The Egyptian American International School
... 9.2 Using Chemical Equations to Calculate Mass To calculate masses from the moles of reactants needed or products formed, we can use the molar masses of substances for finding the masses (g) needed or formed. 9.3 Limiting Reactants and Percent Yield Often, reactants in a chemical reaction are n ...
... 9.2 Using Chemical Equations to Calculate Mass To calculate masses from the moles of reactants needed or products formed, we can use the molar masses of substances for finding the masses (g) needed or formed. 9.3 Limiting Reactants and Percent Yield Often, reactants in a chemical reaction are n ...
Precipitate Lab Report Power Point with Answers
... Temperature change, odor change, precipitate formation, irreversibility, color change, and new bubble formation are the evidence for a chemical reaction occuring. Not every time one of these changes is proof of a chemical reaction, but often they are. Sometimes chemical reactions can occur with no o ...
... Temperature change, odor change, precipitate formation, irreversibility, color change, and new bubble formation are the evidence for a chemical reaction occuring. Not every time one of these changes is proof of a chemical reaction, but often they are. Sometimes chemical reactions can occur with no o ...
File - chemistryattweed
... and was interested in the effect of heat on the chemistry of gases. In the early 1900s, Haber reacted nitrogen with hydrogen, using an iron catalyst, to form ammonia. Ammonia can be readily converted to a range of valuable products. In 1908 he had improved the reaction and in 1911 he was rewarded wi ...
... and was interested in the effect of heat on the chemistry of gases. In the early 1900s, Haber reacted nitrogen with hydrogen, using an iron catalyst, to form ammonia. Ammonia can be readily converted to a range of valuable products. In 1908 he had improved the reaction and in 1911 he was rewarded wi ...
Chemical Reactions
... The limiting reactant is the reactant that determines the maximum amount of product that is formed. The limiting reactant will be completely used up in a reaction. This makes the reaction stop. The other reactant will have some unchanged so it is said to be the excess reactant. For example, if you n ...
... The limiting reactant is the reactant that determines the maximum amount of product that is formed. The limiting reactant will be completely used up in a reaction. This makes the reaction stop. The other reactant will have some unchanged so it is said to be the excess reactant. For example, if you n ...
Chemistry Final - Practice Test I
... 100cm = 1m 2735cg = 27.35g What Metric unit is used to measure Mass? ...
... 100cm = 1m 2735cg = 27.35g What Metric unit is used to measure Mass? ...
FINAL EXAM Review Sheet / Study Guide Honors Chemistry
... 15) In the lab, 0.236 kg of aluminum (initially at 342.0oC) are mixed with an unknown mass of water (initially at 20.0oC). When thermal equilibrium is reached, the system has a temperature of 85.0oC. Find the mass of the water. The specific heat of the metal is 0.900 J/g°C. ...
... 15) In the lab, 0.236 kg of aluminum (initially at 342.0oC) are mixed with an unknown mass of water (initially at 20.0oC). When thermal equilibrium is reached, the system has a temperature of 85.0oC. Find the mass of the water. The specific heat of the metal is 0.900 J/g°C. ...
Chemistry
... volume for gases will also be given when required. Syllabus Chemistry is an experimental science and it is essential that students spend time in a laboratory to see for themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: ...
... volume for gases will also be given when required. Syllabus Chemistry is an experimental science and it is essential that students spend time in a laboratory to see for themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: ...
Unit 8 Homework Packet
... relatively stable compounds. For example, xenon combines directly with elemental fluorine at elevated temperatures in the presence of a nickel catalyst. Xe(g) + 2F2(g) → XeF4(s) ...
... relatively stable compounds. For example, xenon combines directly with elemental fluorine at elevated temperatures in the presence of a nickel catalyst. Xe(g) + 2F2(g) → XeF4(s) ...
Chemistry
... volume for gases will also be given when required. Syllabus Chemistry is an experimental science and it is essential that students spend time in a laboratory to see for themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: ...
... volume for gases will also be given when required. Syllabus Chemistry is an experimental science and it is essential that students spend time in a laboratory to see for themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: ...
Fall.2008.Week9.Lesson.1 - reich
... (g) means the substance is a gas (l) means the substance is a liquid (s) means the substance is a solid (aq) means the substance is aqueous Aqueous means dissolved in water, which does not necessarily mean the compound was a liquid. Ethanol and sugar both become aqueous, but only one of them was a s ...
... (g) means the substance is a gas (l) means the substance is a liquid (s) means the substance is a solid (aq) means the substance is aqueous Aqueous means dissolved in water, which does not necessarily mean the compound was a liquid. Ethanol and sugar both become aqueous, but only one of them was a s ...
e c n i
... destroyed so there must be the same number of atoms on each side of the equation Beginning materials are reactants Ending materials are products Example of Chemical reaction: Reactant + Reactant Product + Product ...
... destroyed so there must be the same number of atoms on each side of the equation Beginning materials are reactants Ending materials are products Example of Chemical reaction: Reactant + Reactant Product + Product ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS 1
... volume for gases will also be given when required. Syllabus Chemistry is an experimental science and it is essential that students spend time in a laboratory to see for themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: ...
... volume for gases will also be given when required. Syllabus Chemistry is an experimental science and it is essential that students spend time in a laboratory to see for themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: ...
Physical Science
... Conservation of Mass - Matter cannot be created nor destroyed so there must be the same number of atoms on each side of the equation Beginning materials are reactants Ending materials are products Example of Chemical reaction: Reactant + Reactant Product + Product ...
... Conservation of Mass - Matter cannot be created nor destroyed so there must be the same number of atoms on each side of the equation Beginning materials are reactants Ending materials are products Example of Chemical reaction: Reactant + Reactant Product + Product ...
Thermodynamics Test Study Guide—AP _____ 1. The entropy
... 10. A student adds 200.0 grams of copper metal shot at 25.0oC to 200.0 mL of water at 80.0oC. The final temperature of the mixture is 75.3oC. Assuming that the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g-oC and that no heat is lost to or gained from the surroundings, what is the specific heat of copper, i ...
... 10. A student adds 200.0 grams of copper metal shot at 25.0oC to 200.0 mL of water at 80.0oC. The final temperature of the mixture is 75.3oC. Assuming that the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g-oC and that no heat is lost to or gained from the surroundings, what is the specific heat of copper, i ...
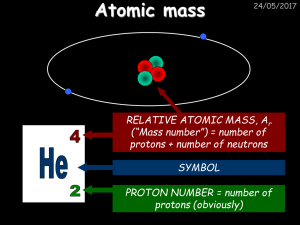
Atomic mass - drseemaljelani
... Mr for magnesium oxide = 24 + 16 = 40 Therefore percentage mass = 24/40 x 100% = 60% Calculate the percentage mass of the following: 1) Hydrogen in hydrochloric acid, HCl 2) Potassium in potassium chloride, KCl 3) Calcium in calcium chloride, CaCl2 4) Oxygen in water, H2O ...
... Mr for magnesium oxide = 24 + 16 = 40 Therefore percentage mass = 24/40 x 100% = 60% Calculate the percentage mass of the following: 1) Hydrogen in hydrochloric acid, HCl 2) Potassium in potassium chloride, KCl 3) Calcium in calcium chloride, CaCl2 4) Oxygen in water, H2O ...
Reactions (The Basics)
... of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different ...
... of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different ...
Kinetics of the Selective Reaction of Diazonium Salts with Single
... properties. Consequently, many techniques have been developed in attempts to separate nanotubes according to their electronic type, w ith varying degrees of success. One such technique involves the selective chemical reaction of CNTs with electron w ithdraw ing diazonium salts, w here metallic nanot ...
... properties. Consequently, many techniques have been developed in attempts to separate nanotubes according to their electronic type, w ith varying degrees of success. One such technique involves the selective chemical reaction of CNTs with electron w ithdraw ing diazonium salts, w here metallic nanot ...
Chem 30A Final Exam
... compound is responsible for what is known as the “French Paradox”, i.e. the relatively low incidence of heart disease in France even though the French eat lots of meat and dairy products high in saturated fats. a. b. c. d. ...
... compound is responsible for what is known as the “French Paradox”, i.e. the relatively low incidence of heart disease in France even though the French eat lots of meat and dairy products high in saturated fats. a. b. c. d. ...
Test Booklet
... 22 Using the solubility graph provided, a student performs an experiment to find the solubility of a substance. The student finds the amount of substance needed to make a saturated solution in 100 g of water at different temperatures. The student’s data are shown in the table below the graph. ...
... 22 Using the solubility graph provided, a student performs an experiment to find the solubility of a substance. The student finds the amount of substance needed to make a saturated solution in 100 g of water at different temperatures. The student’s data are shown in the table below the graph. ...
*6th Grade Science-Chapter 5 Study Guide Lesson 5.1: Observing
... 2. There are two atoms of oxygen and one atom of iron on the left side; there is only on atom of iron and one oxygen atom on the right side. 3. 2 Fe + O2 2 FeO is now balanced Synthesis- reaction when two or more elements or compounds combine to form a more complex substance/product (Ex: A + B C ...
... 2. There are two atoms of oxygen and one atom of iron on the left side; there is only on atom of iron and one oxygen atom on the right side. 3. 2 Fe + O2 2 FeO is now balanced Synthesis- reaction when two or more elements or compounds combine to form a more complex substance/product (Ex: A + B C ...
Extra Unit 3 Problems for the Web Site (Honors
... a) COCl b) COCl2 c) CO2Cl d) CO2Cl2 e) COCl4 15. A certain compound has an empirical formula of NH2O. Its molar mass was experimentally determined to be between 60 and 65 g/mol. Its molecular formula is a) NH2O b) N2H2O2 c) N2H4O2 d) none of these 16. Consider the reaction: Mg2Si(s) + 4H2O(l) ----> ...
... a) COCl b) COCl2 c) CO2Cl d) CO2Cl2 e) COCl4 15. A certain compound has an empirical formula of NH2O. Its molar mass was experimentally determined to be between 60 and 65 g/mol. Its molecular formula is a) NH2O b) N2H2O2 c) N2H4O2 d) none of these 16. Consider the reaction: Mg2Si(s) + 4H2O(l) ----> ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS, SYMBOLS, FORULAS 7
... The law of conservation of matter states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed, but can be changed in form. The total mass of the material(s) before the reaction is the same as the total mass of material(s) after the reaction. A balanced chemical equation has the same number of each kind ...
... The law of conservation of matter states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed, but can be changed in form. The total mass of the material(s) before the reaction is the same as the total mass of material(s) after the reaction. A balanced chemical equation has the same number of each kind ...