1 What is the angular momentum quantum number (l) value for the
... ICC Essential Concept: Structure and Properties of Matter ICC Underlying Skill: Nature and Phases of Matter—Characteristics and Behavior ...
... ICC Essential Concept: Structure and Properties of Matter ICC Underlying Skill: Nature and Phases of Matter—Characteristics and Behavior ...
Chapter 17 - Cengage Learning
... INTRODUCTION Because atoms and molecules are so tiny, it is hard to imagine what happens when they react and form new products. In this chapter you will learn what is necessary for a reaction to occur, why some reactions stop before all the reactants have been used up, and how to speed up a reaction ...
... INTRODUCTION Because atoms and molecules are so tiny, it is hard to imagine what happens when they react and form new products. In this chapter you will learn what is necessary for a reaction to occur, why some reactions stop before all the reactants have been used up, and how to speed up a reaction ...
Final Exam Review Notes
... – eg. changing shape, changing physical state, dissolving – eg. boiling water, melting ice, hammering gold into foil chemical change or reaction: – a process that changes the chemical composition (and thus the chemical formula) of starting materials (reactants) — eg. oxidation of matter (burning or ...
... – eg. changing shape, changing physical state, dissolving – eg. boiling water, melting ice, hammering gold into foil chemical change or reaction: – a process that changes the chemical composition (and thus the chemical formula) of starting materials (reactants) — eg. oxidation of matter (burning or ...
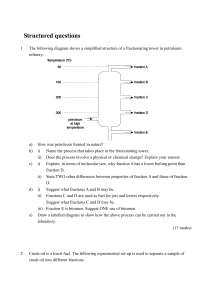
Structured questions
... iii) To which homologous series does compound B belong? iv) Suggest ONE use of B. Which of the hydrocarbon, A or B, gives an equal number of moles of carbon dioxide and water upon complete combustion. Explain your answer. A is used as a fuel for motor vehicles. i) The carbon dioxide formed when A is ...
... iii) To which homologous series does compound B belong? iv) Suggest ONE use of B. Which of the hydrocarbon, A or B, gives an equal number of moles of carbon dioxide and water upon complete combustion. Explain your answer. A is used as a fuel for motor vehicles. i) The carbon dioxide formed when A is ...
12 - einstein classes
... by a lone pair, and the bond angle F — N — F is 102030’. However, the dipole moment is very low (0.23 Debye units) compared with 1.47D for NH3. The highly electronegative F atoms attract electrons, and these moments partly cancel the moment from the lone pair, and this reduces both the dipole moment ...
... by a lone pair, and the bond angle F — N — F is 102030’. However, the dipole moment is very low (0.23 Debye units) compared with 1.47D for NH3. The highly electronegative F atoms attract electrons, and these moments partly cancel the moment from the lone pair, and this reduces both the dipole moment ...
Chemistry 400
... 7) Determine the molecular formula of a compound that is 49.48% carbon, 5.19% hydrogen, 28.85% nitrogen, and 16.48% oxygen. The molecular weight is 194.19 g/mol. A) C8H12N4O2 B) C4H5N2O C) C8H10N4O2 D) C8H10N2O ...
... 7) Determine the molecular formula of a compound that is 49.48% carbon, 5.19% hydrogen, 28.85% nitrogen, and 16.48% oxygen. The molecular weight is 194.19 g/mol. A) C8H12N4O2 B) C4H5N2O C) C8H10N4O2 D) C8H10N2O ...
The 2016 AP Chemistry Exam will be Monday
... 9. Colors of common ions in aqueous solution – most common ions are colorless in solution; however, some have distinctive colors. These colors have appeared on past AP Chemistry exams: Fe2+ and Fe3+ - various colors Cu2+ - blue to green Cr2+ - blue Cr3+ - green or violet Mn2+ - faint pink Ni2+ - gre ...
... 9. Colors of common ions in aqueous solution – most common ions are colorless in solution; however, some have distinctive colors. These colors have appeared on past AP Chemistry exams: Fe2+ and Fe3+ - various colors Cu2+ - blue to green Cr2+ - blue Cr3+ - green or violet Mn2+ - faint pink Ni2+ - gre ...
chemistry
... studies in chemistry, we can only look at the general; more specific knowledge will come in time as you continue to study. Figure 1.2 illustrates the relationships of the components of matter and how they can be classified; some of the terms will be defined in the text below, some will already be fa ...
... studies in chemistry, we can only look at the general; more specific knowledge will come in time as you continue to study. Figure 1.2 illustrates the relationships of the components of matter and how they can be classified; some of the terms will be defined in the text below, some will already be fa ...
honors chemistry harvard-westlake second semester final exam
... 17. Consider the reaction below: 1.7 kJ + NaCl(s) + H2O(ℓ) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Which of the following combinations for H and S is correct? a. +,- b. -,+ c. -,- d. +,+ 18. How many grams of sodium hydroxide pellets are required to prepare 50 mL (to the nearest 1 mL) of a 0.15 M solution? a. 0.30 b ...
... 17. Consider the reaction below: 1.7 kJ + NaCl(s) + H2O(ℓ) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Which of the following combinations for H and S is correct? a. +,- b. -,+ c. -,- d. +,+ 18. How many grams of sodium hydroxide pellets are required to prepare 50 mL (to the nearest 1 mL) of a 0.15 M solution? a. 0.30 b ...
SED122 - National Open University of Nigeria
... Elements can be broadly classified into two groups, metals and nonmetals. Examples of metals are copper and iron. The general characteristics of metals are lustre, good conductor of heat and electricity. Metals can be rolled and hammered into sheets and drawn into wires. They are used for roofing an ...
... Elements can be broadly classified into two groups, metals and nonmetals. Examples of metals are copper and iron. The general characteristics of metals are lustre, good conductor of heat and electricity. Metals can be rolled and hammered into sheets and drawn into wires. They are used for roofing an ...
2015 Dr. Jay L. Wile, All rights reserved.
... e. Several grams of magnesium, which is one of the two simplest substances produced when magnesium oxide breaks down. f. The magnesium oxide from which the magnesium discussed above was produced. g. A strawberry h. A cup of tea with no leaves in it. 3. A student does a chemical reaction with two che ...
... e. Several grams of magnesium, which is one of the two simplest substances produced when magnesium oxide breaks down. f. The magnesium oxide from which the magnesium discussed above was produced. g. A strawberry h. A cup of tea with no leaves in it. 3. A student does a chemical reaction with two che ...
SUPPORT MATERIAL CLASS – X(science) FIRST TERM
... 5) Chemical properties of acids: i) Acids react with active metals to give hydrogen gas. Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 ii) Acids react with metal carbonate and metal hydrogen carbonate to give carbon dioxide. NaHCO3 +HCl NaCl + H2O + CO2 iii) Acids react with bases to give salt and water. This reaction is ...
... 5) Chemical properties of acids: i) Acids react with active metals to give hydrogen gas. Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 ii) Acids react with metal carbonate and metal hydrogen carbonate to give carbon dioxide. NaHCO3 +HCl NaCl + H2O + CO2 iii) Acids react with bases to give salt and water. This reaction is ...
Document
... 5) Chemical properties of acids: i) Acids react with active metals to give hydrogen gas. Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 ii) Acids react with metal carbonate and metal hydrogen carbonate to give carbon dioxide. NaHCO3 +HCl NaCl + H2O + CO2 iii) Acids react with bases to give salt and water. This reaction is ...
... 5) Chemical properties of acids: i) Acids react with active metals to give hydrogen gas. Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 ii) Acids react with metal carbonate and metal hydrogen carbonate to give carbon dioxide. NaHCO3 +HCl NaCl + H2O + CO2 iii) Acids react with bases to give salt and water. This reaction is ...
Year Review Booklet (optional)
... Give directions on how to make 5.00 L of 0.020 M Ca(ClO)2 using solid Ca(ClO)2 and water. Include proper units in your work and in your answers. ...
... Give directions on how to make 5.00 L of 0.020 M Ca(ClO)2 using solid Ca(ClO)2 and water. Include proper units in your work and in your answers. ...
CONDUCTOMETRY
... Advantages and disadvantages of DME Advantages of DME Its surface is reproducible, smooth and continuously renewed, this eliminates the poisoning effect. Mercury forms amalgams (solid solution) with many metals. The diffusion current assumed a steady value immediately after each change of applie ...
... Advantages and disadvantages of DME Advantages of DME Its surface is reproducible, smooth and continuously renewed, this eliminates the poisoning effect. Mercury forms amalgams (solid solution) with many metals. The diffusion current assumed a steady value immediately after each change of applie ...
Oxygen Carriers Materials for Chemical
... an expensive and energy-intensive process resulting in a large decrease in efficiency. Thus there is a need to find cheaper and more efficient methods to perform the separation. Chemical-looping combustion (CLC) and chemical-looping reforming (CLR) are innovative technologies for power and hydrogen ...
... an expensive and energy-intensive process resulting in a large decrease in efficiency. Thus there is a need to find cheaper and more efficient methods to perform the separation. Chemical-looping combustion (CLC) and chemical-looping reforming (CLR) are innovative technologies for power and hydrogen ...
Power Point over chemistry
... oxygen gas using an electric current. When water molecules change chemically into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas, we say that a chemical change has occurred. Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas each have a different set of properties. Substances change into different substances through TAKS Need to Know chemic ...
... oxygen gas using an electric current. When water molecules change chemically into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas, we say that a chemical change has occurred. Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas each have a different set of properties. Substances change into different substances through TAKS Need to Know chemic ...
Chem 111 2:30p section Final Exam
... This exam is composed of 50 questions, 14 of which require mathematics that require a calculator. Go initially through the exam and answer the questions you can answer quickly. Then go back and try the ones that are more challenging to you and/or that require calculations. As discussed in the course ...
... This exam is composed of 50 questions, 14 of which require mathematics that require a calculator. Go initially through the exam and answer the questions you can answer quickly. Then go back and try the ones that are more challenging to you and/or that require calculations. As discussed in the course ...
Chemistry - Set as Home Page
... Valency is a number giving the _________ power of an atom with another atom. ...
... Valency is a number giving the _________ power of an atom with another atom. ...
REACTING MASSES – ACTIVITY SHEET
... 1. The volume of 0.22g of propene is 118cm3. Calculate the volume of 2 moles of propene 2. The volume of 1 g of hydrogen is 11.6 Litres. Calculate the volume of 4 mol of hydrogen. 3. A flask, capacity 600cm3, was used to calculate the molar volume of sulphur dioxide. The following data was obtained. ...
... 1. The volume of 0.22g of propene is 118cm3. Calculate the volume of 2 moles of propene 2. The volume of 1 g of hydrogen is 11.6 Litres. Calculate the volume of 4 mol of hydrogen. 3. A flask, capacity 600cm3, was used to calculate the molar volume of sulphur dioxide. The following data was obtained. ...
Document
... with a high rate. Some reactions take hundreds, maybe even thousands, of years while others can happen in less than one second. If you want to think of a very slow reaction, think about how long it takes plants and ancient fish to become fossils (carbonization). Ultimately: Molecules moving too slow ...
... with a high rate. Some reactions take hundreds, maybe even thousands, of years while others can happen in less than one second. If you want to think of a very slow reaction, think about how long it takes plants and ancient fish to become fossils (carbonization). Ultimately: Molecules moving too slow ...
Unit: Corrosion Science Important Questions with Hints
... 16. Pure copper is immune to stress corrosion than Brass. Why? Hints: Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. So, in corroding environment containing traces of ammonia or amines, copper and zinc present in brass form complexes [Cu(NH3)4]2+ and [Zn(NH3)4]2+ . This results in dissolution of brass leadin ...
... 16. Pure copper is immune to stress corrosion than Brass. Why? Hints: Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. So, in corroding environment containing traces of ammonia or amines, copper and zinc present in brass form complexes [Cu(NH3)4]2+ and [Zn(NH3)4]2+ . This results in dissolution of brass leadin ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.