Minerals
... a mixture in which one substance dissolves in another. When a hot water solution begins to cool, the elements and compounds leave the solution and begin to crystallize as minerals. Pure metals that crystallize underground form veins. A vein is a narrow channel or slab of a mineral that is different ...
... a mixture in which one substance dissolves in another. When a hot water solution begins to cool, the elements and compounds leave the solution and begin to crystallize as minerals. Pure metals that crystallize underground form veins. A vein is a narrow channel or slab of a mineral that is different ...
Part 1 - ISpatula
... Identification of GMO phases Observation of viscosities and optical properties changes upon heating at constant rate (4 C/ min) on a hot stage connected to polarizing microscope. Results: Reversed micellar phase (L2): clear liquid and isotropic. Cubic phase: very viscous gel and isotropic Other pha ...
... Identification of GMO phases Observation of viscosities and optical properties changes upon heating at constant rate (4 C/ min) on a hot stage connected to polarizing microscope. Results: Reversed micellar phase (L2): clear liquid and isotropic. Cubic phase: very viscous gel and isotropic Other pha ...
Chemistry 140
... 2. If the digit removed is less than 5, the preceding number is unchanged : 0.2413 rounds to 0.241 if three significant figures are retained and to 0.24 if two significant figures are retained. 3.If the digit removed is 5, the preceding number increases by 1 if it is odd and remains unchanged if it ...
... 2. If the digit removed is less than 5, the preceding number is unchanged : 0.2413 rounds to 0.241 if three significant figures are retained and to 0.24 if two significant figures are retained. 3.If the digit removed is 5, the preceding number increases by 1 if it is odd and remains unchanged if it ...
Solutions
... quickly increasing with pressure (up to a limit). Pure supercritical carbon dioxide is a relatively nonpolar solvent, but has some limited affinity with polar molecules due to its large molecular quadripole, although modifiers (e.g. methanol, fluorinated hydrocarbons) can be added to improve the sol ...
... quickly increasing with pressure (up to a limit). Pure supercritical carbon dioxide is a relatively nonpolar solvent, but has some limited affinity with polar molecules due to its large molecular quadripole, although modifiers (e.g. methanol, fluorinated hydrocarbons) can be added to improve the sol ...
File
... of the particles in a sample of material. Temperature is not a form of energy. (4.2b) The concepts of kinetic and potential energy can be used to explain physical processes that include: fusion (melting), solidification (freezing), vaporization (boiling, evaporation), condensation, sublimation, and ...
... of the particles in a sample of material. Temperature is not a form of energy. (4.2b) The concepts of kinetic and potential energy can be used to explain physical processes that include: fusion (melting), solidification (freezing), vaporization (boiling, evaporation), condensation, sublimation, and ...
AP Chemistry: Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... The double arrow means that the reaction is significant in both directions. It indicates that there is a balance between the forward and reverse reactions. This balance produces a state of chemical equilibrium. ...
... The double arrow means that the reaction is significant in both directions. It indicates that there is a balance between the forward and reverse reactions. This balance produces a state of chemical equilibrium. ...
YUSO Rocks and Minerals Test 2017
... geologists recognize Specimen A as a different mineral. Give one reason supporting this conjecture. 55) Your coach has probably told you at some point that color is not a very reliable property to identify most minerals by, as the same mineral often comes in different color. These colors are due to ...
... geologists recognize Specimen A as a different mineral. Give one reason supporting this conjecture. 55) Your coach has probably told you at some point that color is not a very reliable property to identify most minerals by, as the same mineral often comes in different color. These colors are due to ...
FELDSPARS, EXSOLUTION, ZONING, and TWINNING
... feldspar species is an important factor in igneous rock classification. Feldspars are also important constituents of many metamorphic rocks and are found in some sedimentary rocks, especially sandstones. Some plagioclase feldspars will have one composition in the interior of the crystal, and a gradu ...
... feldspar species is an important factor in igneous rock classification. Feldspars are also important constituents of many metamorphic rocks and are found in some sedimentary rocks, especially sandstones. Some plagioclase feldspars will have one composition in the interior of the crystal, and a gradu ...
Hierarchically Porous Titania Networks with Controllable
... specific surface areas (up to 71.0 m2 g-1). The photocatalytic performance of the materials was correlated to the anatase:rutile ratio and specific surface area of the materials, with the mixed-phase (rutile content of 15.4%) nanocrystalline titania calcined at 600 °C for 6 h showing the highest pho ...
... specific surface areas (up to 71.0 m2 g-1). The photocatalytic performance of the materials was correlated to the anatase:rutile ratio and specific surface area of the materials, with the mixed-phase (rutile content of 15.4%) nanocrystalline titania calcined at 600 °C for 6 h showing the highest pho ...
Minerals
... In reality, these oxides and elements occur in chemical compounds called minerals which form rocks. We only need a few very simple ideas - later courses will do this in more detail... Most rocks are made up of silicate minerals, primarily Oxygen (O−2 ) and Silicon (Si+4 ). Together these two make up ...
... In reality, these oxides and elements occur in chemical compounds called minerals which form rocks. We only need a few very simple ideas - later courses will do this in more detail... Most rocks are made up of silicate minerals, primarily Oxygen (O−2 ) and Silicon (Si+4 ). Together these two make up ...
Chemical Equilibrium Review Ch 13-14 2015
... I2…the more intense the color, the more I2 in the reaction vessel. When 4.00mol HI was placed in a 5.00L vessel at 458°C, the equilibrium mixture was found to contain 0.442mol I2. What is the value of Kc for the decomposition of HI at this temperature? 4. Phosphorus pentachloride dissociates on heat ...
... I2…the more intense the color, the more I2 in the reaction vessel. When 4.00mol HI was placed in a 5.00L vessel at 458°C, the equilibrium mixture was found to contain 0.442mol I2. What is the value of Kc for the decomposition of HI at this temperature? 4. Phosphorus pentachloride dissociates on heat ...
What Is A Mineral?
... Scale from 1 (softest) to 10 (hardest) Test by seeing if the mineral can scratch different objects ...
... Scale from 1 (softest) to 10 (hardest) Test by seeing if the mineral can scratch different objects ...
the properties and structure of matter
... be observed or measured without changing the identity or composition of the substance • Physical properties used to describe matter can be classified as: 1) Extensive – depends on the amount of matter in the sample - e.g. Mass, volume, length 2) Intensive – depends on the type of matter, not the amo ...
... be observed or measured without changing the identity or composition of the substance • Physical properties used to describe matter can be classified as: 1) Extensive – depends on the amount of matter in the sample - e.g. Mass, volume, length 2) Intensive – depends on the type of matter, not the amo ...
Review #7: Solutions, Acids and Bases 1. Definitions: a) Solution: a
... i) % W / V: a description of the concentration of a solution. Tells the mass of solute per 100 mL of solution. For example, a 5% W/V solution of sugar would contain 5 g of sugar in 100 mL of solution. j) % W / W: a description of the concentration of a solution. Tells the mass of solute per 100 g of ...
... i) % W / V: a description of the concentration of a solution. Tells the mass of solute per 100 mL of solution. For example, a 5% W/V solution of sugar would contain 5 g of sugar in 100 mL of solution. j) % W / W: a description of the concentration of a solution. Tells the mass of solute per 100 g of ...
Preface from the Textbook - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Atomic Orbital and Probable Location of the Electron (l, angular momentum), and spatial orientation (ml, magne ...
... Atomic Orbital and Probable Location of the Electron (l, angular momentum), and spatial orientation (ml, magne ...
A third blind test of crystal structure prediction
... submitted predictions. For brevity, we provide very short descriptions of the methodologies in Table 2. References are provided for most of the methods used and details specific to the work on the CSP2004 molecules are available in the supplementary information.3 Although the techniques vary, all me ...
... submitted predictions. For brevity, we provide very short descriptions of the methodologies in Table 2. References are provided for most of the methods used and details specific to the work on the CSP2004 molecules are available in the supplementary information.3 Although the techniques vary, all me ...
Chapter 7 Review
... a) Write the chemical reaction for the Haber process and write a K equation to describe it. (2) b) Why was this reaction so important when it was developed back in 1909? (2) c) How did Haber manage to keep this reaction moving forward to produce ammonia? (4) ...
... a) Write the chemical reaction for the Haber process and write a K equation to describe it. (2) b) Why was this reaction so important when it was developed back in 1909? (2) c) How did Haber manage to keep this reaction moving forward to produce ammonia? (4) ...
Module 3 -- Lesson 4
... yield. The conditions which produce the highest yield are called the optimum conditions. For example, the optimum conditions for the Haber process are: ...
... yield. The conditions which produce the highest yield are called the optimum conditions. For example, the optimum conditions for the Haber process are: ...
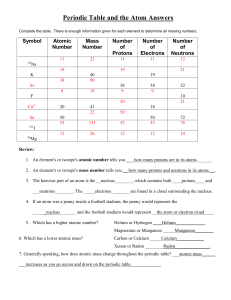
Periodic Table and the Atom Answers
... c) At a smaller volume the atoms will have less room to move around, so they will collide with the sides more often. d) The initial statement is false. Gas pressures do not increase when the volume is decreased. 6) What are the five assumptions we make about an ideal gas? ...
... c) At a smaller volume the atoms will have less room to move around, so they will collide with the sides more often. d) The initial statement is false. Gas pressures do not increase when the volume is decreased. 6) What are the five assumptions we make about an ideal gas? ...
Ch 2 3 Properties of Minerals
... Density is the property of all matter that is the ratio of an object’s mass to its volume Density (d) = mass (m) / Volume (V) Density is usually expressed in g/cm3 in Geology Many common minerals have densities between 2 and 5 g/cm3 The density of a pure mineral is a constant value, and can ...
... Density is the property of all matter that is the ratio of an object’s mass to its volume Density (d) = mass (m) / Volume (V) Density is usually expressed in g/cm3 in Geology Many common minerals have densities between 2 and 5 g/cm3 The density of a pure mineral is a constant value, and can ...
Crystal structure of oxygen-evolving photosystem II at 1.9 Ε
... Mn4Ca-cluster composed of 4 Mn atoms and 1 Ca atom, which cycles through several different Si-states (with i=0-4) upon extraction of each electron by the PSII reaction center (PSII-RC) P6801, 2. When 4 electrons and 4 protons are extracted from 2 molecules of water, 1 molecule of di-oxygen is formed ...
... Mn4Ca-cluster composed of 4 Mn atoms and 1 Ca atom, which cycles through several different Si-states (with i=0-4) upon extraction of each electron by the PSII reaction center (PSII-RC) P6801, 2. When 4 electrons and 4 protons are extracted from 2 molecules of water, 1 molecule of di-oxygen is formed ...
Chapter_4_Minerals
... occurring substance, not manmade. 2) Inorganic – not made of anything that is/was living. 3) Solid and Crystalline in form. ...
... occurring substance, not manmade. 2) Inorganic – not made of anything that is/was living. 3) Solid and Crystalline in form. ...
ppt
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 23, Metamorpic Textures
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
effect of size and temperature on the electric resistance of
... direct proof that the carrier scattering by the sample surface is diffuse, for it is precisely in this case that no difference is observed in the temperature dependence of the resistance in accord with r161, Attention is called to the fact that the curve drawn through the experimental points of[u] c ...
... direct proof that the carrier scattering by the sample surface is diffuse, for it is precisely in this case that no difference is observed in the temperature dependence of the resistance in accord with r161, Attention is called to the fact that the curve drawn through the experimental points of[u] c ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.