FREE Sample Here
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
Test 1
... D) supply NADH. E) supply pentoses and NADPH. 4. Which one of the following types of mechanisms is not known to play a role in the reversible alteration of enzyme activity? A) Activation by cleavage of an inactive zymogen B) Allosteric response to a regulatory molecule C) Alteration of the synthesis ...
... D) supply NADH. E) supply pentoses and NADPH. 4. Which one of the following types of mechanisms is not known to play a role in the reversible alteration of enzyme activity? A) Activation by cleavage of an inactive zymogen B) Allosteric response to a regulatory molecule C) Alteration of the synthesis ...
Stoichiometry intro
... 2) Every time 4 moles of Al atoms react with 3 moles of O2 molecules, 2 moles of Al2O3 molecules form. ...
... 2) Every time 4 moles of Al atoms react with 3 moles of O2 molecules, 2 moles of Al2O3 molecules form. ...
irm_ch11
... decay processes; they are, therefore, less penetrating and are stopped by a thick sheet of paper. Beta particles and gamma rays, having much greater speed than alpha particles, go through a thick sheet of paper. 11.42 Alpha and beta are stopped; gamma goes through. 11.43 Alpha particle velocities ar ...
... decay processes; they are, therefore, less penetrating and are stopped by a thick sheet of paper. Beta particles and gamma rays, having much greater speed than alpha particles, go through a thick sheet of paper. 11.42 Alpha and beta are stopped; gamma goes through. 11.43 Alpha particle velocities ar ...
Q1. This question is about the structure of atoms. (a) Choose words
... Complete the four spaces in the passage. The chemical formula of ammonia is NH3. This shows that there is one atom of .......................................... and three atoms of .................................. in each ......................................... of ammonia. These atoms are joined ...
... Complete the four spaces in the passage. The chemical formula of ammonia is NH3. This shows that there is one atom of .......................................... and three atoms of .................................. in each ......................................... of ammonia. These atoms are joined ...
FREE Sample Here
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
Insertion of SO2 into the Metal−Carbon Bonds of Rhodium and
... (Cp*Rh(PMe3)(Cl)2) was a stable species, unable to bind the free methane sulfinic acid. In the second case (HOTf, HBF4), the inability to form a strong bond between the metal and the labile counterion prevented the release of free sulfinic acid. A third case can be imagined corresponding to an inter ...
... (Cp*Rh(PMe3)(Cl)2) was a stable species, unable to bind the free methane sulfinic acid. In the second case (HOTf, HBF4), the inability to form a strong bond between the metal and the labile counterion prevented the release of free sulfinic acid. A third case can be imagined corresponding to an inter ...
The Preparation of an Explosive: Nitrogen
... One mole of N2 is created at 944 kJ mol-1 and 3 I-I at 151 kJ mol-1 producing 1397 KJ mol-1. The change in energy is equal to the enthalphy of the reactants deducting the enthalphy of the products, giving the highly exothermic reaction (Fig. 3) and overall energy change of -437 kJ mol-1. 5 Results a ...
... One mole of N2 is created at 944 kJ mol-1 and 3 I-I at 151 kJ mol-1 producing 1397 KJ mol-1. The change in energy is equal to the enthalphy of the reactants deducting the enthalphy of the products, giving the highly exothermic reaction (Fig. 3) and overall energy change of -437 kJ mol-1. 5 Results a ...
Arenes - Science Skool!
... Arenes are aromatic hydrocarbons. The term "aromatic" originally referred to their pleasant smells, but now implies a particular sort of delocalised bonding. The arenes are based on benzene rings. The simplest of them is benzene itself, C6H6. Benzene, C6H6, is a planar molecule containing a ring of ...
... Arenes are aromatic hydrocarbons. The term "aromatic" originally referred to their pleasant smells, but now implies a particular sort of delocalised bonding. The arenes are based on benzene rings. The simplest of them is benzene itself, C6H6. Benzene, C6H6, is a planar molecule containing a ring of ...
Chemical Measurements
... • What is the formula and molar mass for glucose, C6H12O6? – C: 6 atoms x 12.01 amu = 72.06 amu – H: 12 atoms x 1.01 amu = 12.12 amu – O: 6 atoms x 16.00 amu = 96.00 amu Formula Mass = 72.06 amu + 12.12amu + 96 amu = 180.18 amu Molar Mass = 180.18 g/mol ...
... • What is the formula and molar mass for glucose, C6H12O6? – C: 6 atoms x 12.01 amu = 72.06 amu – H: 12 atoms x 1.01 amu = 12.12 amu – O: 6 atoms x 16.00 amu = 96.00 amu Formula Mass = 72.06 amu + 12.12amu + 96 amu = 180.18 amu Molar Mass = 180.18 g/mol ...
Flux distributions in anaerobic, glucose-limited
... to the underlying biochemistry. In uitro enzyme assays can be used as a tool to determine the presence or absence of reactions and may also add a constraint to the model, e.g. an estimate of the ratip between two fluxes can be obtained. Any stoichiometric model should be subjected to a sensitivity a ...
... to the underlying biochemistry. In uitro enzyme assays can be used as a tool to determine the presence or absence of reactions and may also add a constraint to the model, e.g. an estimate of the ratip between two fluxes can be obtained. Any stoichiometric model should be subjected to a sensitivity a ...
Fundamentals
... In the case of an elemental material, such as copper, a particle is a single atom. Because the mass of a single atom is very small, atomic mass is usually specified in atomic mass units (amu). One amu is equal to 1.6605402 X 10-24 g (1 g/ 6.022137 X 1023),or about the mass of a single hydrogen atom. ...
... In the case of an elemental material, such as copper, a particle is a single atom. Because the mass of a single atom is very small, atomic mass is usually specified in atomic mass units (amu). One amu is equal to 1.6605402 X 10-24 g (1 g/ 6.022137 X 1023),or about the mass of a single hydrogen atom. ...
Chapter 12 Packet
... iii. If 67L of nitrogen gas were produced upon impact, would 50g of iron (III) oxide be sufficient to convert all of the sodium to sodium oxide. Hint: first determine what mass of sodium would be produced in reaction (2a) and then determine the limiting reactant in (2ci). ...
... iii. If 67L of nitrogen gas were produced upon impact, would 50g of iron (III) oxide be sufficient to convert all of the sodium to sodium oxide. Hint: first determine what mass of sodium would be produced in reaction (2a) and then determine the limiting reactant in (2ci). ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom
... His ideas are also presented in Table 4.1. Because Aristotle was one of the most influential philosophers of his time, Democritus’s atomic theory was eventually rejected. In fairness to Democritus, it was impossible for him or anyone else of his time to determine what held the atoms together. More t ...
... His ideas are also presented in Table 4.1. Because Aristotle was one of the most influential philosophers of his time, Democritus’s atomic theory was eventually rejected. In fairness to Democritus, it was impossible for him or anyone else of his time to determine what held the atoms together. More t ...
Unit 2 – Quantities Review
... 10. Magnesium hydroxide is a base that is used in some antacids. What is the mass in grams of 0.45 mol of magnesium hydroxide? 11. Ammonia is a gas that, dissolved in water, is used as a cleaning agent. Convert 87 mmol of ammonia, NH3(g), into mass in grams. (Hint: 1 mol = 1000 mmol, you will need t ...
... 10. Magnesium hydroxide is a base that is used in some antacids. What is the mass in grams of 0.45 mol of magnesium hydroxide? 11. Ammonia is a gas that, dissolved in water, is used as a cleaning agent. Convert 87 mmol of ammonia, NH3(g), into mass in grams. (Hint: 1 mol = 1000 mmol, you will need t ...
Chapter 8 - Cengage Learning
... Would you say ammonia (NH3) is mostly nitrogen or mostly hydrogen? Your answer depends on if you are looking at the number of atoms or the mass of the atoms. In terms of numbers of atoms, ammonia is ¾ hydrogen (there are four atoms making up an ammonia molecule, and three of them are hydrogen). But ...
... Would you say ammonia (NH3) is mostly nitrogen or mostly hydrogen? Your answer depends on if you are looking at the number of atoms or the mass of the atoms. In terms of numbers of atoms, ammonia is ¾ hydrogen (there are four atoms making up an ammonia molecule, and three of them are hydrogen). But ...
some basic concepts of chemistry
... three physical states viz. solid, liquid and gas. The constituent particles of matter in these three states can be represented as shown in Fig. 1.1. In solids, these particles are held very close to each other in an orderly fashion and there is not much freedom of movement. In liquids, the particles ...
... three physical states viz. solid, liquid and gas. The constituent particles of matter in these three states can be represented as shown in Fig. 1.1. In solids, these particles are held very close to each other in an orderly fashion and there is not much freedom of movement. In liquids, the particles ...
References - WordPress.com
... provide these predictions and their reasoning behind them in written form, and include it with their analysis questions. o Students are asked to work with their lab partner to carry out this experiment. The Students will collect all materials from the teacher's material lab station in the front of t ...
... provide these predictions and their reasoning behind them in written form, and include it with their analysis questions. o Students are asked to work with their lab partner to carry out this experiment. The Students will collect all materials from the teacher's material lab station in the front of t ...
Chapter 3. Analysis of Environmental System 3.1 Analysis of a
... When chemical reaction for (3.2.11) is expressed like Eq. (3.2.12), and Eq. (3.2.13), the reactions are 2nd order reaction. As shown so far, order of chemical reaction may be determined by type of chemical reaction. In water chemistry, chemical reaction rates generally follows to Eq.(3.2.2)~Eq.(3.2. ...
... When chemical reaction for (3.2.11) is expressed like Eq. (3.2.12), and Eq. (3.2.13), the reactions are 2nd order reaction. As shown so far, order of chemical reaction may be determined by type of chemical reaction. In water chemistry, chemical reaction rates generally follows to Eq.(3.2.2)~Eq.(3.2. ...
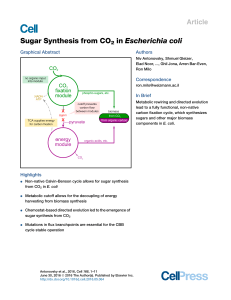
Sugar Synthesis from CO2 in Escherichia coli
... of central carbon metabolism have to be synthesized completely from CO2 by the CBB module (Figure S4). An organic-acid feeding the energy module, such as pyruvate, could provide reducing power and ATP for carbon fixation and thereby allow the synthesis of biomass precursors in the CBB module from CO ...
... of central carbon metabolism have to be synthesized completely from CO2 by the CBB module (Figure S4). An organic-acid feeding the energy module, such as pyruvate, could provide reducing power and ATP for carbon fixation and thereby allow the synthesis of biomass precursors in the CBB module from CO ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.