Secondary metabolism is a term for pathways and products
... Organic natural products are constructed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; frequently nitrogen atoms are also involved, and less frequently sulphur, phosphorus, chlorine, bromine, and iodine atoms. Organometalic compounds, especially metal complexes, also occur. The ultimate sources of these el ...
... Organic natural products are constructed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; frequently nitrogen atoms are also involved, and less frequently sulphur, phosphorus, chlorine, bromine, and iodine atoms. Organometalic compounds, especially metal complexes, also occur. The ultimate sources of these el ...
File
... o 1.E.1 Physical and chemical processes can be depicted symbolically; when it is done, the illustration must conserve all atoms of all types. o 1.E.2 Conservation of atoms makes it possible to compute the masses of substances involved in physical and chemical processes. Chemical processes result in ...
... o 1.E.1 Physical and chemical processes can be depicted symbolically; when it is done, the illustration must conserve all atoms of all types. o 1.E.2 Conservation of atoms makes it possible to compute the masses of substances involved in physical and chemical processes. Chemical processes result in ...
Some basic concepts of chemistry
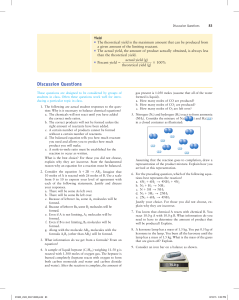
... DEFINITE COMPOSITION (JOSEPH PROUST) Statement: A given chemical compound always contains the same elements combined together in definite proportion by mass, i.e., it has a fixed composition and does not depend on the method of its preparation or the source from which it has been obtained. This law ...
... DEFINITE COMPOSITION (JOSEPH PROUST) Statement: A given chemical compound always contains the same elements combined together in definite proportion by mass, i.e., it has a fixed composition and does not depend on the method of its preparation or the source from which it has been obtained. This law ...
Personal Tutoring Help on Questions and Problems
... 3.26 How many molecules of ethane (C2H6) are present in 0.334 g of C2H6? 3.27 Calculate the number of C, H, and O atoms in 1.50 g of glucose (C6H12O6), a sugar. 3.28 Urea [(NH2)2CO] is used for fertilizer and many other things. Calculate the number of N, C, O, and H atoms in 1.68 ⫻ 104 g of urea. 3. ...
... 3.26 How many molecules of ethane (C2H6) are present in 0.334 g of C2H6? 3.27 Calculate the number of C, H, and O atoms in 1.50 g of glucose (C6H12O6), a sugar. 3.28 Urea [(NH2)2CO] is used for fertilizer and many other things. Calculate the number of N, C, O, and H atoms in 1.68 ⫻ 104 g of urea. 3. ...
Integrative study of Arabidopsis thaliana metabolomic and
... analysis. Furthermore, several metabolites exist only for a short period of time within a protein complex that catalyze more than one reaction step, • they are filtered out by statistical analysis: transcripts may be equally expressed throughout all experimental conditions if the corresponding produ ...
... analysis. Furthermore, several metabolites exist only for a short period of time within a protein complex that catalyze more than one reaction step, • they are filtered out by statistical analysis: transcripts may be equally expressed throughout all experimental conditions if the corresponding produ ...
Organic Molecules
... structures containing thousands of atoms! Although carbon is present in all organic compounds, other elements such as hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), sulfur (S) and phosphorus (P) are also common in these molecules. Until the early nineteenth century, chemists had managed to make many simple ...
... structures containing thousands of atoms! Although carbon is present in all organic compounds, other elements such as hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), sulfur (S) and phosphorus (P) are also common in these molecules. Until the early nineteenth century, chemists had managed to make many simple ...
Section 2.9 Molar Mass: Counting Atoms by Weighing Them
... properties that distinguish them from atoms of other elements Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms only change the way that they are bound together with other atoms. ...
... properties that distinguish them from atoms of other elements Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms only change the way that they are bound together with other atoms. ...
Metalloprotein/Metallocofactor Mass Spectrometry
... Figure 8 ESI-FTICR mass spectrum of [3Fe-4S]ferredoxin from Pf (top) in which the intact cluster can be seen at m/z 1866. Peaks at higher mass-to-charge ratios represent oxygen, sodium, and sulfur adducts, whereas more intense peaks at lower mass-to-charge ratios represent losses of inorganic sulfid ...
... Figure 8 ESI-FTICR mass spectrum of [3Fe-4S]ferredoxin from Pf (top) in which the intact cluster can be seen at m/z 1866. Peaks at higher mass-to-charge ratios represent oxygen, sodium, and sulfur adducts, whereas more intense peaks at lower mass-to-charge ratios represent losses of inorganic sulfid ...
Introduction - MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
... pyruvate as the primary carbon source does not show the same abolition of PER2 rhythmicity (±SD, n=3, normalised) c) Replacing glucose with pyruvate does cause significant period lengthening ...
... pyruvate as the primary carbon source does not show the same abolition of PER2 rhythmicity (±SD, n=3, normalised) c) Replacing glucose with pyruvate does cause significant period lengthening ...
Chapter 7 Lecture
... • Complete ionic equations show aqueous ionic compounds that normally dissociate in solution as they are actually present in solution. • When writing complete ionic equations, separate only aqueous ionic compounds into their constituent ions. • Do NOT separate solid, liquid, or gaseous compounds. ...
... • Complete ionic equations show aqueous ionic compounds that normally dissociate in solution as they are actually present in solution. • When writing complete ionic equations, separate only aqueous ionic compounds into their constituent ions. • Do NOT separate solid, liquid, or gaseous compounds. ...
chapter 3 - Denton ISD
... When you crush a lump of sugar, you can see that it is made up of many smaller particles of sugar. You may grind these particles into a very fine powder, but each tiny piece is still sugar. Now suppose you dissolve the sugar in water. The tiny particles seem to disappear completely. Even if you look ...
... When you crush a lump of sugar, you can see that it is made up of many smaller particles of sugar. You may grind these particles into a very fine powder, but each tiny piece is still sugar. Now suppose you dissolve the sugar in water. The tiny particles seem to disappear completely. Even if you look ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... 10. How many times larger is the number of hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms in a disaccharide? ________ 11. How many monosaccharide molecules are needed to form one sucrose molecule? ________ The production of a disaccharide is a chemical reaction called a dehydration synthesis reaction. In such a r ...
... 10. How many times larger is the number of hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms in a disaccharide? ________ 11. How many monosaccharide molecules are needed to form one sucrose molecule? ________ The production of a disaccharide is a chemical reaction called a dehydration synthesis reaction. In such a r ...
FREE Sample Here
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
Mass and Stoichiometry
... “galena”), was “calcined” by early metallurgists to form a lead oxide used to purify silver from other metals. Calcined means to burn in the presence of oxygen. At low temperatures the yellow lead oxide PbO, litharge, is formed. At higher temperatures the a red lead oxide, minium, is formed, Pb3O4. ...
... “galena”), was “calcined” by early metallurgists to form a lead oxide used to purify silver from other metals. Calcined means to burn in the presence of oxygen. At low temperatures the yellow lead oxide PbO, litharge, is formed. At higher temperatures the a red lead oxide, minium, is formed, Pb3O4. ...
MidtermReview2012
... 3. When a small amount of carbon is mixed in with molten iron, the cooled resulting alloy is called steel. Would you consider the iron to be changed physically or chemically? Explain. ...
... 3. When a small amount of carbon is mixed in with molten iron, the cooled resulting alloy is called steel. Would you consider the iron to be changed physically or chemically? Explain. ...
Polysulfane Antitumor Agents from o
... Various heterocycles may be expected to arise from the reaction of o-benzyne with cyclic S8. B3LYP/6-31G(d) calculations are used to predict the stability of possible ortho-fused heterocycles, o-C6H4Sx (where x ) 1-8). Lowenergy conformers of the rings containing up to 8 sulfurs were identified by a ...
... Various heterocycles may be expected to arise from the reaction of o-benzyne with cyclic S8. B3LYP/6-31G(d) calculations are used to predict the stability of possible ortho-fused heterocycles, o-C6H4Sx (where x ) 1-8). Lowenergy conformers of the rings containing up to 8 sulfurs were identified by a ...
Discussion Questions
... 60. Terephthalic acid is an important chemical used in the manufacture of polyesters and plasticizers. It contains only C, H, and O. Combustion of 19.81 mg terephthalic acid produces 41.98 mg CO2 and 6.45 mg H2O. If 0.250 mole of terephthalic acid has a mass of 41.5 g, determine the molecular fo ...
... 60. Terephthalic acid is an important chemical used in the manufacture of polyesters and plasticizers. It contains only C, H, and O. Combustion of 19.81 mg terephthalic acid produces 41.98 mg CO2 and 6.45 mg H2O. If 0.250 mole of terephthalic acid has a mass of 41.5 g, determine the molecular fo ...
unit_k_reading_notes
... Let us begin with defining stoichiometry. Most texts break it down into 2 categories. The first one we’ve already seen—it’s composition stoichiometry, which is the study of mass relationships of elements in compounds. Examples of this include calculating percentage composition, and determination of ...
... Let us begin with defining stoichiometry. Most texts break it down into 2 categories. The first one we’ve already seen—it’s composition stoichiometry, which is the study of mass relationships of elements in compounds. Examples of this include calculating percentage composition, and determination of ...
FREE Sample Here
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
Key Words Questions and Problems
... The empirical formula of a compound is CH. If the molar mass of this compound is about 78 g, what is its molecular formula? The molar mass of caffeine is 194.19 g. Is the molecular formula of caffeine C4H5N2O or C8H10N4O2? Monosodium glutamate (MSG), a food-flavor enhancer, has been blamed for “Chin ...
... The empirical formula of a compound is CH. If the molar mass of this compound is about 78 g, what is its molecular formula? The molar mass of caffeine is 194.19 g. Is the molecular formula of caffeine C4H5N2O or C8H10N4O2? Monosodium glutamate (MSG), a food-flavor enhancer, has been blamed for “Chin ...
POGIL - Basic Skills Supplement - The Mole-1
... chemical reactions. The purpose of the mole is to normalize quantities of atoms and molecules when working with them in chemical reactions. In a molecule of water (H2O), for example, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. When combining these two elements to make water, 2 hydrogen atoms a ...
... chemical reactions. The purpose of the mole is to normalize quantities of atoms and molecules when working with them in chemical reactions. In a molecule of water (H2O), for example, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. When combining these two elements to make water, 2 hydrogen atoms a ...
Document
... When two elements C and O separately combine with H to from methane (CH) and water (H O) respectively it is very clear, that in methane 3g of C combine with 1g of hydrogen and in water (H O) 8g of O combine with the same (fixed) mass i.e. (1g) of H now when C and O combine with each other to form ca ...
... When two elements C and O separately combine with H to from methane (CH) and water (H O) respectively it is very clear, that in methane 3g of C combine with 1g of hydrogen and in water (H O) 8g of O combine with the same (fixed) mass i.e. (1g) of H now when C and O combine with each other to form ca ...
FREE Sample Here
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
... 4) What factors are most important in determining which elements are most common in living matter? A) the relative abundances of the elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere B) the emergent properties of the simple compounds made from these elements C) the reactivity of the elements with water D) th ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.