Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry (Chapter 4)
... Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry (Chapter 4) Water has many unique chemical and physical properties. Possibly one of the most important is its ability to dissolve other substances to form solutions. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances. The solvent (usually the su ...
... Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry (Chapter 4) Water has many unique chemical and physical properties. Possibly one of the most important is its ability to dissolve other substances to form solutions. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances. The solvent (usually the su ...
Name Date
... 1. Luster - the way a mineral reflects light 2. Crystal shape 3. Streak - the color of the minerals powder 4. Cleavage - the tendency of a mineral to split easily or to separate along flat surfaces 5. Fracture - when a mineral breaks along surfaces other than cleavage surfaces 6. Hardness - a minera ...
... 1. Luster - the way a mineral reflects light 2. Crystal shape 3. Streak - the color of the minerals powder 4. Cleavage - the tendency of a mineral to split easily or to separate along flat surfaces 5. Fracture - when a mineral breaks along surfaces other than cleavage surfaces 6. Hardness - a minera ...
Final Review
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
Chapter 3, Section 1, “Minerals” 1) All 4000 on Earth share four
... 2) _______________________ is a gemstone of quartz that has a purple color. 3) The __________________ diamond and the ________________ diamonds are famous historical gems. 4) The ______________diamond was the largest uncut diamond ever discovered. 5) The __________________ diamond gained a reputatio ...
... 2) _______________________ is a gemstone of quartz that has a purple color. 3) The __________________ diamond and the ________________ diamonds are famous historical gems. 4) The ______________diamond was the largest uncut diamond ever discovered. 5) The __________________ diamond gained a reputatio ...
Lesson Plan Form
... Definite Crystalline Structure. The last part of the definition of minerals relates to crystalline structures. The atoms in minerals are arranged in regular geometric patterns that are repeated again and again. A crystal is a solid in which the atoms are arranged in repeating patterns. At times, a m ...
... Definite Crystalline Structure. The last part of the definition of minerals relates to crystalline structures. The atoms in minerals are arranged in regular geometric patterns that are repeated again and again. A crystal is a solid in which the atoms are arranged in repeating patterns. At times, a m ...
CLAY MINERALS
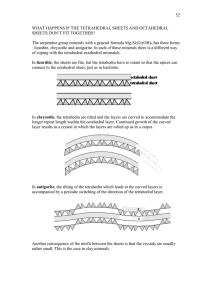
... When these structures are cooled they should transform cristobalite tridymite quartz. As mentioned above, these are reconstructive transitions, and so very slow and difficult. If they do not occur, the crustobalite (and tridymite) will cool to lower temperatures (~ 200oC) and then distort by a d ...
... When these structures are cooled they should transform cristobalite tridymite quartz. As mentioned above, these are reconstructive transitions, and so very slow and difficult. If they do not occur, the crustobalite (and tridymite) will cool to lower temperatures (~ 200oC) and then distort by a d ...
Fe(H2O)63+ + H2O → ← H3O+ + Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+
... 4 H+ + NO3− + Cu (s) Æ Cu2+ + NO + 2 H2O 2 H2O + NO3− + Cu(s) Æ NO + Cu2++ 4 H+ 2 NO3− + 8 H+ + 3 Cu (s) Æ 3 Cu2+ + 2 NO + 4 H2O 3 NO3− + 6 H+ + 2 Cu (s) Æ 2 Cu2++ NO + 3 H2O 6 H+ + 3 NO3− + 2 Cu2+ Æ Cu (s) + NO + 3 H2O ...
... 4 H+ + NO3− + Cu (s) Æ Cu2+ + NO + 2 H2O 2 H2O + NO3− + Cu(s) Æ NO + Cu2++ 4 H+ 2 NO3− + 8 H+ + 3 Cu (s) Æ 3 Cu2+ + 2 NO + 4 H2O 3 NO3− + 6 H+ + 2 Cu (s) Æ 2 Cu2++ NO + 3 H2O 6 H+ + 3 NO3− + 2 Cu2+ Æ Cu (s) + NO + 3 H2O ...
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Three
... Matter can be neither created nor destroyed. Law of Definite Proportions: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by weight. Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, then the masses of one element that combines with a f ...
... Matter can be neither created nor destroyed. Law of Definite Proportions: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by weight. Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, then the masses of one element that combines with a f ...
Tall: 1) The decomposition of CaCO3 is an endothermic process:
... Neither PbCl2 nor PbF2 are appreciably soluble in water. If solid PbCl2 and solid PbF2 are placed in separate beakers, in which beaker is the [Pb2+] greatest? Explain your choice. The equilibrium constants for the solids dissolving in water are: PbCl2(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2 Cl¯(aq) PbF2(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2 ...
... Neither PbCl2 nor PbF2 are appreciably soluble in water. If solid PbCl2 and solid PbF2 are placed in separate beakers, in which beaker is the [Pb2+] greatest? Explain your choice. The equilibrium constants for the solids dissolving in water are: PbCl2(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2 Cl¯(aq) PbF2(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2 ...
In Class Overview of Chapter
... and translational energies populated by a collection of molecules means greater entropy. Consider a group of molecules, without translational, vibrational, or rotational energies and highly ordered. This would represent the lowest possible amount of entropy. 3rd Law of Thermodynamics: The entropy of ...
... and translational energies populated by a collection of molecules means greater entropy. Consider a group of molecules, without translational, vibrational, or rotational energies and highly ordered. This would represent the lowest possible amount of entropy. 3rd Law of Thermodynamics: The entropy of ...
Final Exam Review
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
CHAPTER 4: CHEMICAL QUANTITIES and AQUEOUS REACTIONS
... 14.4 g of salicylic acid (limiting reactant) gives actual yield of 6.26 g of aspirin. Calculate the percent yield of aspirin using the following equation. ...
... 14.4 g of salicylic acid (limiting reactant) gives actual yield of 6.26 g of aspirin. Calculate the percent yield of aspirin using the following equation. ...
The use of recombinant methods and molecular engineering in
... 75% of proteins for crystallization are expressed as fusion constructs [31] using a number of small proteins and tags for aYnity puriWcation as well as for solubility enhancement. A wide choice of systems is available for bacterial hosts, and a smaller but ever expanding selection is available for e ...
... 75% of proteins for crystallization are expressed as fusion constructs [31] using a number of small proteins and tags for aYnity puriWcation as well as for solubility enhancement. A wide choice of systems is available for bacterial hosts, and a smaller but ever expanding selection is available for e ...
Slide 1
... Crystal Formation • A successful crystallization depends on a large difference between the solubility of a material in a hot solvent and its solubility in the same solvent when it is cold. • A material can be purified by crystallization when both the desired product and the impurity have similar so ...
... Crystal Formation • A successful crystallization depends on a large difference between the solubility of a material in a hot solvent and its solubility in the same solvent when it is cold. • A material can be purified by crystallization when both the desired product and the impurity have similar so ...
What is a mineral? "A mineral is a naturally occurring, homogeneous
... ion - ions that have lost electrons (cations) are smaller than their neutral state, ions that have gained electrons (anions) are larger. ...
... ion - ions that have lost electrons (cations) are smaller than their neutral state, ions that have gained electrons (anions) are larger. ...
solid state qp
... short range order. These solids are isotropic in nature and melt over a range of temperature. Therefore, amorphous solids are sometimes called pseudo solids or super cooled liquids. They do not have definite heat of fusion. When cut with a sharp-edged tool, they cut into two pieces with irregular su ...
... short range order. These solids are isotropic in nature and melt over a range of temperature. Therefore, amorphous solids are sometimes called pseudo solids or super cooled liquids. They do not have definite heat of fusion. When cut with a sharp-edged tool, they cut into two pieces with irregular su ...
Combined
... CH3COCH2I + H+ + IThe reaction progress is monitored by titrimetric analysis. At 5-minute intervals, 25.00 cm3 of the reaction mixture is transferred into a beaker and a fixed amount of excess standard sodium hydrogencarbonate solution is added to it immediately. (i) What is the purpose of adding ex ...
... CH3COCH2I + H+ + IThe reaction progress is monitored by titrimetric analysis. At 5-minute intervals, 25.00 cm3 of the reaction mixture is transferred into a beaker and a fixed amount of excess standard sodium hydrogencarbonate solution is added to it immediately. (i) What is the purpose of adding ex ...
Minerals are all around us.
... structure of a crystal, a solid in which the atoms are arranged in an orderly, repeating three-dimensional pattern. Each mineral has its own type of crystal structure. In some cases, two minerals have the same chemical composition but different crystal structures. For example, both diamond and graph ...
... structure of a crystal, a solid in which the atoms are arranged in an orderly, repeating three-dimensional pattern. Each mineral has its own type of crystal structure. In some cases, two minerals have the same chemical composition but different crystal structures. For example, both diamond and graph ...
Chapter 4. Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... We often think that all atoms of the same element must have the same oxidation number and that this number is uniquely related to the atom’s location in the periodic table. It is important that we know that titrations can be conducted not only using acids and bases, but also in precipitation and oxi ...
... We often think that all atoms of the same element must have the same oxidation number and that this number is uniquely related to the atom’s location in the periodic table. It is important that we know that titrations can be conducted not only using acids and bases, but also in precipitation and oxi ...
Final Exam Practice Questions for General Chemistry NOTICE TO
... 4. Which one of the following statements is incorrect for an ideal gas, according to the Kinetic Molecular Theory? a) Molecules of a gas are widely separated from one another. b) Molecules of a gas occupy negligible volume. c) Molecules of a gas move with an average speed determined by the temperatu ...
... 4. Which one of the following statements is incorrect for an ideal gas, according to the Kinetic Molecular Theory? a) Molecules of a gas are widely separated from one another. b) Molecules of a gas occupy negligible volume. c) Molecules of a gas move with an average speed determined by the temperatu ...
Mr. Dehne AP Chem Name: ___________ Date: Per#: ___ AP
... hydroxide salt was filtered and heated in a flame, forming cobalt (III) oxide. The mass of cobalt (III) oxide formed was 0.145g. a. What is the percent composition, by mass, of the compound? b. Assuming the compound contains one cobalt atom per formula unit, what is the molecular formula? c. Write b ...
... hydroxide salt was filtered and heated in a flame, forming cobalt (III) oxide. The mass of cobalt (III) oxide formed was 0.145g. a. What is the percent composition, by mass, of the compound? b. Assuming the compound contains one cobalt atom per formula unit, what is the molecular formula? c. Write b ...
Chapter 4 - GEOCITIES.ws
... NaOH(aq) + FeCl3(aq) NaCl(aq) + Fe(OH)3(s) is really Na+(aq)+OH-(aq) + Fe+3 + Cl-(aq) Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + Fe(OH)3(s) So all that really happens is OH-(aq) + Fe+3 Fe(OH)3(s) ...
... NaOH(aq) + FeCl3(aq) NaCl(aq) + Fe(OH)3(s) is really Na+(aq)+OH-(aq) + Fe+3 + Cl-(aq) Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + Fe(OH)3(s) So all that really happens is OH-(aq) + Fe+3 Fe(OH)3(s) ...
Principles of Crystal Chemistry
... 1- The r+/r- limiting values for the different coordination numbers are derived by simple rules of geometry and trigonometry (Figs 4 & 5). 2- If the r+/r- falls very close to one of the limiting values (e.g. 0.414), then the same compound may have two different structures (in this case, one with a C ...
... 1- The r+/r- limiting values for the different coordination numbers are derived by simple rules of geometry and trigonometry (Figs 4 & 5). 2- If the r+/r- falls very close to one of the limiting values (e.g. 0.414), then the same compound may have two different structures (in this case, one with a C ...
Element Approx.
... A Mineral is... •naturally occurring, not synthetic •solid at Earth’s temps. ...
... A Mineral is... •naturally occurring, not synthetic •solid at Earth’s temps. ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.