Exam 980415 - NTOU-Chem
... 3) Which of the following describes what happens to the solubility of a slightly soluble ionic compound when a common ion is added to the solution? A) More of the ionic compound dissolves. B) The solubility of the ionic compound is increased. C) There is no effect on the solubility of the ionic comp ...
... 3) Which of the following describes what happens to the solubility of a slightly soluble ionic compound when a common ion is added to the solution? A) More of the ionic compound dissolves. B) The solubility of the ionic compound is increased. C) There is no effect on the solubility of the ionic comp ...
Complete Solution Manual
... a. Cathode: The electrode at which reduction occurs. b. Anode: The electrode at which oxidation occurs. c. Oxidation half-reaction: The half-reaction in which electrons are products. In a galvanic cell, the oxidation half-reaction always occurs at the anode. d. Reduction half-reaction: The half-reac ...
... a. Cathode: The electrode at which reduction occurs. b. Anode: The electrode at which oxidation occurs. c. Oxidation half-reaction: The half-reaction in which electrons are products. In a galvanic cell, the oxidation half-reaction always occurs at the anode. d. Reduction half-reaction: The half-reac ...
General and Inorganic Chemistry
... 5.4.1. III.5.4.1 Experimental task: Fractional distillation of a methanol-water mixture ...
... 5.4.1. III.5.4.1 Experimental task: Fractional distillation of a methanol-water mixture ...
mass mass calc
... a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas that will actually be needed to react with all of the carbon available. (So, use the number of moles of carbon available as the “known” and the number of m ...
... a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas that will actually be needed to react with all of the carbon available. (So, use the number of moles of carbon available as the “known” and the number of m ...
15.0 EquilibriumIHS2014
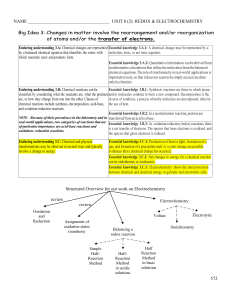
... • At A, the concentration (or pressure) of every chemical in the system is decreased by increasing the container volume. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left (the side with more moles of gas) • At B, the temperature is increased. Then the equilibrium shifts to left. • At C, C2H6(g) is added to th ...
... • At A, the concentration (or pressure) of every chemical in the system is decreased by increasing the container volume. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left (the side with more moles of gas) • At B, the temperature is increased. Then the equilibrium shifts to left. • At C, C2H6(g) is added to th ...
Complete Solution Manual
... a. Cathode: The electrode at which reduction occurs. b. Anode: The electrode at which oxidation occurs. c. Oxidation half-reaction: The half-reaction in which electrons are products. In a galvanic cell, the oxidation half-reaction always occurs at the anode. d. Reduction half-reaction: The half-reac ...
... a. Cathode: The electrode at which reduction occurs. b. Anode: The electrode at which oxidation occurs. c. Oxidation half-reaction: The half-reaction in which electrons are products. In a galvanic cell, the oxidation half-reaction always occurs at the anode. d. Reduction half-reaction: The half-reac ...
LECTURE_pptnotes Fipps Stochiometry
... C5H10O2 (5x12) + (10x1) + (2x16) = 102 g/mol Empirical mass = molecular mass, so molecular formula is the same C5H10O2 ...
... C5H10O2 (5x12) + (10x1) + (2x16) = 102 g/mol Empirical mass = molecular mass, so molecular formula is the same C5H10O2 ...
SYLLABUS 5070 Cambridge O Level Chemistry
... This syllabus is available to private candidates. However, it is expected that private candidates learn in an environment where practical work is an integral part of the course. Candidates will not be able to perform well in this assessment or progress successfully to further study without this nece ...
... This syllabus is available to private candidates. However, it is expected that private candidates learn in an environment where practical work is an integral part of the course. Candidates will not be able to perform well in this assessment or progress successfully to further study without this nece ...
Solubility Equilibria
... The pH. It is another example of applying Le Chatelier’s principle in solubility reactions. o Dissolution of ionic compounds containing OH ions are directly affected by the pH of the solution they are dissolved in. Increasing the pH by adding OH ...
... The pH. It is another example of applying Le Chatelier’s principle in solubility reactions. o Dissolution of ionic compounds containing OH ions are directly affected by the pH of the solution they are dissolved in. Increasing the pH by adding OH ...
chemistry sp.indd
... (c) On the structure of X below identify the functional group level of each of the carbons indicated by an arrow. [Assume R is alkyl.] ...
... (c) On the structure of X below identify the functional group level of each of the carbons indicated by an arrow. [Assume R is alkyl.] ...
analytical chemistry - Львівський національний медичний
... selection of reaction conditions. By changing these conditions, we can increase or decrease the yield of product. We might change the yield by: 1. Changing concentrations by removing products or adding reactants to the reaction vessel. 2. Changing the partial pressure of gaseous reactants and produc ...
... selection of reaction conditions. By changing these conditions, we can increase or decrease the yield of product. We might change the yield by: 1. Changing concentrations by removing products or adding reactants to the reaction vessel. 2. Changing the partial pressure of gaseous reactants and produc ...
In_Class_Practice Chapter 17 PreAP
... A chemist studying the equilibrium N2O4(g) 2NO2(g) controls the temperature so that Keq = 0.028. At one equilibrium position, the concentration of N2O4 is 1.5 times greater than the concentration of NO2. Find the concentrations of the two gases in mol/L. (Hint: Let x = [NO2] and 1.5x = [N2O4] in t ...
... A chemist studying the equilibrium N2O4(g) 2NO2(g) controls the temperature so that Keq = 0.028. At one equilibrium position, the concentration of N2O4 is 1.5 times greater than the concentration of NO2. Find the concentrations of the two gases in mol/L. (Hint: Let x = [NO2] and 1.5x = [N2O4] in t ...
Factors Controlling the Redox Activity of Oxygen in Perovskites
... The physical properties of oxygen vacancies, such as their density, in crystal structure, enthalpy of formation, diffusion kinetics or else playing an important role in catalytic reactions, has been extensively studied and for which the use of high temperature provides the energy to drive their form ...
... The physical properties of oxygen vacancies, such as their density, in crystal structure, enthalpy of formation, diffusion kinetics or else playing an important role in catalytic reactions, has been extensively studied and for which the use of high temperature provides the energy to drive their form ...
Physiological and phylogenetic studies of thermophilic
... The present study is based on two earlier projects. One, supervised by Ólafur Friðjónsson at Prokaria ehf, was based on the study of three mesophilic hydrogen oxidizing (HOX) bacteria, Wautersia eutropha, Hydrogenomonas pseudoflava and Acidovorax facilis. This research emphasised on genetic engineer ...
... The present study is based on two earlier projects. One, supervised by Ólafur Friðjónsson at Prokaria ehf, was based on the study of three mesophilic hydrogen oxidizing (HOX) bacteria, Wautersia eutropha, Hydrogenomonas pseudoflava and Acidovorax facilis. This research emphasised on genetic engineer ...
Chapter 9 Review, pages 628–633
... 25. (a) Separate the equation H2O(l) + Au3+(aq) → O2(g) + Au(s) into two half-reactions. H2O(l) → O2(g) (oxidation) Au3+(aq) → Au(s) (reduction) For the oxidation half-reaction, first balance oxygen. 2 H2O(l) → O2(g) Balance hydrogen by adding hydrogen ions. 2 H2O(l) → O2(g) + 4 H+(aq) Balance the c ...
... 25. (a) Separate the equation H2O(l) + Au3+(aq) → O2(g) + Au(s) into two half-reactions. H2O(l) → O2(g) (oxidation) Au3+(aq) → Au(s) (reduction) For the oxidation half-reaction, first balance oxygen. 2 H2O(l) → O2(g) Balance hydrogen by adding hydrogen ions. 2 H2O(l) → O2(g) + 4 H+(aq) Balance the c ...
5 organic chemistry: functional groups
... The longest chain contains the OOH group, which means the compound is named as a derivative of octane. Because it is an alcohol, it would be tempting to name it as an octanol. But it contains a CPC double bond, which means it must be an octenol. We now have to indicate that the OOH group is on one e ...
... The longest chain contains the OOH group, which means the compound is named as a derivative of octane. Because it is an alcohol, it would be tempting to name it as an octanol. But it contains a CPC double bond, which means it must be an octenol. We now have to indicate that the OOH group is on one e ...
chapter - Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie
... DCN/HCN= 1.6 × 10−5 . As another important example, water would have HDO/H2 O=2 × AD = 3.2 × 10−5 . Similarly, a species with two hydrogens will have a relative abundance of molecules with two D-atoms proportional to A2D (e.g., D2 O/H2 O= 2.6 × 10−10 ) and so on. In practice, if there were no deuter ...
... DCN/HCN= 1.6 × 10−5 . As another important example, water would have HDO/H2 O=2 × AD = 3.2 × 10−5 . Similarly, a species with two hydrogens will have a relative abundance of molecules with two D-atoms proportional to A2D (e.g., D2 O/H2 O= 2.6 × 10−10 ) and so on. In practice, if there were no deuter ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... Analyze: We are given four equations and asked to predict the sign of ΔS for each chemical reaction. Plan: The sign of ΔS will be positive if there is an increase in temperature, an increase in the volume in which the molecules move, or an increase in the number of gas particles in the reaction. The ...
... Analyze: We are given four equations and asked to predict the sign of ΔS for each chemical reaction. Plan: The sign of ΔS will be positive if there is an increase in temperature, an increase in the volume in which the molecules move, or an increase in the number of gas particles in the reaction. The ...
3.Redox
... the solution, (b) the Molarity of the solution. 10. Suppose a 8.75 M aqueous CH3OH solution has a density of 0.789 g / mL. Calculate the mole fraction of CH3OH in the solution.. 11. A solution prepared by dissolving 6.0 g of NaCl in enough water to give 500 mL of solution has a density of 1.05 g / m ...
... the solution, (b) the Molarity of the solution. 10. Suppose a 8.75 M aqueous CH3OH solution has a density of 0.789 g / mL. Calculate the mole fraction of CH3OH in the solution.. 11. A solution prepared by dissolving 6.0 g of NaCl in enough water to give 500 mL of solution has a density of 1.05 g / m ...
Electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen gas (H2) due to an electric current being passed through the water.This technique can be used to make hydrogen fuel (hydrogen gas) and breathable oxygen; though currently most industrial methods make hydrogen fuel from natural gas instead.