xmas review questions 01516 with hints
... 30. A 27.0–gram sample of an unknown hydrocarbon was burned in excess oxygen to form 88.0 grams of carbon dioxide and 27.0 grams of water. What is a possible molecular formula of the hydrocarbon? (A) CH4 (C) C4H3 (E) C4H10 (B) C2H2 (D) C4H6 Did you see the significance of the 88 g CO2 and 27 g H2O? ...
... 30. A 27.0–gram sample of an unknown hydrocarbon was burned in excess oxygen to form 88.0 grams of carbon dioxide and 27.0 grams of water. What is a possible molecular formula of the hydrocarbon? (A) CH4 (C) C4H3 (E) C4H10 (B) C2H2 (D) C4H6 Did you see the significance of the 88 g CO2 and 27 g H2O? ...
The s-Block Elements
... 2. For Group II sulphates, the cations are much smaller than the anions. The changing in size of cations does not cause a significant change in H lattice (proportional to 1/(r+ + r-). However, the changing in size of cations does cause H hydration (proportional to 1/r+ and 1/r-) to become less exo ...
... 2. For Group II sulphates, the cations are much smaller than the anions. The changing in size of cations does not cause a significant change in H lattice (proportional to 1/(r+ + r-). However, the changing in size of cations does cause H hydration (proportional to 1/r+ and 1/r-) to become less exo ...
Chapter 14 Review
... the other samples? a. It will scratch only E. b. It will scratch only F. c. It will scratch only H. d. It will scratch F and H. 4. Which statement accurately describes how one of the samples will affect a magnet? a. E will attract the magnet. b. F will attract the magnet. c. G will be pushed away fr ...
... the other samples? a. It will scratch only E. b. It will scratch only F. c. It will scratch only H. d. It will scratch F and H. 4. Which statement accurately describes how one of the samples will affect a magnet? a. E will attract the magnet. b. F will attract the magnet. c. G will be pushed away fr ...
Mineral Formation - cK-12
... hotter than 1,000o C. Magma cools slowly inside Earth, which gives mineral crystals time to grow large enough to be seen clearly ( Figure 1.1). When magma erupts onto Earth’s surface, it is called lava. Lava cools much more rapidly than magma when it is below the surface. In a cooling lava, mineral ...
... hotter than 1,000o C. Magma cools slowly inside Earth, which gives mineral crystals time to grow large enough to be seen clearly ( Figure 1.1). When magma erupts onto Earth’s surface, it is called lava. Lava cools much more rapidly than magma when it is below the surface. In a cooling lava, mineral ...
Moles - University of Leicester
... 2) Enter the data given into the first two columns 3) Find the relative atomic masses for the elements and enter them in the third column 4) Perform the calculation in the fourth column (i.e. divide the value in column 2 by that in column 1). 5) To determine the test ratio, take the smallest number ...
... 2) Enter the data given into the first two columns 3) Find the relative atomic masses for the elements and enter them in the third column 4) Perform the calculation in the fourth column (i.e. divide the value in column 2 by that in column 1). 5) To determine the test ratio, take the smallest number ...
Unit 8 Student Notes
... constant and can therefore be easily determined from the one measured value. Consider the following example: A sample of GaF3(s) is added to pure water and allowed to come to equilibrium at 25ºC. The concentration of Ga 3+ is 0.049 M at equilibrium. What is the value of K sp for GaF3? Step 1. Write ...
... constant and can therefore be easily determined from the one measured value. Consider the following example: A sample of GaF3(s) is added to pure water and allowed to come to equilibrium at 25ºC. The concentration of Ga 3+ is 0.049 M at equilibrium. What is the value of K sp for GaF3? Step 1. Write ...
Packet 4
... Each element has a symbol, an atomic number and an atomic mass number listed on the periodic table. Some elements have a symbol made up of one letter, others have two. It is important when writing the two letter symbols to ensure that you use a lower case letter for the second letter. This may sound ...
... Each element has a symbol, an atomic number and an atomic mass number listed on the periodic table. Some elements have a symbol made up of one letter, others have two. It is important when writing the two letter symbols to ensure that you use a lower case letter for the second letter. This may sound ...
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
... Heat the filtrate from the above test with 10 mL dil. H2SO4 and using a litmus paper, make sure that the solution is acidic. Add dropwise dilute KMnO4 solution shaking the solution after each addition. Note the colour of the resulting solution. ...
... Heat the filtrate from the above test with 10 mL dil. H2SO4 and using a litmus paper, make sure that the solution is acidic. Add dropwise dilute KMnO4 solution shaking the solution after each addition. Note the colour of the resulting solution. ...
SAMPLE EXAMINATION IV Section I – Multiple Choice
... In Chapter 5, we discussed reactions that go to completion; that is, reactions in which the limiting reactant is consumed and a maximum quantity of product is formed. However, in actual practice, many reaction systems reach a condition in which some quantity of each reactant remains in contact with ...
... In Chapter 5, we discussed reactions that go to completion; that is, reactions in which the limiting reactant is consumed and a maximum quantity of product is formed. However, in actual practice, many reaction systems reach a condition in which some quantity of each reactant remains in contact with ...
Chem 400 Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory
... by pouring this solution down the reflux condenser. Measure out these liquids using a syringe or pipet. Rinse the pyrrole and benzaldehyde down the condenser with 10 mL of propanoic acid. Continue to reflux the solution for 30 minutes, and then remove the heat and let the flask cool for a few minute ...
... by pouring this solution down the reflux condenser. Measure out these liquids using a syringe or pipet. Rinse the pyrrole and benzaldehyde down the condenser with 10 mL of propanoic acid. Continue to reflux the solution for 30 minutes, and then remove the heat and let the flask cool for a few minute ...
Structural studies of protein arginine methyltransferase 2 reveals its
... structures. The alignment is restricted to the catalytic core. The secondary structure of mPRMT2 is drawn above the alignment with color. The SAM-binding domain, the b-barrel domains, and the dimerization arm are colored green, yellow, and blue, respectively. The mPRMT2 residue numbering is shown be ...
... structures. The alignment is restricted to the catalytic core. The secondary structure of mPRMT2 is drawn above the alignment with color. The SAM-binding domain, the b-barrel domains, and the dimerization arm are colored green, yellow, and blue, respectively. The mPRMT2 residue numbering is shown be ...
Crystal Structure of an Enzyme-Substrate Complex Provides Insight
... same conditions as the wild-type, thus minimizing variability, and as the structure was solved by replacement with the wild-type coordinates, differences would be more likely to be downweighted due to model bias than to be artifacts. In fact, the mean Ca deviation between the structures of wildÊ. ty ...
... same conditions as the wild-type, thus minimizing variability, and as the structure was solved by replacement with the wild-type coordinates, differences would be more likely to be downweighted due to model bias than to be artifacts. In fact, the mean Ca deviation between the structures of wildÊ. ty ...
ppt - National Single Crystal X
... (often requiring a disorder model). • Example: An Organometallic-AuCl compound from the CSD with the Cl in the wrong position Very Short C-H..Cl ?! ALERTED by validation (C..Cl = 2.19 Ang) • Moving Cl to the correct position drops R from 4 to 2 % ( see next two slides). ...
... (often requiring a disorder model). • Example: An Organometallic-AuCl compound from the CSD with the Cl in the wrong position Very Short C-H..Cl ?! ALERTED by validation (C..Cl = 2.19 Ang) • Moving Cl to the correct position drops R from 4 to 2 % ( see next two slides). ...
Chapter 8 – Symmetry in Crystal Physics – p. 1
... ml = (∂J l / ∂T ) = (∂S / ∂H l ) . Thus the above set of equations can be simplified significantly: dεij = sijkl dσ kl + d kij dEk + qlij dH l + α ij dT ...
... ml = (∂J l / ∂T ) = (∂S / ∂H l ) . Thus the above set of equations can be simplified significantly: dεij = sijkl dσ kl + d kij dEk + qlij dH l + α ij dT ...
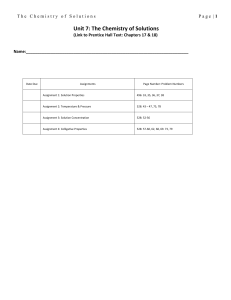
The Chemistry of Solutions Page | 1 Unit 7: The Chemistry of
... the solution is heated to 90°C, how many grams must be added to saturate the solution? _____________ ...
... the solution is heated to 90°C, how many grams must be added to saturate the solution? _____________ ...
Page 1 of 25
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
Full Text PDF
... “isotropic points” and the nature of the high-temperature hexagonal-orthorhombic phase transition. Crystals of rubidium sulfate are poorly studied. It is known that at near-room temperatures a crystal has an “isotropic point” featuring the temperature-and-spectrum dependence of birefringence sign in ...
... “isotropic points” and the nature of the high-temperature hexagonal-orthorhombic phase transition. Crystals of rubidium sulfate are poorly studied. It is known that at near-room temperatures a crystal has an “isotropic point” featuring the temperature-and-spectrum dependence of birefringence sign in ...
Chemistry1100 Practice Exam 4 Choose the best answer for
... Choose the best answer for questions 1-20. You must show your work for all questions to receive credit. Be sure to include units and correct numbers of significant figures. Calculators cannot be shared. pico p 10-12 micro μ 10-6 centi c 10-2 mega M 106 NA = 6.022 x 1023/mol ...
... Choose the best answer for questions 1-20. You must show your work for all questions to receive credit. Be sure to include units and correct numbers of significant figures. Calculators cannot be shared. pico p 10-12 micro μ 10-6 centi c 10-2 mega M 106 NA = 6.022 x 1023/mol ...
Non-Linear Optics Lecture 3: Achieving Phase Matching Learning
... We can see that there’s an angle, θ0 where the ordinary polarised fundamental and the extraordinary polarised second harmonic have the same refractive index. This implies that when the radiation propagates in the crystal at angle θ0 relative to the optical axis, perfect phase ...
... We can see that there’s an angle, θ0 where the ordinary polarised fundamental and the extraordinary polarised second harmonic have the same refractive index. This implies that when the radiation propagates in the crystal at angle θ0 relative to the optical axis, perfect phase ...
Potentiated electron transference in
... importance of this problem and the paucity of quantitative experimental results, the goal of our study is to determine this antimicrobacterial effect. Therefore, both AWO and AWO:Ag samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), FTRaman spectroscopy, ultraviolet−visible (UV−vis) measurements, ...
... importance of this problem and the paucity of quantitative experimental results, the goal of our study is to determine this antimicrobacterial effect. Therefore, both AWO and AWO:Ag samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), FTRaman spectroscopy, ultraviolet−visible (UV−vis) measurements, ...
solid state
... short range order. These solids are isotropic in nature and melt over a range of temperature. Therefore, amorphous solids are sometimes called pseudo solids or super cooled liquids. They do not have definite heat of fusion. When cut with a sharp-edged tool, they cut into two pieces with irregular su ...
... short range order. These solids are isotropic in nature and melt over a range of temperature. Therefore, amorphous solids are sometimes called pseudo solids or super cooled liquids. They do not have definite heat of fusion. When cut with a sharp-edged tool, they cut into two pieces with irregular su ...
2nd Semester final review
... A mixture is created when two or more elements or compounds are combined together but do not form a new substance but retain their original properties. 5. Describe each of the diagrams below as either: A) Element B) Compound C) Mixture of elements D) Mixture of compounds E) Mixture of elements and c ...
... A mixture is created when two or more elements or compounds are combined together but do not form a new substance but retain their original properties. 5. Describe each of the diagrams below as either: A) Element B) Compound C) Mixture of elements D) Mixture of compounds E) Mixture of elements and c ...
CHEMISTRY 101 Name Mock Final Exam Spring 2014 Signature Dr
... a) The most positively charged species has the largest atomic radius, and the most negatively charged species has the smallest atomic radius. b) The noble gas has the largest atomic radius, and the most negatively charged species has the smallest atomic radius. c) The noble gas has the largest atomi ...
... a) The most positively charged species has the largest atomic radius, and the most negatively charged species has the smallest atomic radius. b) The noble gas has the largest atomic radius, and the most negatively charged species has the smallest atomic radius. c) The noble gas has the largest atomi ...
Elements compounds and mixtures
... CHARACTERISTICS OF PURE & IMPURE SUBSTANCES – A pure substance boils at a constant temperature i.e. it has a fix boiling point. An impure liquid could boil higher than the expected boiling point and over a range of temperature. – A pure substance melts quite sharply at the melting point. An impure ...
... CHARACTERISTICS OF PURE & IMPURE SUBSTANCES – A pure substance boils at a constant temperature i.e. it has a fix boiling point. An impure liquid could boil higher than the expected boiling point and over a range of temperature. – A pure substance melts quite sharply at the melting point. An impure ...
File
... (b) On the same diagram indicate the change or changes that result from the addition of the catalyst. Explain the role of the catalyst in changing the rate of the reaction. (c) If the temperature is increased, will the ratio kf/kr increase, remain the same, or decrease? Justify your answer with a on ...
... (b) On the same diagram indicate the change or changes that result from the addition of the catalyst. Explain the role of the catalyst in changing the rate of the reaction. (c) If the temperature is increased, will the ratio kf/kr increase, remain the same, or decrease? Justify your answer with a on ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.