Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Solids 21 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
... as determined by the Knudsen method. The Knudsen cell is often used in combination with a mass spectrometer (Identification of the gaseous species). Knudsen-Effusion: Determination of the mass at room temperature before and after the experiment or in combination with a vacuum microbalance (25 g, 1 m ...
... as determined by the Knudsen method. The Knudsen cell is often used in combination with a mass spectrometer (Identification of the gaseous species). Knudsen-Effusion: Determination of the mass at room temperature before and after the experiment or in combination with a vacuum microbalance (25 g, 1 m ...
CHEM 101 Final (Term 141)
... C) The pressure at the triple point for substance A is higher than that of substance B, but the normal boiling and normal melting point for substance A are lower than those of substance B. D) The pressure at the triple point, normal boiling and normal melting point for substance B and for substance ...
... C) The pressure at the triple point for substance A is higher than that of substance B, but the normal boiling and normal melting point for substance A are lower than those of substance B. D) The pressure at the triple point, normal boiling and normal melting point for substance B and for substance ...
FRACTAL-LIKE SQUARE LATTICES OF AIR HOLES H. T. Hattori
... with most of the holes having a lattice constant of Λ while others are repeated with a lattice constant of 2Λ. We change the radii of these holes and analyze their effects on the bandgap regions and transmission properties. The analysis conducted here is based upon band diagrams and 2D Finite differen ...
... with most of the holes having a lattice constant of Λ while others are repeated with a lattice constant of 2Λ. We change the radii of these holes and analyze their effects on the bandgap regions and transmission properties. The analysis conducted here is based upon band diagrams and 2D Finite differen ...
American-Journal-of-Oil-and-Chemical-Technologies
... on Varian CH7A. Atomic absorption analysis was carried out on a flame atomic absorption spectroscopy, Shimadzu AA 670, Japan. Melting points determined on a Barnstead Electrothermal 9300 apparatus. 1.2. Methods 1.1.2. Synthesis of pyridine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid N-oxide (2,5-H2pydco) Pyridine-2,5-dic ...
... on Varian CH7A. Atomic absorption analysis was carried out on a flame atomic absorption spectroscopy, Shimadzu AA 670, Japan. Melting points determined on a Barnstead Electrothermal 9300 apparatus. 1.2. Methods 1.1.2. Synthesis of pyridine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid N-oxide (2,5-H2pydco) Pyridine-2,5-dic ...
How thin sections of rocks are made
... corner. The irregular black band is a glass-filled fracture. The fracture and hot silicate liquid (now glass) were formed during a meteorite impact of the lunar surface, and the liquid was infected into the fracture. The round things are gas bubbles in the glass. Petrified wood cells: This is Cretac ...
... corner. The irregular black band is a glass-filled fracture. The fracture and hot silicate liquid (now glass) were formed during a meteorite impact of the lunar surface, and the liquid was infected into the fracture. The round things are gas bubbles in the glass. Petrified wood cells: This is Cretac ...
Reaction Systems Engineering II (part 1)
... Kw = exp(–rG° / RT) = exp[–79.851000 / (8.3145298)] = 1.0110–14 mol2 kg–2 2) rG° = rH° – TrS° = 55.8 – 348(–80.7) / 1000 = 83.88 kJ mol–1 Kw = exp(–rG° / RT) = exp[–83.881000 / (8.3145348)] = 2.610–13 mol2 kg–2 ...
... Kw = exp(–rG° / RT) = exp[–79.851000 / (8.3145298)] = 1.0110–14 mol2 kg–2 2) rG° = rH° – TrS° = 55.8 – 348(–80.7) / 1000 = 83.88 kJ mol–1 Kw = exp(–rG° / RT) = exp[–83.881000 / (8.3145348)] = 2.610–13 mol2 kg–2 ...
microanalysis of rare-earth elements using an electron beam
... et al., 2005; Imashuku et al., 2012), electron beam generator (Brownridge et al., 2001; 2005), Xray fluorescence measurement setup (Kawai et al., 2005), neutron generator (Tornow et al., 2008; Gillich et al., 2009), and mass spectrometer setup (Neidholdt et al., 2007). We also used the pyroelectric ...
... et al., 2005; Imashuku et al., 2012), electron beam generator (Brownridge et al., 2001; 2005), Xray fluorescence measurement setup (Kawai et al., 2005), neutron generator (Tornow et al., 2008; Gillich et al., 2009), and mass spectrometer setup (Neidholdt et al., 2007). We also used the pyroelectric ...
Chemistry Log Books - Social Circle City Schools
... 3. If one liquid is soluble in another liquid, such as food coloring in water, the two liquids are considered ________________. 4. If one liquid is insoluble in another, such as oil in water, the two liquids are _____________. 5. Discuss the two processes that occur during solution formation. ...
... 3. If one liquid is soluble in another liquid, such as food coloring in water, the two liquids are considered ________________. 4. If one liquid is insoluble in another, such as oil in water, the two liquids are _____________. 5. Discuss the two processes that occur during solution formation. ...
Exam Review_Key_All Topics.082
... 1. Provide an example for each of the following solution types a) ...
... 1. Provide an example for each of the following solution types a) ...
Answers - Scioly.org
... 20. The student concludes that she has synthesized ethyl butanoate. Use evidence from the two experiments to support or to refute her claim. The peak of highest mass to charge ratio is approximately 116; therefore, the unknown molecule would have a molecular mass of 116. Ethyl butanoate has the chem ...
... 20. The student concludes that she has synthesized ethyl butanoate. Use evidence from the two experiments to support or to refute her claim. The peak of highest mass to charge ratio is approximately 116; therefore, the unknown molecule would have a molecular mass of 116. Ethyl butanoate has the chem ...
Final Exam Practice Problems: R = 0.0821 Latm/molK NA = 6.022
... 3. Which of the following are examples of a chemical change? A) coffee brewing B) water boiling C) leaves turning color in the fall D) salt dissolves in water E) None of the above are chemical changes. 4. A student performs an experiment to determine the density of a sugar solution. She obtains the ...
... 3. Which of the following are examples of a chemical change? A) coffee brewing B) water boiling C) leaves turning color in the fall D) salt dissolves in water E) None of the above are chemical changes. 4. A student performs an experiment to determine the density of a sugar solution. She obtains the ...
solid state - einstein classes
... characteristic of metals is their lustre and colour in certain cases. This is also due to the presence of free electrons in them. Metals are highly malleable and ductile. Q. Write a short note about covalent or network solids with examples. Solution : Crystalline solids of non-metals result from the ...
... characteristic of metals is their lustre and colour in certain cases. This is also due to the presence of free electrons in them. Metals are highly malleable and ductile. Q. Write a short note about covalent or network solids with examples. Solution : Crystalline solids of non-metals result from the ...
Recrystallisation Benzoic Acid Determination Melting Point
... (C 6 H 5COOH). A molecular crystal rather than an ionic crystal, shown by its low melting point of 122 °C, benzoic acid is used as an antimicrobial agent and is found in toothpastes, mouthwashes, cosmetics and deodorants. Impure benzoic acid contains the impurities phthalic acid and benzylbenzoate. ...
... (C 6 H 5COOH). A molecular crystal rather than an ionic crystal, shown by its low melting point of 122 °C, benzoic acid is used as an antimicrobial agent and is found in toothpastes, mouthwashes, cosmetics and deodorants. Impure benzoic acid contains the impurities phthalic acid and benzylbenzoate. ...
Mineral:
... • “Non Example”: Coal – it is organic because it comes from plants that lived millions of years ago. ...
... • “Non Example”: Coal – it is organic because it comes from plants that lived millions of years ago. ...
Calculating Enthalpy Changes
... Definition of free energy of formation The standard Gibbs free energy of formation of a compound is the change of Gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of that substance from its component elements, at their standard states. The standard state is defined as the most stable form ...
... Definition of free energy of formation The standard Gibbs free energy of formation of a compound is the change of Gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of that substance from its component elements, at their standard states. The standard state is defined as the most stable form ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... (energy necessary for reactants to become products), therefore helping the reaction reach a state of equilibrium sooner – the addition of a catalyst does NOT change the equilibrium constant. 7. What does it mean when an equilibrium system is described as a dynamic system? Explain. Dynamic is a term ...
... (energy necessary for reactants to become products), therefore helping the reaction reach a state of equilibrium sooner – the addition of a catalyst does NOT change the equilibrium constant. 7. What does it mean when an equilibrium system is described as a dynamic system? Explain. Dynamic is a term ...
sheet-key - Scioly.org
... *Explain colors: substitution in the crystal lattice of trace amounts of different elements (usually transition metals) causes the different colors – changes the energies of the electromagnetic fields inside the crystal lattice so different energies in the electron transitions when interacting with ...
... *Explain colors: substitution in the crystal lattice of trace amounts of different elements (usually transition metals) causes the different colors – changes the energies of the electromagnetic fields inside the crystal lattice so different energies in the electron transitions when interacting with ...
Defect Density Waves and Specific Manifestations of the Memory
... of the lattice constants remained unchanged. We suggest that the increase in the transition temperature between the normal and incommensurate phases only seems to be a manifestation of the phase-correlated pinning of phase fluctuations by the defect density wave. The incommensurate phase fluctuation ...
... of the lattice constants remained unchanged. We suggest that the increase in the transition temperature between the normal and incommensurate phases only seems to be a manifestation of the phase-correlated pinning of phase fluctuations by the defect density wave. The incommensurate phase fluctuation ...
1-Three states of matter . A: density, volume and weight B: solid
... Non-polar molecular crystals are very soft and are soluble in non-polar solvents. Non-polar molecular crystals are formed from symmetrical molecules with covalent bonds between atoms with small electronegativity differences. ...
... Non-polar molecular crystals are very soft and are soluble in non-polar solvents. Non-polar molecular crystals are formed from symmetrical molecules with covalent bonds between atoms with small electronegativity differences. ...
Test - Angelfire
... and trigonometric functions and may also include graphing functions. Computers, calculators with a QWERTY keyboard, and electronic writing pads will not be allowed. Students must not bring any external support devices such as manuals, printed or electronic cards, printers, memory expansion chips, or ...
... and trigonometric functions and may also include graphing functions. Computers, calculators with a QWERTY keyboard, and electronic writing pads will not be allowed. Students must not bring any external support devices such as manuals, printed or electronic cards, printers, memory expansion chips, or ...
interior structure of the earth
... in magma are silicon and oxygen. The oxide SiO2, silica, is the most abundant oxide in magma. VISCOSITY The term viscosity describes a fluid’s resistance to flow, or its internal friction. Lava becomes more viscous as it cools. The amount of silica in lava also affects viscosity. Lava that is low in ...
... in magma are silicon and oxygen. The oxide SiO2, silica, is the most abundant oxide in magma. VISCOSITY The term viscosity describes a fluid’s resistance to flow, or its internal friction. Lava becomes more viscous as it cools. The amount of silica in lava also affects viscosity. Lava that is low in ...
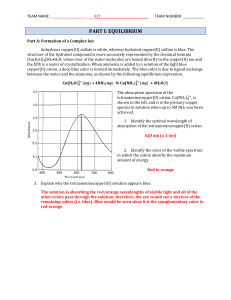
pH scale. Buffer solutions. Colligative properties of solutions
... R – universal gas constant, M1 – molar mass of the solvent, ΔH°vap – enthalpy change of vaporization of the pure solvent. ...
... R – universal gas constant, M1 – molar mass of the solvent, ΔH°vap – enthalpy change of vaporization of the pure solvent. ...
MP 2 workbook 2016
... us—rocks, houses, water, air, people, ants, trees, etc. All matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, or a gas. Matter includes all the things we can weigh (to find the mass) and measure to find the volume (because they take up space). The properties of matter can be divided into two categories: physic ...
... us—rocks, houses, water, air, people, ants, trees, etc. All matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, or a gas. Matter includes all the things we can weigh (to find the mass) and measure to find the volume (because they take up space). The properties of matter can be divided into two categories: physic ...
What Is A Mineral?
... The compositions of some minerals vary because of ionic substitution, whereby one ion in a crystal structure can be replaced by another ion having a like electrical charge and a like ionic radius. ...
... The compositions of some minerals vary because of ionic substitution, whereby one ion in a crystal structure can be replaced by another ion having a like electrical charge and a like ionic radius. ...
FM 10-67-2 Chapter 7
... Indicators are dyes that change color or shade of color when the pH (degree of acidity or alkalinity) of a solution changes. Therefore, they can be used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions in solutions of acids and bases. They are also used in volumetric analysis to mark the end point of ...
... Indicators are dyes that change color or shade of color when the pH (degree of acidity or alkalinity) of a solution changes. Therefore, they can be used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions in solutions of acids and bases. They are also used in volumetric analysis to mark the end point of ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.