Stoichiometry - Cloudfront.net
... 7. A 105.5 mg sample of a white substance is suspected to be cocaine, C 17H21NO4. The substance formed 279.3 mg of CO2 and 66.46 mg H2O on combustion. The compound contains 4.680% N by mass. Is the white solid cocaine? 8. An unknown compound (molar mass = 176 g/mol) contains 68.2 mass % C, 6.86 mass ...
... 7. A 105.5 mg sample of a white substance is suspected to be cocaine, C 17H21NO4. The substance formed 279.3 mg of CO2 and 66.46 mg H2O on combustion. The compound contains 4.680% N by mass. Is the white solid cocaine? 8. An unknown compound (molar mass = 176 g/mol) contains 68.2 mass % C, 6.86 mass ...
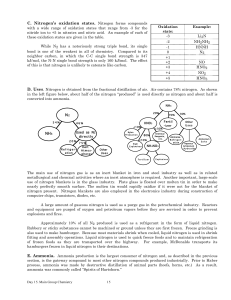
Nitrogen`s oxidation states
... makes up the rings on Saturn. Ammonia is a weak base with a pKb = 4.76 at 25 o C. Its melting point is 77.7 o C and boiling point is -33.3 o C. The density of liquid ammonia is 0.6826 g/mL. The structure of ammonia, predicted by VSEPR is that of a trigonal pyramid. At room temperature ammonia molecu ...
... makes up the rings on Saturn. Ammonia is a weak base with a pKb = 4.76 at 25 o C. Its melting point is 77.7 o C and boiling point is -33.3 o C. The density of liquid ammonia is 0.6826 g/mL. The structure of ammonia, predicted by VSEPR is that of a trigonal pyramid. At room temperature ammonia molecu ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment - Belle Vernon Area School District
... water. How many moles of HCl would be required to react with 7.5 moles of lime? How many moles of water would be formed? (15 mol HCl; 7.5 mol water) ______________ For each of the following write balanced chemical equations and then solve the problem. ...
... water. How many moles of HCl would be required to react with 7.5 moles of lime? How many moles of water would be formed? (15 mol HCl; 7.5 mol water) ______________ For each of the following write balanced chemical equations and then solve the problem. ...
Chemistry: Unit Organizer Name 6-__ Matter has physical properties
... Atom: The smallest unit of matter. ex. a carbon atom Chemical Reaction: a process in which chemical bonds are broken and atoms rearranged. During the process a new substance is formed. Compound: 2 or more elements combined to make something new, Ex. Na (sodium) + Cl (chlorine) = NaCl (salt) Density: ...
... Atom: The smallest unit of matter. ex. a carbon atom Chemical Reaction: a process in which chemical bonds are broken and atoms rearranged. During the process a new substance is formed. Compound: 2 or more elements combined to make something new, Ex. Na (sodium) + Cl (chlorine) = NaCl (salt) Density: ...
Synthesis Reactions occur when two of more reactants combine to
... Empirical/Molecular Practice: 1. Zinc form an ionic compound with an oxyanion. The formula is 44.97% Zn and 22.02% S. What is the formula and the name of the compound? 2. Naphthalenedisulfonic acid is found to be 41.7% C, 2.8% H, 22.2% S, and 33.3% O. The molar mass is 288 g/mol. Write the formula. ...
... Empirical/Molecular Practice: 1. Zinc form an ionic compound with an oxyanion. The formula is 44.97% Zn and 22.02% S. What is the formula and the name of the compound? 2. Naphthalenedisulfonic acid is found to be 41.7% C, 2.8% H, 22.2% S, and 33.3% O. The molar mass is 288 g/mol. Write the formula. ...
Bonding practice lessons 1-3
... The results of these tests suggest that A) both solids contain only ionic bonds B) both solids contain only covalent bonds C) solid A contains only covalent bonds and solid B contains only ionic bonds D) solid A contains only ionic bonds and solid B contains only covalent bonds 22. The bonds between ...
... The results of these tests suggest that A) both solids contain only ionic bonds B) both solids contain only covalent bonds C) solid A contains only covalent bonds and solid B contains only ionic bonds D) solid A contains only ionic bonds and solid B contains only covalent bonds 22. The bonds between ...
2011
... hexane has more surface area for interacting with neighbouring hexane molecules. C) hexane has hydrogen bonding. D) hexane has less surface area for interacting with neighbouring hexane molecules. ...
... hexane has more surface area for interacting with neighbouring hexane molecules. C) hexane has hydrogen bonding. D) hexane has less surface area for interacting with neighbouring hexane molecules. ...
November 2016 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry A-level
... from ............................................................ to ............................................................ [1] ...
... from ............................................................ to ............................................................ [1] ...
Chemical Equations PowerPoint
... will require trial and error, the following guidelines may be helpful) a) balance the different types of atoms one at a time b) first, balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation ...
... will require trial and error, the following guidelines may be helpful) a) balance the different types of atoms one at a time b) first, balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry
... (C) all points on the curve between Q and S (D) all points on the curve between R and T (E) no point on the curve . . .C10H12O4S(s) + . . O2(g) ---> . . . CO2(g) + . . . SO2(g) + . . . H2O(g) 26. When the equation above is balanced and all coefficients are reduced to their lowest whole-number terms, ...
... (C) all points on the curve between Q and S (D) all points on the curve between R and T (E) no point on the curve . . .C10H12O4S(s) + . . O2(g) ---> . . . CO2(g) + . . . SO2(g) + . . . H2O(g) 26. When the equation above is balanced and all coefficients are reduced to their lowest whole-number terms, ...
Rates of Reaction: Chemical Kinetics 50
... A. Mg(s) + 2H+(aq) Mg2+(aq) + H2(g) B. Zn(s) + S(s) ZnS(s) C. 2Ag+(aq) + CrO42-(aq) Ag2CrO42-(aq) D. 3 Fe2+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + 4 H+(aq) 3 Fe3+(aq) + NO(g) + 2 H2O(l) ...
... A. Mg(s) + 2H+(aq) Mg2+(aq) + H2(g) B. Zn(s) + S(s) ZnS(s) C. 2Ag+(aq) + CrO42-(aq) Ag2CrO42-(aq) D. 3 Fe2+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + 4 H+(aq) 3 Fe3+(aq) + NO(g) + 2 H2O(l) ...
November 2016 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry A-level
... from ............................................................ to ............................................................ [1] ...
... from ............................................................ to ............................................................ [1] ...
35. Number of reactions - Royal Society of Chemistry
... (Cu(OH)2.CuCO3) is formed initially. On adding excess A this dissolves to form a deep blue solution of Cu(NH3)42+(aq). ...
... (Cu(OH)2.CuCO3) is formed initially. On adding excess A this dissolves to form a deep blue solution of Cu(NH3)42+(aq). ...
AP Chemistry Summer Work
... [email protected] - feel free to email me with questions over the summer WELCOME to AP chemistry! The AP curriculum includes all of the topics and the labs that we need to complete before the 2015 AP test on Monday, May 4th. All of you will find AP chemistry to be challenging, some of you will find i ...
... [email protected] - feel free to email me with questions over the summer WELCOME to AP chemistry! The AP curriculum includes all of the topics and the labs that we need to complete before the 2015 AP test on Monday, May 4th. All of you will find AP chemistry to be challenging, some of you will find i ...
Ch 8 Bonding and Molecular Structure 06-Nov
... Oxoacids and their Anions: in the absence of water, which helps ionize the acid and form hydrogen bonding, these acids form covalent bonds (See Table 8.4 below). ...
... Oxoacids and their Anions: in the absence of water, which helps ionize the acid and form hydrogen bonding, these acids form covalent bonds (See Table 8.4 below). ...
Chem 30A, Test Review #2
... Classify each of the following as an ionic or a molecular/covalent compound. (a) CS2 = ____________________; ...
... Classify each of the following as an ionic or a molecular/covalent compound. (a) CS2 = ____________________; ...
- Catalyst
... – isotopes have the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons (chemically indistinguishable) – an atom of an element usually comes in at least 2 or 3 different ...
... – isotopes have the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons (chemically indistinguishable) – an atom of an element usually comes in at least 2 or 3 different ...
Atomic and Molecular Structure
... and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. On the periodic tables given ...
... and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. On the periodic tables given ...
A2 Module 2814: Chains, Rings and Spectroscopy
... because of the Cu(H2O)62+ ion. It first forms a pale blue precipitate of Cu(OH)2, and then this dissolves to give a deep blue coloured solution, containing the Cu(NH3)4(H2O)22+ ion. [N.B. the hydroxide is formed first because ammonia solution is alkaline – see below for the effect of alkaline soluti ...
... because of the Cu(H2O)62+ ion. It first forms a pale blue precipitate of Cu(OH)2, and then this dissolves to give a deep blue coloured solution, containing the Cu(NH3)4(H2O)22+ ion. [N.B. the hydroxide is formed first because ammonia solution is alkaline – see below for the effect of alkaline soluti ...
RULES OF CHEMICAL NOMENCLATURE I. Elements (periodic
... B. Naming salts (other than binary) 1. name of metal plus name of ...
... B. Naming salts (other than binary) 1. name of metal plus name of ...
REDOX ZONATION IN THE PHANEROZOIC ANOXIC OCEAN Part I
... Interest in anoxia in the water column has been generated through investigations of the origins of various "black" shales or sapropels in the general geologic record [Demaison and Moore, 1980] and particularly in the Paleozoic [Berry and Wilde, 1978] and in the Mesozoic [eg. Arthur and Schlanger, 19 ...
... Interest in anoxia in the water column has been generated through investigations of the origins of various "black" shales or sapropels in the general geologic record [Demaison and Moore, 1980] and particularly in the Paleozoic [Berry and Wilde, 1978] and in the Mesozoic [eg. Arthur and Schlanger, 19 ...
02_Lecture_Presentation
... • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
... • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.