Sample Problems
... 5. 56 grams of nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia (NH3). How many grams of ammonia are produced? Assignment: Page 311, 1- 5 ...
... 5. 56 grams of nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia (NH3). How many grams of ammonia are produced? Assignment: Page 311, 1- 5 ...
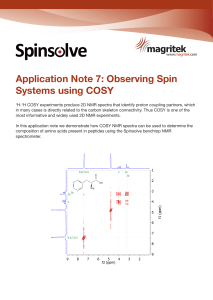
Application Note 7: Observing Spin Systems using COSY
... Glycyl-L-Phenylalanine is produced in a third year synthesis laboratory experiment where students synthesise the dipeptide from the corresponding amino acids. Analysing the COSY NMR spectra of the amino acids shows that the dipeptide can be easily characterised. ...
... Glycyl-L-Phenylalanine is produced in a third year synthesis laboratory experiment where students synthesise the dipeptide from the corresponding amino acids. Analysing the COSY NMR spectra of the amino acids shows that the dipeptide can be easily characterised. ...
Principles of Drug Action I, Winter 2005 ISOMERISM AND
... beam of polarized light. It also was noted that certain organic liquids, as well as solutions of certain organic compounds, can rotate the plane of polarized light. Biot attributed this effect on plane-polarized light to a property of the individual organic molecules through which the light is passe ...
... beam of polarized light. It also was noted that certain organic liquids, as well as solutions of certain organic compounds, can rotate the plane of polarized light. Biot attributed this effect on plane-polarized light to a property of the individual organic molecules through which the light is passe ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... You should be able to recognize a limiting reactant problem because they have 2 amounts given – one for each reactant! To solve these problems first write the balanced equation for the reaction. Second determine which of the reactants the limiting reactant is. (To determine which the limiting reacta ...
... You should be able to recognize a limiting reactant problem because they have 2 amounts given – one for each reactant! To solve these problems first write the balanced equation for the reaction. Second determine which of the reactants the limiting reactant is. (To determine which the limiting reacta ...
LIQUIDS
... in Group 1 have one electron in their outer shell, so we can say that Rb, Cs and Fr will all have one electron in their outer shell. Therefore elements in Group 3 always have three electrons in their outer shell. Elements in Group 7 always have seven electrons in their outer shell. The elements on t ...
... in Group 1 have one electron in their outer shell, so we can say that Rb, Cs and Fr will all have one electron in their outer shell. Therefore elements in Group 3 always have three electrons in their outer shell. Elements in Group 7 always have seven electrons in their outer shell. The elements on t ...
1920
... Similar results* were observed in the collision between a-particles and atoms of nitrogen and oxygen for the recoil atoms appeared to be shot forward mainly in the direction of the a-particles and the region where special ...
... Similar results* were observed in the collision between a-particles and atoms of nitrogen and oxygen for the recoil atoms appeared to be shot forward mainly in the direction of the a-particles and the region where special ...
Untitled
... The half-life for different chemicals can range from ______seconds to ___________ of years! ...
... The half-life for different chemicals can range from ______seconds to ___________ of years! ...
Biological Membrane Structure By Solid-State NMR
... of both the lipid and the protein components of model and biological membranes. Different approaches have been developed to study these systems in which the restricted molecular motions result in broad NMR spectra. This contribution will first present an overview of the different techniques used to ...
... of both the lipid and the protein components of model and biological membranes. Different approaches have been developed to study these systems in which the restricted molecular motions result in broad NMR spectra. This contribution will first present an overview of the different techniques used to ...
File
... to Number Of Atoms Is C an element or compound? Element- 1 mole is 6.02 x 1023 atoms Is CO2 an element or compound? Compound – 1 mole is 6.02 x 1023 molecules (or ...
... to Number Of Atoms Is C an element or compound? Element- 1 mole is 6.02 x 1023 atoms Is CO2 an element or compound? Compound – 1 mole is 6.02 x 1023 molecules (or ...
- Angelo State University
... • In the examples we’ve seen, we have assumed that all of the reactions “go to completion” — that is, that all reactant molecules are converted into products. In real life, some product is almost always lost due to small amounts of contamination present in the glassware, impurities in the reactants, ...
... • In the examples we’ve seen, we have assumed that all of the reactions “go to completion” — that is, that all reactant molecules are converted into products. In real life, some product is almost always lost due to small amounts of contamination present in the glassware, impurities in the reactants, ...
Kinetic isotope effects of 12CH3D+OH and 13CH3D+OH from 278 to
... Good agreement between the experimental, quantum chemical, and available literature values was obtained. Based on the results we conclude that the OH reaction (the main sink of methane) at steady state can produce an atmospheric clumped isotope signal (1(13 CH3 D) = ln([CH4 ][13 CH3 D]/[13 CH4 ][CH3 ...
... Good agreement between the experimental, quantum chemical, and available literature values was obtained. Based on the results we conclude that the OH reaction (the main sink of methane) at steady state can produce an atmospheric clumped isotope signal (1(13 CH3 D) = ln([CH4 ][13 CH3 D]/[13 CH4 ][CH3 ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
... chemical reactions, mass must be conserved. If elements could be changed into other elements during chemical reactions (as the alchemists were trying to do), then masses of atoms would change during reactions and mass would not be conserved. ...
... chemical reactions, mass must be conserved. If elements could be changed into other elements during chemical reactions (as the alchemists were trying to do), then masses of atoms would change during reactions and mass would not be conserved. ...
FREE Sample Here
... chemical reactions, mass must be conserved. If elements could be changed into other elements during chemical reactions (as the alchemists were trying to do), then masses of atoms would change during reactions and mass would not be conserved. ...
... chemical reactions, mass must be conserved. If elements could be changed into other elements during chemical reactions (as the alchemists were trying to do), then masses of atoms would change during reactions and mass would not be conserved. ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
... chemical reactions, mass must be conserved. If elements could be changed into other elements during chemical reactions (as the alchemists were trying to do), then masses of atoms would change during reactions and mass would not be conserved. ...
... chemical reactions, mass must be conserved. If elements could be changed into other elements during chemical reactions (as the alchemists were trying to do), then masses of atoms would change during reactions and mass would not be conserved. ...
eBook AQA GCSE Chemistry Unit C2 Part 1
... made up of two or more atoms chemically bonded together. In ammonia, each molecule consists of one atom of nitrogen joined to three atoms of hydrogen. The atoms are held together by covalent bonds. A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. Covalent bonds form so that atoms can achieve stable el ...
... made up of two or more atoms chemically bonded together. In ammonia, each molecule consists of one atom of nitrogen joined to three atoms of hydrogen. The atoms are held together by covalent bonds. A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. Covalent bonds form so that atoms can achieve stable el ...
Chemistry 11 Exam 1 Spring 2006 When answering questions be
... 13. The atomic radii for the first four alkali metals are shown below. Explain this pattern. Moving down the periodic table the outermost occupied orbitals increase ( n= 1,2,3,4,5,...). As the outermost occupied orbital increases for n the size of the orbital also increases. For Na the outermost occ ...
... 13. The atomic radii for the first four alkali metals are shown below. Explain this pattern. Moving down the periodic table the outermost occupied orbitals increase ( n= 1,2,3,4,5,...). As the outermost occupied orbital increases for n the size of the orbital also increases. For Na the outermost occ ...
The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry Part I – Multiple
... (d) Compound Z contains carbon, hydrogen, and element Q. When 1.00 gram of compound Z is oxidized and all of the carbon and hydrogen are converted to oxides, 1.37 grams of CO2 and 0.281 gram of water are produced. Determine the most probable molecular formula of compound Z. ...
... (d) Compound Z contains carbon, hydrogen, and element Q. When 1.00 gram of compound Z is oxidized and all of the carbon and hydrogen are converted to oxides, 1.37 grams of CO2 and 0.281 gram of water are produced. Determine the most probable molecular formula of compound Z. ...
Notes mole molar mass ions compounds
... Law of Conservation of Mass: total mass remains constant during a chemical reaction. Total mass of reactants = total mass of products. Law of Definite Proportions: All samples of a compound have the same atomic composition (or) all samples have the same proportions by mass of the elements present. L ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass: total mass remains constant during a chemical reaction. Total mass of reactants = total mass of products. Law of Definite Proportions: All samples of a compound have the same atomic composition (or) all samples have the same proportions by mass of the elements present. L ...
Chemistry English
... Performing experiments in chemistry and interpreting their results is what chemists do. It is with the devices used to produce measured quantities, the units in which they are expressed, and the techniques used to do calculations upon them that the study of chemistry begins. 1.2 Experiments Chemical ...
... Performing experiments in chemistry and interpreting their results is what chemists do. It is with the devices used to produce measured quantities, the units in which they are expressed, and the techniques used to do calculations upon them that the study of chemistry begins. 1.2 Experiments Chemical ...
Preliminary studies for anapole moment measurements in rubidium
... number alternation in Fr due to the pairing of neutrons. For Rb, the alternation is no longer evident due to changes in the orbitals for the valence nucleons. In particular the value of κa has a different sign for the two stable isotopes of rubidium (85 Rb and 87 Rb). The nucleon orbitals used for r ...
... number alternation in Fr due to the pairing of neutrons. For Rb, the alternation is no longer evident due to changes in the orbitals for the valence nucleons. In particular the value of κa has a different sign for the two stable isotopes of rubidium (85 Rb and 87 Rb). The nucleon orbitals used for r ...
AP Chem – Unit 1 Part 2 AP Chemistry 2016-‐2017 Unit 1
... End of the Chapter (after page 137) AP MC Review Questions (1-‐17) – Solutions (PRACTICE THESE) ...
... End of the Chapter (after page 137) AP MC Review Questions (1-‐17) – Solutions (PRACTICE THESE) ...
No Slide Title
... Write the Lewis structure of the carbonate ion (CO32-). Step 1 – C is less electronegative than O, put C in center Step 2 – Count valence electrons C - 4 (2s22p2) and O - 6 (2s22p4) -2 charge – 2e4 + (3 x 6) + 2 = 24 valence electrons Step 3 – Draw single bonds between C and O atoms and complete oc ...
... Write the Lewis structure of the carbonate ion (CO32-). Step 1 – C is less electronegative than O, put C in center Step 2 – Count valence electrons C - 4 (2s22p2) and O - 6 (2s22p4) -2 charge – 2e4 + (3 x 6) + 2 = 24 valence electrons Step 3 – Draw single bonds between C and O atoms and complete oc ...
percent composition and formulas
... 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
... 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.