New Materials from Metal Vapour Chemistry
... This continues to be the philosophy and practice of chemists who investigate the utility and scope of metal atomic reagents for the synthesis of organometallic and inorganic compounds. Some recent literature highlights are presented in Scheme II. Of a more recent vintage is the entry of metal vapour ...
... This continues to be the philosophy and practice of chemists who investigate the utility and scope of metal atomic reagents for the synthesis of organometallic and inorganic compounds. Some recent literature highlights are presented in Scheme II. Of a more recent vintage is the entry of metal vapour ...
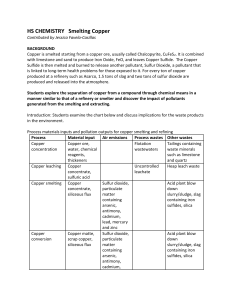
Smelting Copper
... Copper is smelted starting from a copper ore, usually called Chalcopyrite, CuFeS 2. It is combined with limestone and sand to produce Iron Oxide, FeO, and leaves Copper Sulfide. The Copper Sulfide is then melted and burned to release another pollutant, Sulfur Dioxide, a pollutant that is linked to l ...
... Copper is smelted starting from a copper ore, usually called Chalcopyrite, CuFeS 2. It is combined with limestone and sand to produce Iron Oxide, FeO, and leaves Copper Sulfide. The Copper Sulfide is then melted and burned to release another pollutant, Sulfur Dioxide, a pollutant that is linked to l ...
Energetics 5
... information that one mole of methane gas reacts with two moles of oxygen gas to give one mole of gaseous carbon dioxide and two moles of liquid water and releases 890 kJ of heat energy. A few reactions are endothermic as they result in an energy transfer from the surroundings to the system. In this ...
... information that one mole of methane gas reacts with two moles of oxygen gas to give one mole of gaseous carbon dioxide and two moles of liquid water and releases 890 kJ of heat energy. A few reactions are endothermic as they result in an energy transfer from the surroundings to the system. In this ...
James Ruse with Solutions
... A soft drink may be decarbonated by heating. In observing the results, the equilibrium between gaseous and dissolved carbon dioxide can be examined. CO2 (g) ...
... A soft drink may be decarbonated by heating. In observing the results, the equilibrium between gaseous and dissolved carbon dioxide can be examined. CO2 (g) ...
Chapter One
... that no longer retains any of the characteristics of the element. An atom is therefore the smallest particle that can be used to identify an element. Compounds are substances that contain more than one element combined in fixed proportions. Water, for example, is composed of the elements hydrogen an ...
... that no longer retains any of the characteristics of the element. An atom is therefore the smallest particle that can be used to identify an element. Compounds are substances that contain more than one element combined in fixed proportions. Water, for example, is composed of the elements hydrogen an ...
Class 3 updated Sep 30 2011
... (Siemens Process) Today, silicon is purified by converting it to a silicon compound that can be more easily purified than silicon itself, and then converting that silicon compound back into pure silicon. Trichlorosilane is the silicon compound most commonly used as the intermediate. In the Siemens p ...
... (Siemens Process) Today, silicon is purified by converting it to a silicon compound that can be more easily purified than silicon itself, and then converting that silicon compound back into pure silicon. Trichlorosilane is the silicon compound most commonly used as the intermediate. In the Siemens p ...
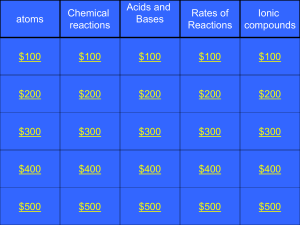
2P chem jeopardy 2011
... This NOT a chemical reaction. You can reverse it! (water vapour condenses to liquid water again). **Caution,bubbles DON’T ALWAYS mean a Chemical reaction! Category 2: $400: Q ...
... This NOT a chemical reaction. You can reverse it! (water vapour condenses to liquid water again). **Caution,bubbles DON’T ALWAYS mean a Chemical reaction! Category 2: $400: Q ...
exam2gc1sum11+key
... 394 kJ/mol, ΔH°f[H2O(l)] = –286 kJ/mol) C8H8 + 10O2(g) → 8CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) ΔH°rxn = –4439 kJ/mol A. 143 kJ/mol B. -143 kJ/mol C. 8735 kJ/mol D. –3759 kJ/mol ____18. A gas is allowed to expand doing 5 J of work. If the gas absorbs 250 J of heat from the surroundings, what is the change in internal en ...
... 394 kJ/mol, ΔH°f[H2O(l)] = –286 kJ/mol) C8H8 + 10O2(g) → 8CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) ΔH°rxn = –4439 kJ/mol A. 143 kJ/mol B. -143 kJ/mol C. 8735 kJ/mol D. –3759 kJ/mol ____18. A gas is allowed to expand doing 5 J of work. If the gas absorbs 250 J of heat from the surroundings, what is the change in internal en ...
Syllabus_summer 2014_1411_ZF_learning web
... objectives is useful to review before each test and the final exam! Chapter 1: Chemistry 1. Define homogeneous mixture, heterogeneous mixture, element, and compound. 2. Differentiate between a physical change and a chemical change. 3. Know the SI base units and the prefixes used with SI units. 4. Ca ...
... objectives is useful to review before each test and the final exam! Chapter 1: Chemistry 1. Define homogeneous mixture, heterogeneous mixture, element, and compound. 2. Differentiate between a physical change and a chemical change. 3. Know the SI base units and the prefixes used with SI units. 4. Ca ...
Combustion
... The products of incomplete combustion are varied and can include carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), energy, carbon monoxide (CO) and/or soot (C(s)). Soot is the solid, black ash that can be observed and is made up of a mixture of carbon-rich molecules which are often represented in chemical equation ...
... The products of incomplete combustion are varied and can include carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), energy, carbon monoxide (CO) and/or soot (C(s)). Soot is the solid, black ash that can be observed and is made up of a mixture of carbon-rich molecules which are often represented in chemical equation ...
Reduction and Emergence in Chemistry - Philsci
... Admittedly the quantum mechanical theory of bonding that McLaughlin appeals to does, provide a more fundamental account of chemical bonding that the classical, or Lewis theory. Nevertheless, it does not permit one to predict in advance the behavior of elements or the properties that a compound might ...
... Admittedly the quantum mechanical theory of bonding that McLaughlin appeals to does, provide a more fundamental account of chemical bonding that the classical, or Lewis theory. Nevertheless, it does not permit one to predict in advance the behavior of elements or the properties that a compound might ...
Reduction and Emergence in Chemistry
... Admittedly the quantum mechanical theory of bonding that McLaughlin appeals to does, provide a more fundamental account of chemical bonding than the classical, or Lewis theory. Nevertheless, it does not permit one to predict in advance the behavior of elements or the properties that a compound might ...
... Admittedly the quantum mechanical theory of bonding that McLaughlin appeals to does, provide a more fundamental account of chemical bonding than the classical, or Lewis theory. Nevertheless, it does not permit one to predict in advance the behavior of elements or the properties that a compound might ...
Stoichiometry File
... is octane, C8H18. If we start by assuming that gasoline can be represented reasonably by octane, then it is fairly easy to write and balance a chemical equation for its combustion. If we further assume complete combustion, then our equation should show octane and oxygen as reactants, and carbon diox ...
... is octane, C8H18. If we start by assuming that gasoline can be represented reasonably by octane, then it is fairly easy to write and balance a chemical equation for its combustion. If we further assume complete combustion, then our equation should show octane and oxygen as reactants, and carbon diox ...
Chemistry XXI
... Analyzing chemical systems from both the thermodynamic and kinetic point of view is crucial in making decisions about the actual “stability” of substances. For example, the decomposition or transformation of a substance may be favored thermodynamically, but can take millions of years to occur. How s ...
... Analyzing chemical systems from both the thermodynamic and kinetic point of view is crucial in making decisions about the actual “stability” of substances. For example, the decomposition or transformation of a substance may be favored thermodynamically, but can take millions of years to occur. How s ...
Equilibrium STUDY GUIDE by Keshara Senanayake ---
... square root of (2.4 X 10^-5 ) = x 4.9 X 10^-3 M = x Since both [Ca^2+] and [SO4^-2] ions have equal concentrations they both are 4.9 X 10^-3 M ...
... square root of (2.4 X 10^-5 ) = x 4.9 X 10^-3 M = x Since both [Ca^2+] and [SO4^-2] ions have equal concentrations they both are 4.9 X 10^-3 M ...
Chemistry - Sanskriti School
... Q 12 What volume of oxygen at S.T.P is needed to cause the complete combustion of 200mL of C2H2? Also calculate the volume of carbon dioxide formed? [500 ml of O2, 400 ml of CO2] Class XI / Chemistry/12 ...
... Q 12 What volume of oxygen at S.T.P is needed to cause the complete combustion of 200mL of C2H2? Also calculate the volume of carbon dioxide formed? [500 ml of O2, 400 ml of CO2] Class XI / Chemistry/12 ...
ch16powerpoint
... The elementary steps must add up to the overall equation. • The elementary steps must be physically reasonable. • The mechanism must correlated with the rate law. ...
... The elementary steps must add up to the overall equation. • The elementary steps must be physically reasonable. • The mechanism must correlated with the rate law. ...
Slide 1
... • Elements with similar chemical and physical properties are in the same column • columns are called Groups or Families designated by a number and letter at top ...
... • Elements with similar chemical and physical properties are in the same column • columns are called Groups or Families designated by a number and letter at top ...
Acids, bases and combustion
... The longer an atom is the higher the forces of attraction that hold the molecules of the element together (d) 3Z (g) + 2Fe(s) FeZ3(s) red that bleached. This is because it dissolves in water to form\ (e) The blue litmus paper turned an acid and bleaching solution of HO-1 (i) Down the group an extr ...
... The longer an atom is the higher the forces of attraction that hold the molecules of the element together (d) 3Z (g) + 2Fe(s) FeZ3(s) red that bleached. This is because it dissolves in water to form\ (e) The blue litmus paper turned an acid and bleaching solution of HO-1 (i) Down the group an extr ...
E2 and E11 Acid Deposition Past Paper Questions
... the pH must be lower than 5.6 for acid rain / OWTTE; (b) H2SO3 / H2SO4 and burning coal / sulfur-containing fuels / smelting of sulfide ores; HNO2 / HNO3 and reaction (between N2 and O2) in internal combustion/jet engine (c) CO3 ...
... the pH must be lower than 5.6 for acid rain / OWTTE; (b) H2SO3 / H2SO4 and burning coal / sulfur-containing fuels / smelting of sulfide ores; HNO2 / HNO3 and reaction (between N2 and O2) in internal combustion/jet engine (c) CO3 ...
Research on Hydrogenation of FAME to Fatty Alcohols
... velocity increased. Compared with 0.15~0.4h-1 space velocity which calculated according to tradition process of hydrogenolysis of fatty acid methyl ester, supercritical reaction technology was taken, but there was 90% solvent remaining in reaction materials. When the space velocity of mixture made o ...
... velocity increased. Compared with 0.15~0.4h-1 space velocity which calculated according to tradition process of hydrogenolysis of fatty acid methyl ester, supercritical reaction technology was taken, but there was 90% solvent remaining in reaction materials. When the space velocity of mixture made o ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.