Homo-coupling of terminal alkynes on a noble metal surface
... image shows a smooth connexion between the two TEB moieties, which has an apparent height slightly lower than the two benzene rings. For comparison, the Ag bis-acetylide complex, further referred to as organometallic dimer, would exhibit a characteristic substructure in the connecting waist originat ...
... image shows a smooth connexion between the two TEB moieties, which has an apparent height slightly lower than the two benzene rings. For comparison, the Ag bis-acetylide complex, further referred to as organometallic dimer, would exhibit a characteristic substructure in the connecting waist originat ...
Chemistry 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 40. What effect does a catalyst have? A. increases the reaction rate by decreasing the heat of reaction B. increases the reaction rate by increasing the activation energy of the reverse reaction C. increases the reaction rate by lowering the activation energy of the forward reaction only D. increase ...
... 40. What effect does a catalyst have? A. increases the reaction rate by decreasing the heat of reaction B. increases the reaction rate by increasing the activation energy of the reverse reaction C. increases the reaction rate by lowering the activation energy of the forward reaction only D. increase ...
Calculations on the equations reaction
... professor Tulebaev K.A. ________________ to conform on central methodogical meeting protocol _____of ____________2012 y. ...
... professor Tulebaev K.A. ________________ to conform on central methodogical meeting protocol _____of ____________2012 y. ...
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen
... response in the space provided following each question. Your responses to these questions will be scored on the basis of the accuracy and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Specific answers are preferable to broad, diffuse responses. For calculations ...
... response in the space provided following each question. Your responses to these questions will be scored on the basis of the accuracy and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Specific answers are preferable to broad, diffuse responses. For calculations ...
Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL ) www.mtel
... taking or retaking the MTEL test is strongly recommended. How much preparation and study you need depends on how comfortable and knowledgeable you are with the content of the test. The first step in preparing to take the MTEL is to identify what information the test will address by reviewing the obj ...
... taking or retaking the MTEL test is strongly recommended. How much preparation and study you need depends on how comfortable and knowledgeable you are with the content of the test. The first step in preparing to take the MTEL is to identify what information the test will address by reviewing the obj ...
Study guide for final
... A) two bonding and two unshared pairs of electrons. B) one bonding and three unshared pairs of electrons. C) three bonding and one unshared pair of electrons. D) two double bonds and no unshared pairs of electrons. E) none of the above. 33) The central atom in the chlorite anion, ClO2- is surrounded ...
... A) two bonding and two unshared pairs of electrons. B) one bonding and three unshared pairs of electrons. C) three bonding and one unshared pair of electrons. D) two double bonds and no unshared pairs of electrons. E) none of the above. 33) The central atom in the chlorite anion, ClO2- is surrounded ...
mass
... the theoretical yield and the actual yield. The theoretical yield is the maximum mass of product expected from the reaction, using reacting masses. The actual yield is the mass of the product that is actually obtained from the real chemical reaction. Why is the actual yield usually less than the the ...
... the theoretical yield and the actual yield. The theoretical yield is the maximum mass of product expected from the reaction, using reacting masses. The actual yield is the mass of the product that is actually obtained from the real chemical reaction. Why is the actual yield usually less than the the ...
Synthesis of esterified solid fat from fractionated
... mixing. The sample was incubated in water bath at 50 °C for 30 minutes under continuous shaking. Two mililiters (50% NaHSO4: 25% NacL in water) solution were added and cool under running water. Three milliliters water and 1 mL hexane were added and vortexed vigorously (Azardmard-Damirchi & Dutta, 20 ...
... mixing. The sample was incubated in water bath at 50 °C for 30 minutes under continuous shaking. Two mililiters (50% NaHSO4: 25% NacL in water) solution were added and cool under running water. Three milliliters water and 1 mL hexane were added and vortexed vigorously (Azardmard-Damirchi & Dutta, 20 ...
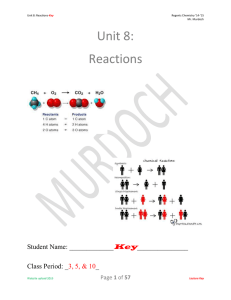
Unit 8: Reactions
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
5 SURFACE CHEMISTRY CATEGORY
... freezing point by 7.5°C? The freezing point depression constant, Kf , for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1. Assume van’t Hoff factor for NaCl is 1.87. 8. 18 g of glucose, C6H12O6 (Molar Mass = 180 g mol–1) is dissolved in 1 kg of water in a sauce pan. At what temperature will this solution boil? 9.Determine ...
... freezing point by 7.5°C? The freezing point depression constant, Kf , for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1. Assume van’t Hoff factor for NaCl is 1.87. 8. 18 g of glucose, C6H12O6 (Molar Mass = 180 g mol–1) is dissolved in 1 kg of water in a sauce pan. At what temperature will this solution boil? 9.Determine ...
Appendix N CONCENTRATION UNITS
... concentration units because molar solutions are easy to prepare. In general, a molar solution is prepared by placing a known quantity of solute in a volumetric flask and adding solvent until the flask is filled to the calibration mark. Molar concentration is used in many common laboratory applicatio ...
... concentration units because molar solutions are easy to prepare. In general, a molar solution is prepared by placing a known quantity of solute in a volumetric flask and adding solvent until the flask is filled to the calibration mark. Molar concentration is used in many common laboratory applicatio ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... by both enthalpy and entropy. • Gibb’s Free Energy is a thermodynamic function that combines enthalpy and entropy. • For a reaction occurring at constant pressure and temperature, the sign of Gibb’s Free Energy relates to the spontaneity of the ...
... by both enthalpy and entropy. • Gibb’s Free Energy is a thermodynamic function that combines enthalpy and entropy. • For a reaction occurring at constant pressure and temperature, the sign of Gibb’s Free Energy relates to the spontaneity of the ...
AP Chemistry:
... This Practice Exam from the 2013 international administration is provided by the College Board for AP Exam preparation. Teachers are permitted to download the materials and make copies to use with their students in a classroom setting only. To maintain the security of this exam, teachers should coll ...
... This Practice Exam from the 2013 international administration is provided by the College Board for AP Exam preparation. Teachers are permitted to download the materials and make copies to use with their students in a classroom setting only. To maintain the security of this exam, teachers should coll ...
Section 4.9 Oxidation–Reduction Reactions
... • We have already seen how the coefficients in a balanced equation can be used as conversion factors between moles of reactants and moles of products. • grams reactant → moles reactant → moles ...
... • We have already seen how the coefficients in a balanced equation can be used as conversion factors between moles of reactants and moles of products. • grams reactant → moles reactant → moles ...
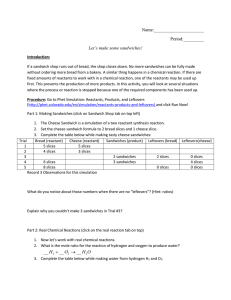
Name: Period:______ Let`s make some sandwiches! Introduction: If
... without ordering more bread from a bakery. A similar thing happens in a chemical reaction. If there are fixed amounts of reactants to work with in a chemical reaction, one of the reactants may be used up first. This prevents the production of more products. In this activity, you will look at several ...
... without ordering more bread from a bakery. A similar thing happens in a chemical reaction. If there are fixed amounts of reactants to work with in a chemical reaction, one of the reactants may be used up first. This prevents the production of more products. In this activity, you will look at several ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Request a Spot account
... In your kitchen, this equilibrium would make it appear as if the total number of sandwiches, slices of bread, and slices of cheese were not changing (macroscopic); however, you would still be breaking apart sandwiches as fast as you were making sandwiches (molecular). This constant action on the mol ...
... In your kitchen, this equilibrium would make it appear as if the total number of sandwiches, slices of bread, and slices of cheese were not changing (macroscopic); however, you would still be breaking apart sandwiches as fast as you were making sandwiches (molecular). This constant action on the mol ...