrium 3Fe(s) + C(s) Fe3C(s) is established in a solid solution. For such a solution, one can write an equilibrium constant in the usual way except that here one has concentrations that refer to solids in the solid solution. Determine the equilibrium constant for the formation of cementi ...
N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 2.5 Transition Metals Substitution
... This is called the chelate effect This chelate effect can be explained in terms of a positive entropy change in these reactions as more molecules of products than reactants [Cu(H2O)6]2+ (aq) + EDTA4- (aq) [Cu (EDTA)]2- (aq) + 6H2O (l) The copper complex ion has changed from having unidentate ligan ...
... This is called the chelate effect This chelate effect can be explained in terms of a positive entropy change in these reactions as more molecules of products than reactants [Cu(H2O)6]2+ (aq) + EDTA4- (aq) [Cu (EDTA)]2- (aq) + 6H2O (l) The copper complex ion has changed from having unidentate ligan ...
Dr. Baxley`s Equilibrium Worksheet
... 13. If the system given below is at equilibrium, predict each of the following (answers are increase, decrease, or no change): H2(g) + 1/8 S8(s) ⇌ H2S(g) ...
... 13. If the system given below is at equilibrium, predict each of the following (answers are increase, decrease, or no change): H2(g) + 1/8 S8(s) ⇌ H2S(g) ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.