The Process of Chemical Reactions
... than is consumed in the breaking of old bonds, a reaction will be endergonic and will absorb energy overall as it takes place. If this energy comes from the motion (kinetic energy) of the reactants, the particles in the system will be moving more slowly after the reaction than before. The system wil ...
... than is consumed in the breaking of old bonds, a reaction will be endergonic and will absorb energy overall as it takes place. If this energy comes from the motion (kinetic energy) of the reactants, the particles in the system will be moving more slowly after the reaction than before. The system wil ...
Moles Class Packet Unit 2
... A compound is a substance composed of two or more different elements that are chemically combined in a fixed proportion. A chemical compound can be broken down by chemical means. A chemical compound can be represented by a specific chemical formula and assigned a name based on the IUPAC system. (3.1 ...
... A compound is a substance composed of two or more different elements that are chemically combined in a fixed proportion. A chemical compound can be broken down by chemical means. A chemical compound can be represented by a specific chemical formula and assigned a name based on the IUPAC system. (3.1 ...
Periodic table, elements and physical chemistry
... (a) The student wants to prepare a standard solution of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid that has a pH of 2.19. Plan how the student could prepare 250 cm3 of this standard solution from solid 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. In your answer you should provide detail of the practical procedure that would be carried ou ...
... (a) The student wants to prepare a standard solution of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid that has a pH of 2.19. Plan how the student could prepare 250 cm3 of this standard solution from solid 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. In your answer you should provide detail of the practical procedure that would be carried ou ...
Unit- 5.pmd
... adsorption, i.e., ∆S is negative. Adsorption is thus accompanied by decrease in enthalpy as well as decrease in entropy of the system. For a process to be spontaneous, the thermodynamic requirement is that, at constant temperature and pressure, ∆G must be negative, i.e., there is a decrease in Gibbs ...
... adsorption, i.e., ∆S is negative. Adsorption is thus accompanied by decrease in enthalpy as well as decrease in entropy of the system. For a process to be spontaneous, the thermodynamic requirement is that, at constant temperature and pressure, ∆G must be negative, i.e., there is a decrease in Gibbs ...
1 Chemistry HP Unit 5 – Stoichiometry Learning Targets (Your exam
... Now you try. Practice Problem 28: A compound is composed of 53.30% carbon 11.19% hydrogen and 35.51% oxygen by mass. Calculate the empirical formula of the compound. If its molar mass is 90.12 g/mol, what is the molecular formula for the compound? ...
... Now you try. Practice Problem 28: A compound is composed of 53.30% carbon 11.19% hydrogen and 35.51% oxygen by mass. Calculate the empirical formula of the compound. If its molar mass is 90.12 g/mol, what is the molecular formula for the compound? ...
CLUE - virtual laboratories
... combination that leads to the widespread public misunderstanding of chemical principles. How many times do we hear about “natural remedies, without drugs or chemicals,” despite the fact that everything is composed of chemicals and the most toxic chemicals known are natural products.2 A growing body ...
... combination that leads to the widespread public misunderstanding of chemical principles. How many times do we hear about “natural remedies, without drugs or chemicals,” despite the fact that everything is composed of chemicals and the most toxic chemicals known are natural products.2 A growing body ...
2 CHEMICAL ARITHMATICS W MODULE - 1
... We have just seen that if we know the formula of a compound we can calculate the percentage composition. Now the question arises, can we determine the formula of the compound if we know the percentage composition of a compound. The answer will be ‘yes’, but this formula will not be molecular formula ...
... We have just seen that if we know the formula of a compound we can calculate the percentage composition. Now the question arises, can we determine the formula of the compound if we know the percentage composition of a compound. The answer will be ‘yes’, but this formula will not be molecular formula ...
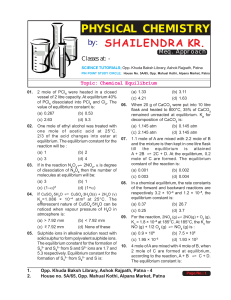
Chemical Equilibrium - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... 2B (g) + 3C (g). If the concentration of C at equilibrium is increased by a factor 2, it will cause the equilibrium concentration of B to change to: (a) two times of its original value (b) one half of its original value (c) 2√2 times of its original value (d) 1/2√2 times of its original value ...
... 2B (g) + 3C (g). If the concentration of C at equilibrium is increased by a factor 2, it will cause the equilibrium concentration of B to change to: (a) two times of its original value (b) one half of its original value (c) 2√2 times of its original value (d) 1/2√2 times of its original value ...
PDF File
... ~ tenfold faster than that for the substrate with a 2′-fluoro group at U(–1), despite the weaker electron-withdrawing ability of 2′-OH than 2′-F [2]. As a 2′-fluoro group contains lone-pair electrons that can accept hydrogen bonds but cannot donate hydrogen bonds, the higher reactivity of the substr ...
... ~ tenfold faster than that for the substrate with a 2′-fluoro group at U(–1), despite the weaker electron-withdrawing ability of 2′-OH than 2′-F [2]. As a 2′-fluoro group contains lone-pair electrons that can accept hydrogen bonds but cannot donate hydrogen bonds, the higher reactivity of the substr ...
1 - A-Level Chemistry
... there is no change in the number of moles (of gases) Can only score these marks if the equation in (e) has equal number of moles on each side Numbers, if stated must match equation ...
... there is no change in the number of moles (of gases) Can only score these marks if the equation in (e) has equal number of moles on each side Numbers, if stated must match equation ...
2014 International Practice Exam: Chemistry
... these specific multiple-choice questions at any time in any form with anyone, including your teacher and other students. If you disclose these questions through any means, your AP Exam score will be canceled. Are there any questions? . . . You must complete the answer sheet using a No. 2 pencil only ...
... these specific multiple-choice questions at any time in any form with anyone, including your teacher and other students. If you disclose these questions through any means, your AP Exam score will be canceled. Are there any questions? . . . You must complete the answer sheet using a No. 2 pencil only ...
AS Support Pack Module 2 Developing Fuels
... energy transferred = mass of solution × specific heat capacity × temperature change Assume that the mass of solution is 25 g and that the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.18 J g−1 K−1. Ignore the energy transferred to the zinc and to the polystyrene cup. Because the zinc was in excess, you ...
... energy transferred = mass of solution × specific heat capacity × temperature change Assume that the mass of solution is 25 g and that the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.18 J g−1 K−1. Ignore the energy transferred to the zinc and to the polystyrene cup. Because the zinc was in excess, you ...
chapter 3 Questions
... 54. Each copper(II) sulfate unit is associated with five water molecules in crystalline copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O). When this compound is heated in air above 100° C, it loses the water molecules and also its blue color: CuSO4.5H2O CuSO4 + 5H2O If 9.60 g of CuSO4 are left after he ...
... 54. Each copper(II) sulfate unit is associated with five water molecules in crystalline copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O). When this compound is heated in air above 100° C, it loses the water molecules and also its blue color: CuSO4.5H2O CuSO4 + 5H2O If 9.60 g of CuSO4 are left after he ...
study material(2014-15) class xii-chemistry
... Reviewed Support Materials of the previous year. In order to ensure that the participants come well-prepared for the Workshop, the topics/chapters were distributed among them well in advance. During the Workshop the materials prepared by each participant were thoroughly reviewed by their co-particip ...
... Reviewed Support Materials of the previous year. In order to ensure that the participants come well-prepared for the Workshop, the topics/chapters were distributed among them well in advance. During the Workshop the materials prepared by each participant were thoroughly reviewed by their co-particip ...
KINETICS questions
... (a) (i) Determine the order for each of the reactants, NO and H2, from the data given and show your reasoning. (ii) Write the overall rate law for the reaction. (b) Calculate the value of the rate constant, k, for the reaction. Include units. (c) For experiment 2, calculate the concentration of NO r ...
... (a) (i) Determine the order for each of the reactants, NO and H2, from the data given and show your reasoning. (ii) Write the overall rate law for the reaction. (b) Calculate the value of the rate constant, k, for the reaction. Include units. (c) For experiment 2, calculate the concentration of NO r ...
CHAPTER 21 ELECTROCHEMISTRY: CHEMICAL CHANGE AND
... a) The metal A is being oxidized to form the metal cation. To form positive ions, an atom must always lose electrons, so this half-reaction is always an oxidation. b) The metal ion B is gaining electrons to form the metal B, so it is displaced. c) The anode is the electrode at which oxidation takes ...
... a) The metal A is being oxidized to form the metal cation. To form positive ions, an atom must always lose electrons, so this half-reaction is always an oxidation. b) The metal ion B is gaining electrons to form the metal B, so it is displaced. c) The anode is the electrode at which oxidation takes ...
Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law
... The intermolecular interactions of significance for the substances listed are London forces for C6H6 and CH4, metallic bonding for Hg, and hydrogen bonding for CH3OH. The relative strength of intermolecular forces increases in the order London forces, hydrogen bonding, and metallic interactions. The ...
... The intermolecular interactions of significance for the substances listed are London forces for C6H6 and CH4, metallic bonding for Hg, and hydrogen bonding for CH3OH. The relative strength of intermolecular forces increases in the order London forces, hydrogen bonding, and metallic interactions. The ...
Basic Concepts
... The Reaction Quotient (Q) • Comparing the magnitudes of Q and K allows the determination of whether a reaction mixture is already at equilibrium and, if it is not, how to predict whether its composition will change with time (whether the reaction will proceed to the right or to the left) 1. If Q = ...
... The Reaction Quotient (Q) • Comparing the magnitudes of Q and K allows the determination of whether a reaction mixture is already at equilibrium and, if it is not, how to predict whether its composition will change with time (whether the reaction will proceed to the right or to the left) 1. If Q = ...
oxidation–reduction reaction
... • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an oxidation–reduction reaction. • Also called redox reactions ...
... • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an oxidation–reduction reaction. • Also called redox reactions ...
Electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen gas (H2) due to an electric current being passed through the water.This technique can be used to make hydrogen fuel (hydrogen gas) and breathable oxygen; though currently most industrial methods make hydrogen fuel from natural gas instead.