Chemical Equations
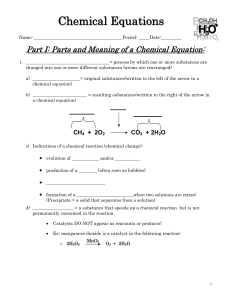
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
AP Thermodynamics ppt.
... • Chemical systems in equilibrium are reversible. • In any spontaneous process, the path between reactants and products is irreversible. • Thermodynamics gives us the direction of a process but it cannot predict the speed at which the process will occur. Prentice Hall © 2003 ...
... • Chemical systems in equilibrium are reversible. • In any spontaneous process, the path between reactants and products is irreversible. • Thermodynamics gives us the direction of a process but it cannot predict the speed at which the process will occur. Prentice Hall © 2003 ...
Examination - SCSA - School Curriculum and Standards Authority
... pH of the solutions at 25.0 °C mass of the solute used to form each solution conductivity of the solutions at 25.0 °C and standard atmospheric pressure number of moles of hydrochloric acid needed for neutralisation ...
... pH of the solutions at 25.0 °C mass of the solute used to form each solution conductivity of the solutions at 25.0 °C and standard atmospheric pressure number of moles of hydrochloric acid needed for neutralisation ...
Chapter 4: Oxidation and Reduction MH5 4
... Unit 3 Oxidation and Reduction Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin 1 Introduction Another important type of reaction in aqueous solution involves the transfer of electrons between two species. This is called an oxidation-reduction or a redox reaction. What happens when zinc pellets are added to an acid? The ...
... Unit 3 Oxidation and Reduction Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin 1 Introduction Another important type of reaction in aqueous solution involves the transfer of electrons between two species. This is called an oxidation-reduction or a redox reaction. What happens when zinc pellets are added to an acid? The ...
Chemical Thermodynamics - Winona State University
... the synthesis of ammonia at 298 K. [ΔHorxn = -92.38 kJ/mol] Srxn = -198.7 J mol-1 K-1 . Calculate the Gibbs Free Energy change for the reaction. Answer for Suniv ...
... the synthesis of ammonia at 298 K. [ΔHorxn = -92.38 kJ/mol] Srxn = -198.7 J mol-1 K-1 . Calculate the Gibbs Free Energy change for the reaction. Answer for Suniv ...
CHEM 1211 and CHEM 1212 National ACS Exams About the Exam
... There is an emphasis on conceptual questions. The actual exam will be multiple choice. The below questions are guaranteed not to be on the exam. Atomic Structure 1. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in each of the following? ...
... There is an emphasis on conceptual questions. The actual exam will be multiple choice. The below questions are guaranteed not to be on the exam. Atomic Structure 1. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in each of the following? ...
The mole concept Since Compounds are formed
... As the product only contains oxygen and magnesium any gain in mass must be due to oxygen chemically bound in the compound. 350.1 mg – 211.5 mg = 138.6 mg of oxygen in the product. To get to the stoichiometric ratio of the two elements and express an empirical formula we need to convert mass to moles ...
... As the product only contains oxygen and magnesium any gain in mass must be due to oxygen chemically bound in the compound. 350.1 mg – 211.5 mg = 138.6 mg of oxygen in the product. To get to the stoichiometric ratio of the two elements and express an empirical formula we need to convert mass to moles ...
James W. Whittaker - Oxygen reactions of the copper oxidases
... oxygen is formally reduced by two electrons, being bound as peroxide during transport. In each case, the reduced oxygen species remains tightly bound to the protein and is unavailable for other reactions. In addition to these oxygen carriers, there is a wide variety of enzymes that metabolize O2. En ...
... oxygen is formally reduced by two electrons, being bound as peroxide during transport. In each case, the reduced oxygen species remains tightly bound to the protein and is unavailable for other reactions. In addition to these oxygen carriers, there is a wide variety of enzymes that metabolize O2. En ...
1. Potentiometric determination of the dissociation constant of week
... consists of a single phase, or we may say the solution is a one-phase system. The components which constitutes the largest proportion of the solution is called the solvent, while the other, the dissolved substance, is referred to as the solute. A solution may be gaseous, liquid or solid. This treatm ...
... consists of a single phase, or we may say the solution is a one-phase system. The components which constitutes the largest proportion of the solution is called the solvent, while the other, the dissolved substance, is referred to as the solute. A solution may be gaseous, liquid or solid. This treatm ...
Option A Materials - Cambridge Resources for the IB Diploma
... Because aluminium is more reactive than carbon, aluminium oxide cannot be reduced to aluminium by heating with carbon and electrolysis must be used. Alumina (aluminium oxide) is an ionic solid made up of Al3+ and O2− ions. In order to conduct electricity, the ions must be free to move. This requires ...
... Because aluminium is more reactive than carbon, aluminium oxide cannot be reduced to aluminium by heating with carbon and electrolysis must be used. Alumina (aluminium oxide) is an ionic solid made up of Al3+ and O2− ions. In order to conduct electricity, the ions must be free to move. This requires ...
Review Answers - cloudfront.net
... If the volume of the combustion container is 10.0 liters, calculate the final pressure in the container when the temperature is changed to 110. °C. (Assume no oxygen remains unreacted and that all products are gaseous.) Here I will use PV=nRT. The trick will be finding the moles of gaseous product. ...
... If the volume of the combustion container is 10.0 liters, calculate the final pressure in the container when the temperature is changed to 110. °C. (Assume no oxygen remains unreacted and that all products are gaseous.) Here I will use PV=nRT. The trick will be finding the moles of gaseous product. ...
Electro-Kinetics
... number of Cu2+ is 0.4 and that of SO42- = 0.6. • t+ + t- = 0.4 + 0.6 = 1 • Since the migration current depends on the ionic strength of the solution it is usually eliminated by addition of excess of an inert supporting electrolyte (100 – 1000 fold excess in concentration) • The current is carried by ...
... number of Cu2+ is 0.4 and that of SO42- = 0.6. • t+ + t- = 0.4 + 0.6 = 1 • Since the migration current depends on the ionic strength of the solution it is usually eliminated by addition of excess of an inert supporting electrolyte (100 – 1000 fold excess in concentration) • The current is carried by ...
Chapter 7: Recent advances in enzyme technology
... Enzymic reactions in biphasic liquid systems It would often be useful if enzyme catalysed reactions could be performed in solvents other than water, as this is not the ideal medium for the majority of organic reactions. Many reactants (e.g. molecular oxygen, steroids and lipids) are more soluble in ...
... Enzymic reactions in biphasic liquid systems It would often be useful if enzyme catalysed reactions could be performed in solvents other than water, as this is not the ideal medium for the majority of organic reactions. Many reactants (e.g. molecular oxygen, steroids and lipids) are more soluble in ...
N5 Chemistry Course Specification 2017-18 session
... Given a balanced equation for the reaction occurring in any titration: the concentration of one reactant can be calculated given the concentration of the other reactant and the volumes of both solutions the volume of one reactant can be calculated given the volume of the other reactant and the c ...
... Given a balanced equation for the reaction occurring in any titration: the concentration of one reactant can be calculated given the concentration of the other reactant and the volumes of both solutions the volume of one reactant can be calculated given the volume of the other reactant and the c ...
chapter 13 solubility.notebook
... Heat of Hydration: enthalpy changes for separating water molecules ( H solvent ) and mixing with solute ( H mix ) ...
... Heat of Hydration: enthalpy changes for separating water molecules ( H solvent ) and mixing with solute ( H mix ) ...
C1 – Topic 2 notes - ARK Elvin Academy
... Word equation: Calcium oxide + water calcium hydroxide Chemical equation: CaO (s) + H2O (l) Ca(OH)2 (s) In this reaction calcium oxide dissolves in water to form calcium hydroxide – a crumbly, white solid... o Heat is given off o Fizzing o Steam is produced When more water is added, calcium hydr ...
... Word equation: Calcium oxide + water calcium hydroxide Chemical equation: CaO (s) + H2O (l) Ca(OH)2 (s) In this reaction calcium oxide dissolves in water to form calcium hydroxide – a crumbly, white solid... o Heat is given off o Fizzing o Steam is produced When more water is added, calcium hydr ...
Seebeck and Peltier coefficients of hydrogen electrodes
... Gibbs free energy, and then the entropy change of different solutions in a concentration cell to the corresponding measured amount of the electrical potential produced [1]. The thermodynamic and kinetic parameters of electrochemical reactions can thus be obtained by simultaneous measurements and ana ...
... Gibbs free energy, and then the entropy change of different solutions in a concentration cell to the corresponding measured amount of the electrical potential produced [1]. The thermodynamic and kinetic parameters of electrochemical reactions can thus be obtained by simultaneous measurements and ana ...
Topic 2 notes - WordPress.com
... Word equation: Calcium oxide + water calcium hydroxide Chemical equation: CaO (s) + H2O (l) Ca(OH)2 (s) In this reaction calcium oxide dissolves in water to form calcium hydroxide – a crumbly, white solid... o Heat is given off o Fizzing o Steam is produced When more water is added, calcium hydr ...
... Word equation: Calcium oxide + water calcium hydroxide Chemical equation: CaO (s) + H2O (l) Ca(OH)2 (s) In this reaction calcium oxide dissolves in water to form calcium hydroxide – a crumbly, white solid... o Heat is given off o Fizzing o Steam is produced When more water is added, calcium hydr ...
Electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen gas (H2) due to an electric current being passed through the water.This technique can be used to make hydrogen fuel (hydrogen gas) and breathable oxygen; though currently most industrial methods make hydrogen fuel from natural gas instead.























