Chemical Reactions
... 2. Find the number of atoms for each element on the left side. Compare those against the number of the atoms of the same element on the right side. 3. Determine where to place coefficients in front of formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in o ...
... 2. Find the number of atoms for each element on the left side. Compare those against the number of the atoms of the same element on the right side. 3. Determine where to place coefficients in front of formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in o ...
I. Earth spheres A. Three major spheres 1. atmosphere, thin
... most isotopes are stable unstable isotopes are ‘radioactive’, and disintegrate over time i. in a certain length of time, one half of the atoms of an unstable isotope will decay into another substance ii. this length of time is the ‘half-life; of the isotope a. half-life is constant for an isotope b. ...
... most isotopes are stable unstable isotopes are ‘radioactive’, and disintegrate over time i. in a certain length of time, one half of the atoms of an unstable isotope will decay into another substance ii. this length of time is the ‘half-life; of the isotope a. half-life is constant for an isotope b. ...
Unit 6 Moles and Stoichiometry Short Answer Review
... Unit 6 Moles and Stoichiometry Short Answer Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information below. Rust on an automobile door contains Fe 2O3(s). The balanced equation representing one of the reactions between iron in the door of the automobile and oxygen in the atmosphere is gi ...
... Unit 6 Moles and Stoichiometry Short Answer Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information below. Rust on an automobile door contains Fe 2O3(s). The balanced equation representing one of the reactions between iron in the door of the automobile and oxygen in the atmosphere is gi ...
Unit 1: Building Blocks Homework
... 8. What is the relative formula mass of ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2SO4? A B C D ...
... 8. What is the relative formula mass of ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2SO4? A B C D ...
Name: Date: AP Chemistry/Chemistry 145 Summer Assignment
... How many moles of carbon dioxide is released by the reaction of 0.250 moles of calcium carbonate? ...
... How many moles of carbon dioxide is released by the reaction of 0.250 moles of calcium carbonate? ...
Chemical Bond - Cobb Learning
... using your periodic table) Write the symbol for the negative ion second (determine the charge or oxidation number using your periodic table). An oxidation number (or charge) indicates how many electrons are lost, gained or shared when bonding occurs. ...
... using your periodic table) Write the symbol for the negative ion second (determine the charge or oxidation number using your periodic table). An oxidation number (or charge) indicates how many electrons are lost, gained or shared when bonding occurs. ...
Packet
... 56. __ BaCl2 + ___ NaOH → ____ Ba(OH)2 + ___ NaCl 57. ___ Fe+ ___ CuSO4 → ____ Cu + ___ FeSO4 58. ___ NbI3 + ___ I2 → ___ NbI5 Identify the type of chemical reaction shown below as synthesis (S), decomposition (D), single replacement (SR), double replacement (DR), or combustion (C). ...
... 56. __ BaCl2 + ___ NaOH → ____ Ba(OH)2 + ___ NaCl 57. ___ Fe+ ___ CuSO4 → ____ Cu + ___ FeSO4 58. ___ NbI3 + ___ I2 → ___ NbI5 Identify the type of chemical reaction shown below as synthesis (S), decomposition (D), single replacement (SR), double replacement (DR), or combustion (C). ...
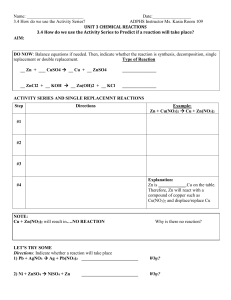
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
Chapter 1
... A ______Chemical Formula______ is a shorthand way to use chemical symbols and numbers to represent a substance. *Notes-A ______Subscript_________ is a number written below and to the right of a chemical symbol. C6H12O6 The 6, 12, and 6 are all subscripts. *To find the number of atoms in a compound y ...
... A ______Chemical Formula______ is a shorthand way to use chemical symbols and numbers to represent a substance. *Notes-A ______Subscript_________ is a number written below and to the right of a chemical symbol. C6H12O6 The 6, 12, and 6 are all subscripts. *To find the number of atoms in a compound y ...
K,7th Grade Test Review: Atoms and Chemical Reactions PART
... PART FOUR: Chemical Equations. For each equation, label the products and reactants. Then, count the number of atoms of each element on each side. Then fill in the blanks. ...
... PART FOUR: Chemical Equations. For each equation, label the products and reactants. Then, count the number of atoms of each element on each side. Then fill in the blanks. ...
GY 111 Lecture Note Series Elemental Chemistry
... (although several of them were produced in labs rather than found in nature). Each has a specific chemical symbol. The elements can combine through various chemical reactions to for compounds. For example: water is H2O (one part hydrogen + 2 parts oxygen) galena is PbS (one part lead - Latin is plum ...
... (although several of them were produced in labs rather than found in nature). Each has a specific chemical symbol. The elements can combine through various chemical reactions to for compounds. For example: water is H2O (one part hydrogen + 2 parts oxygen) galena is PbS (one part lead - Latin is plum ...
name - cloudfront.net
... If the reaction of 150. g of ammonia with 150. g of oxygen gas yields 87. g of nitric oxide (NO), what is the percent yield of this reaction? (77%) 14.The Hall process for the production of aluminum involves the reaction of aluminum oxide with elemental carbon to give aluminum metal and carbon monox ...
... If the reaction of 150. g of ammonia with 150. g of oxygen gas yields 87. g of nitric oxide (NO), what is the percent yield of this reaction? (77%) 14.The Hall process for the production of aluminum involves the reaction of aluminum oxide with elemental carbon to give aluminum metal and carbon monox ...
Unit #7 Take Home Test
... b. The proportion by mass of elements combined in potassium chlorate varies. c. Potassium chlorate is composed of four elements. d. Potassium chlorate is composed of five elements. 25. If a chemical equation is balanced properly, both sides of the equation must have the same number of a. atoms b. co ...
... b. The proportion by mass of elements combined in potassium chlorate varies. c. Potassium chlorate is composed of four elements. d. Potassium chlorate is composed of five elements. 25. If a chemical equation is balanced properly, both sides of the equation must have the same number of a. atoms b. co ...
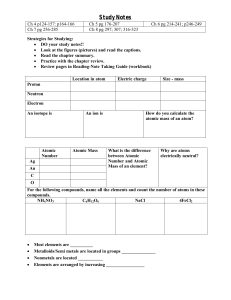
Study Notes
... • Read the chapter summary. • Practice with the chapter review. • Review pages in Reading-Note Taking Guide (workbook) Location in atom ...
... • Read the chapter summary. • Practice with the chapter review. • Review pages in Reading-Note Taking Guide (workbook) Location in atom ...
gr11chemreview
... 12. Explain why polar molecules have higher boiling and melting points than non polar molecules. ...
... 12. Explain why polar molecules have higher boiling and melting points than non polar molecules. ...
What are the general types of reactions?
... – Mass is not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction – For practical purposes • Same types of atoms before and after a reaction • Same number of each type of atom before and after ...
... – Mass is not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction – For practical purposes • Same types of atoms before and after a reaction • Same number of each type of atom before and after ...
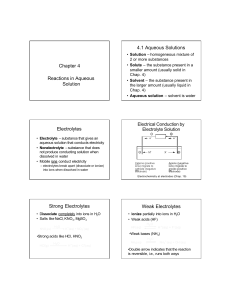
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 Aqueous Solutions
... – There are no ionic charges shown, but it is a redox reaction ...
... – There are no ionic charges shown, but it is a redox reaction ...
nature of Matter
... Nitrogen-14 (7 protons & 7 neutrons) An isotope is when atoms of the same element have a different number of NEUTRONS. Isotopes are identified by their mass number. Since they still have the same number of electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. A compound is a sub ...
... Nitrogen-14 (7 protons & 7 neutrons) An isotope is when atoms of the same element have a different number of NEUTRONS. Isotopes are identified by their mass number. Since they still have the same number of electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. A compound is a sub ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... 23. Determine the pH of a 2.0 x 10-2 M Sr(OH)2? 24. The pH of a solution is measured and determined to be 7.52? What is the hydrogen ion concentration? Is the solution acidic or basic? Objective 6.5A, B & C 1. What do the coefficients mean in a chemical equation? 2. Calculate the mole ratio between ...
... 23. Determine the pH of a 2.0 x 10-2 M Sr(OH)2? 24. The pH of a solution is measured and determined to be 7.52? What is the hydrogen ion concentration? Is the solution acidic or basic? Objective 6.5A, B & C 1. What do the coefficients mean in a chemical equation? 2. Calculate the mole ratio between ...
Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
... For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
... For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
CHEM1405 2012-J-2 June 2012 • What is the ground state electron
... • Show clearly the reagents you would use to carry out the following chemical conversions. Note that more than one step is required and you should indicate all necessary steps and the constitutional formulas of any intermediate compounds. ...
... • Show clearly the reagents you would use to carry out the following chemical conversions. Note that more than one step is required and you should indicate all necessary steps and the constitutional formulas of any intermediate compounds. ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.