lEVEl I SCHWESER`S QuickSheet
... obligation) to retire all or part of issue prior to maturity. Issuer owns option to call the bonds away from investor. • Refunding provisions. Nonrefundable bonds prohibit premature retirement of an issue from proceeds of a lower coupon bond. Bonds that carry these provisions can be freely callable ...
... obligation) to retire all or part of issue prior to maturity. Issuer owns option to call the bonds away from investor. • Refunding provisions. Nonrefundable bonds prohibit premature retirement of an issue from proceeds of a lower coupon bond. Bonds that carry these provisions can be freely callable ...
Problem Set - Kanit Kuevibulvanich
... 18. In the expansionary monetary policy via open market operations - The Fed [ buys / sells ] Treasury securities to banks. Banks have [ less / more ] reserves to lend. Money supply [ increases / decreases ]. - As a result, the short-term interest rate [ increases / decreases ]; therefore, consumpti ...
... 18. In the expansionary monetary policy via open market operations - The Fed [ buys / sells ] Treasury securities to banks. Banks have [ less / more ] reserves to lend. Money supply [ increases / decreases ]. - As a result, the short-term interest rate [ increases / decreases ]; therefore, consumpti ...
Company Name
... practice, long-term interest rates reflect the average expectation in the market about what’s going to happen to short-term rates in the future. ...
... practice, long-term interest rates reflect the average expectation in the market about what’s going to happen to short-term rates in the future. ...
Chapter 14 - Capital Markets
... A security, such as a CMO, is called a “derivative” because its value is derived from some underlying, more basic security such as a mortgage. Other examples include futures contracts on commodities, metals, and foreign currencies and options on common stocks or indexes of common stocks. ...
... A security, such as a CMO, is called a “derivative” because its value is derived from some underlying, more basic security such as a mortgage. Other examples include futures contracts on commodities, metals, and foreign currencies and options on common stocks or indexes of common stocks. ...
Chapter 24 -- International Financial Management
... Currency-option bonds provide the holder with the option to choose the currency in which payment is received. For example, a bond might allow you to choose between yen and U.S. dollars. Currency cocktail bonds provide a degree of exchangerate stability by having principal and interest payments being ...
... Currency-option bonds provide the holder with the option to choose the currency in which payment is received. For example, a bond might allow you to choose between yen and U.S. dollars. Currency cocktail bonds provide a degree of exchangerate stability by having principal and interest payments being ...
presentation source
... facilities (buildings, machines and equipment), firms will borrow more money to spend on facilities, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase. 3. Tax on interest income. A tax on interest income decreases the benefit of saving: For each dollar saved, the individual gets to keep only a part of ...
... facilities (buildings, machines and equipment), firms will borrow more money to spend on facilities, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase. 3. Tax on interest income. A tax on interest income decreases the benefit of saving: For each dollar saved, the individual gets to keep only a part of ...
Discrete Math Review, Chapter 8
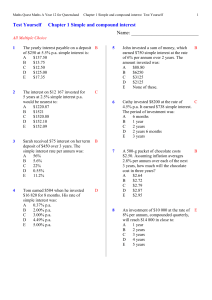
... will be in the account after the given number of years. B. Find the interest earned. 13. Principal = $30,000, interest rate = 2.5% compounded quarterly for 10 years. $38,490.80 / $8,490.80 14. Principal = $2,500, interest rate = 4% compounded monthly for 20 years. $5,556.46 / $3,056.46 15. Suppose y ...
... will be in the account after the given number of years. B. Find the interest earned. 13. Principal = $30,000, interest rate = 2.5% compounded quarterly for 10 years. $38,490.80 / $8,490.80 14. Principal = $2,500, interest rate = 4% compounded monthly for 20 years. $5,556.46 / $3,056.46 15. Suppose y ...
1 Solutions to End-of-Chapter Problems in
... seems very unlikely to happen in the real world). A negative real rate would occur if the expected rate of price inflation were greater than the nominal rate of interest. For example, suppose ðet = 10% and it = 8%. Then rt = -2.0% (approximately). In this case lenders are effectively paying borrower ...
... seems very unlikely to happen in the real world). A negative real rate would occur if the expected rate of price inflation were greater than the nominal rate of interest. For example, suppose ðet = 10% and it = 8%. Then rt = -2.0% (approximately). In this case lenders are effectively paying borrower ...
English
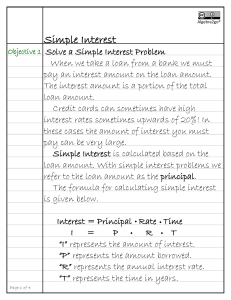
... Credit cards can sometimes have high interest rates sometimes upwards of 20%! In these cases the amount of interest you must pay can be very large. Simple Interest is calculated based on the loan amount. With simple interest problems we refer to the loan amount as the principal. The formula for calc ...
... Credit cards can sometimes have high interest rates sometimes upwards of 20%! In these cases the amount of interest you must pay can be very large. Simple Interest is calculated based on the loan amount. With simple interest problems we refer to the loan amount as the principal. The formula for calc ...
52111imp - Aberdeenshire Council
... Based upon the prospects for interest rates outlined above, there are a number of strategy options available. The anticipation is that short-term rates will continue to be cheaper than long fixed rate borrowing for most of 2004/05. Short term rates are expected to be relatively stable at or near cur ...
... Based upon the prospects for interest rates outlined above, there are a number of strategy options available. The anticipation is that short-term rates will continue to be cheaper than long fixed rate borrowing for most of 2004/05. Short term rates are expected to be relatively stable at or near cur ...
Interest rate swap

An interest rate swap (IRS) is a liquid financial derivative instrument in which two parties agree to exchange interest rate cash flows, based on a specified notional amount from a fixed rate to a floating rate (or vice versa) or from one floating rate to another. Interest rate swaps can be used for both hedging and speculating.