
Active Learning Questions
... 1. Consider two beakers of pure water at different temperatures. How do their pH values compare? Which is more acidic? more basic? Explain. 2. Differentiate between the terms strength and concentration as they apply to acids and bases. When is HCl strong? Weak? Concentrated? Dilute? Answer the same ...
... 1. Consider two beakers of pure water at different temperatures. How do their pH values compare? Which is more acidic? more basic? Explain. 2. Differentiate between the terms strength and concentration as they apply to acids and bases. When is HCl strong? Weak? Concentrated? Dilute? Answer the same ...
Theoretical problems
... Preparatory Problems, Theoretical contaminations. The reaction of sulfuric acid with colemanite takes place in two steps: In the first step colemanite is dissolved in sulfuric acid forming the calcium(II) ion and boric acid. In the second step, calcium sulfate, formed from Ca 2+ and SO4 ions, pre ...
... Preparatory Problems, Theoretical contaminations. The reaction of sulfuric acid with colemanite takes place in two steps: In the first step colemanite is dissolved in sulfuric acid forming the calcium(II) ion and boric acid. In the second step, calcium sulfate, formed from Ca 2+ and SO4 ions, pre ...
equilibrium - TeacherWeb
... The direction in which you write the chemical equation for an equilibrium is arbitrary, because equilibrium can be approached from either direction. The equilibrium constant expression for a reaction written in one direction is the reciprocal of the one for the reaction in the reverse direction. The ...
... The direction in which you write the chemical equation for an equilibrium is arbitrary, because equilibrium can be approached from either direction. The equilibrium constant expression for a reaction written in one direction is the reciprocal of the one for the reaction in the reverse direction. The ...
Questions
... III The acidic solution in the beaker was filtered into a 250 cm3 volumetric flask. A small amount of solid impurity remained in the filter paper. The solution in the volumetric flask was carefully made up to 250 cm3 with distilled water. IV A pipette was used to transfer 25.0 cm3 portions of the ac ...
... III The acidic solution in the beaker was filtered into a 250 cm3 volumetric flask. A small amount of solid impurity remained in the filter paper. The solution in the volumetric flask was carefully made up to 250 cm3 with distilled water. IV A pipette was used to transfer 25.0 cm3 portions of the ac ...
Acrobat () verson
... The approach here is to use the relation K = e – Δ Greaxn /RT and the thermodynamic data provided with the examination to calculate a numerical value for the equilibrium constant K. This requires that we determine Δ Goreaxn = Δ Horeaxn – T Δ Soreaxn . From the thermodynamic data provided, we can cal ...
... The approach here is to use the relation K = e – Δ Greaxn /RT and the thermodynamic data provided with the examination to calculate a numerical value for the equilibrium constant K. This requires that we determine Δ Goreaxn = Δ Horeaxn – T Δ Soreaxn . From the thermodynamic data provided, we can cal ...
ioan stamatin
... (chemical thermodynamics), one for biology and one for students at physics. For century that is truth when the interdisciplinary sciences still were not born. Departments from Faculty of Physics, University of Bucharest, have developed in the last decade large interdisciplinary fields such as Medica ...
... (chemical thermodynamics), one for biology and one for students at physics. For century that is truth when the interdisciplinary sciences still were not born. Departments from Faculty of Physics, University of Bucharest, have developed in the last decade large interdisciplinary fields such as Medica ...
Topic 7.2 Equilibrium The Position of Equilibrium
... Hydrogen and iodine are in equilibrium with Hydrogen iodide to this reaction: H2 + I2 2HI Suppose that 1.5 mole of H2 and 1.2 mole of I2 are placed in a 1.0 dm3 container. At equilibrium it was found that there were 0.4 mole of HI. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of [H2] and [I2] and the ...
... Hydrogen and iodine are in equilibrium with Hydrogen iodide to this reaction: H2 + I2 2HI Suppose that 1.5 mole of H2 and 1.2 mole of I2 are placed in a 1.0 dm3 container. At equilibrium it was found that there were 0.4 mole of HI. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of [H2] and [I2] and the ...
17 - Wiley
... with the strength of the basic anion, which in turn is inversely proportional to the strength of the parent weak acid. Here is the order for these compounds: NaI (neutral) < NaF (Ka = 6.3 × 10–4) < NaC6H5CO2 (Ka = 6.3 × 10–5) < Na3PO4 (Ka3 = 4.8 × 10–13) < NaOH (strong base) 14.45 (a) H2SO4 is stron ...
... with the strength of the basic anion, which in turn is inversely proportional to the strength of the parent weak acid. Here is the order for these compounds: NaI (neutral) < NaF (Ka = 6.3 × 10–4) < NaC6H5CO2 (Ka = 6.3 × 10–5) < Na3PO4 (Ka3 = 4.8 × 10–13) < NaOH (strong base) 14.45 (a) H2SO4 is stron ...
AP Chemistry Notes and Worksheets 2014
... o Shows that each element consists of a certain type of atom and that compounds were formed from specific combinations of atoms. 2.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory Dalton's Atomic Theory -1808 o Each element is made up of particles called atoms. o Atoms in an element are all identical and are different th ...
... o Shows that each element consists of a certain type of atom and that compounds were formed from specific combinations of atoms. 2.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory Dalton's Atomic Theory -1808 o Each element is made up of particles called atoms. o Atoms in an element are all identical and are different th ...
PPT - Physikalisches Institut Heidelberg
... to those usually related to XFELs. Even of not less importance is the unique feature of RCE as a tunable source of polarized X-ray radiation. True, RCE will never compete with lasers in whole. But the wide experience gained in experimental and theoretical RCE studies, especially concerning polarizat ...
... to those usually related to XFELs. Even of not less importance is the unique feature of RCE as a tunable source of polarized X-ray radiation. True, RCE will never compete with lasers in whole. But the wide experience gained in experimental and theoretical RCE studies, especially concerning polarizat ...
Dr. Spencer`s PPT
... Complete Ionic Equation - in solutions, where the reactants and products are ionized, it is more useful (and accurate) to indicate ions. Ba2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2NO3- (aq) Ba2+(aq) + 2NO3- (aq) + 2 H2O(l) ...
... Complete Ionic Equation - in solutions, where the reactants and products are ionized, it is more useful (and accurate) to indicate ions. Ba2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2NO3- (aq) Ba2+(aq) + 2NO3- (aq) + 2 H2O(l) ...
Fatty acid bile acid conjugates (FABACs)—New molecules for the
... faster from model solutions than from human bile at identical lipid concentrations.16 In vivo, in two animal species, FABACs prevented the formation of cholesterol crystals at biliary concentrations of 0.4–0.65 mM. This is lower than the concentrations required in vitro. Long chain saturated free fa ...
... faster from model solutions than from human bile at identical lipid concentrations.16 In vivo, in two animal species, FABACs prevented the formation of cholesterol crystals at biliary concentrations of 0.4–0.65 mM. This is lower than the concentrations required in vitro. Long chain saturated free fa ...
Unit 4 - Chemical Equilibrium
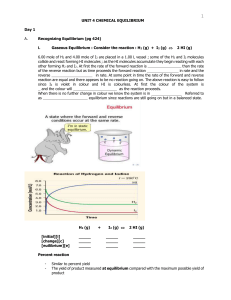
... Dynamic Equilibrium When the _ _ _ _ _ in a chemical reaction looks like this ⇌ , it shows that the reaction is _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. This means the products can react together and turn back into the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ reactants. In other words, the reaction can go _ _ _ _ ways. When a reversible reacti ...
... Dynamic Equilibrium When the _ _ _ _ _ in a chemical reaction looks like this ⇌ , it shows that the reaction is _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. This means the products can react together and turn back into the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ reactants. In other words, the reaction can go _ _ _ _ ways. When a reversible reacti ...
CHAPTER 18
... Suppose two substances, A and B, react to form products C and D. In turn, C and D react to produce A and B. Under appropriate conditions, equilibrium occurs for this reversible reaction. This hypothetical equilibrium reaction is described by the following general equation. n A + m B $ x C + yD Initi ...
... Suppose two substances, A and B, react to form products C and D. In turn, C and D react to produce A and B. Under appropriate conditions, equilibrium occurs for this reversible reaction. This hypothetical equilibrium reaction is described by the following general equation. n A + m B $ x C + yD Initi ...
chap15pptlecture_chapte.ppt [Read-Only]
... 1.! Express the equilibrium concentrations of all species in terms of the initial concentrations and a single unknown x, which represents the change in concentration. 2.! Write the equilibrium constant expression in terms of the equilibrium concentrations. Knowing the value of the equilibrium consta ...
... 1.! Express the equilibrium concentrations of all species in terms of the initial concentrations and a single unknown x, which represents the change in concentration. 2.! Write the equilibrium constant expression in terms of the equilibrium concentrations. Knowing the value of the equilibrium consta ...
Solubility of platinum in aqueous solutions at 25°C and pHs 4 to 10
... The understanding of the geochemical cycle of platinum group elements (PGEs) is very important scientifically, industrially, and economically. These metals have always been more or less considered as immobile in supergene environments. McKibben et al. (1990) analyzed the concentrations of Pt, Pd, Au ...
... The understanding of the geochemical cycle of platinum group elements (PGEs) is very important scientifically, industrially, and economically. These metals have always been more or less considered as immobile in supergene environments. McKibben et al. (1990) analyzed the concentrations of Pt, Pd, Au ...
Principles of Reactivity: Chemical Equilibria
... balanced equation are multiplied by some factor, the equilibrium constant for the new equation (Knew) is the old equilibrium constant (Kold) raised to the power of the multiplication factor. The equilibrium constants for a reaction and its reverse are the reciprocals of each other. When two or more ...
... balanced equation are multiplied by some factor, the equilibrium constant for the new equation (Knew) is the old equilibrium constant (Kold) raised to the power of the multiplication factor. The equilibrium constants for a reaction and its reverse are the reciprocals of each other. When two or more ...
Document
... Horner et al. (2009, 2012). This crystal macropattern is predominant for the genus Peperomia. The other two major druse macropatterns represented in the genus are: species with larger druses over the veins (DUVbig) and smaller druses in the lamina or areole (Asmall) regions (DUVbigAsmall – /– ); and ...
... Horner et al. (2009, 2012). This crystal macropattern is predominant for the genus Peperomia. The other two major druse macropatterns represented in the genus are: species with larger druses over the veins (DUVbig) and smaller druses in the lamina or areole (Asmall) regions (DUVbigAsmall – /– ); and ...
Minerals
... metallic mineral that can be mined at a profit. Some of the most important mineral deposits form through igneous processes and from hydrothermal solutions. Igneous processes produce important deposits of metallic minerals such as gold silver, copper, mercury, lead, platinum and nickel. Hydrothermal ...
... metallic mineral that can be mined at a profit. Some of the most important mineral deposits form through igneous processes and from hydrothermal solutions. Igneous processes produce important deposits of metallic minerals such as gold silver, copper, mercury, lead, platinum and nickel. Hydrothermal ...
Title
... NMR spectrum is indistinguishable from the starting complex 1Cl2, confirming that the cationic complex 1 remains unaltered. The crystal structure obtained for 1(PF6)2 confirms the cisdisposition of the ligands (Fig. 7). The trans-isomer complex 2(CF3SO3)2 was synthesized (Scheme 2) by reaction of tr ...
... NMR spectrum is indistinguishable from the starting complex 1Cl2, confirming that the cationic complex 1 remains unaltered. The crystal structure obtained for 1(PF6)2 confirms the cisdisposition of the ligands (Fig. 7). The trans-isomer complex 2(CF3SO3)2 was synthesized (Scheme 2) by reaction of tr ...
Module 2
... Gibbs free energy:For any change at constant temperature and pressure we have: ∆G = ∆H – T·∆S For a spontaneous process the change in the Gibbs free energy, ∆G must be negative. In other words, the Gibbs free energy decreases during a spontaneous process. The standard free energy of formation, ∆Gf, ...
... Gibbs free energy:For any change at constant temperature and pressure we have: ∆G = ∆H – T·∆S For a spontaneous process the change in the Gibbs free energy, ∆G must be negative. In other words, the Gibbs free energy decreases during a spontaneous process. The standard free energy of formation, ∆Gf, ...
File
... sig figs and always include proper units. Underline, use capital letters or use any device you choose to help organize this section well. Space things out – don’t try to cram everything on one page. A data table must have a label and a title. e.g. – Table 1: Density Values for Sugar Solutions. 7. Ca ...
... sig figs and always include proper units. Underline, use capital letters or use any device you choose to help organize this section well. Space things out – don’t try to cram everything on one page. A data table must have a label and a title. e.g. – Table 1: Density Values for Sugar Solutions. 7. Ca ...
AP Chemistry Lab Manual
... sig figs and always include proper units. Underline, use capital letters or use any device you choose to help organize this section well. Space things out – don’t try to cram everything on one page. A data table must have a label and a title. e.g. – Table 1: Density Values for Sugar Solutions. 7. Ca ...
... sig figs and always include proper units. Underline, use capital letters or use any device you choose to help organize this section well. Space things out – don’t try to cram everything on one page. A data table must have a label and a title. e.g. – Table 1: Density Values for Sugar Solutions. 7. Ca ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.












![chap15pptlecture_chapte.ppt [Read-Only]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015369082_1-00cbf06a2d468a4ae1c963f5ca674e31-300x300.png)








