The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
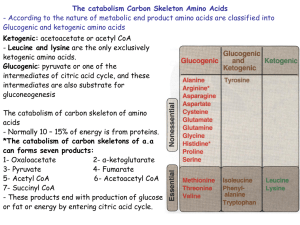
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms and Elements
... receptor molecules in our taste buds. Due to their structure, the ethanol molecules travel easily through the human body (they are soluble in both water and fat) until they reach their target, the brain. Chemistry is often termed “the central science”. It lies between biology and physics, and chemic ...
... receptor molecules in our taste buds. Due to their structure, the ethanol molecules travel easily through the human body (they are soluble in both water and fat) until they reach their target, the brain. Chemistry is often termed “the central science”. It lies between biology and physics, and chemic ...
File
... Practice with ions… – Magnesium makes ions with a 2+ charge. Are electrons lost or gained? How many electrons are moved? – Fluorine makes ions with a 1- charge. Are electrons lost or gained? How many electrons are moved? – An ion has 13 p+ and 10 e-. Give the symbol and charge for the ion. – An ion ...
... Practice with ions… – Magnesium makes ions with a 2+ charge. Are electrons lost or gained? How many electrons are moved? – Fluorine makes ions with a 1- charge. Are electrons lost or gained? How many electrons are moved? – An ion has 13 p+ and 10 e-. Give the symbol and charge for the ion. – An ion ...
radioactivity-ppt
... accomplished by radioactive minerals, such as Uranium. Uranium decays very slowly. Rocks on Earth have been dated to 3.7 bil yrs old Rocks on Moon dated to 4.2 bil yrs old The Earth has been dated to 4.6 bil yrs old ...
... accomplished by radioactive minerals, such as Uranium. Uranium decays very slowly. Rocks on Earth have been dated to 3.7 bil yrs old Rocks on Moon dated to 4.2 bil yrs old The Earth has been dated to 4.6 bil yrs old ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms and Elements
... receptor molecules in our taste buds. Due to their structure, the ethanol molecules travel easily through the human body (they are soluble in both water and fat) until they reach their target, the brain. Chemistry is often termed “the central science”. It lies between biology and physics, and chemic ...
... receptor molecules in our taste buds. Due to their structure, the ethanol molecules travel easily through the human body (they are soluble in both water and fat) until they reach their target, the brain. Chemistry is often termed “the central science”. It lies between biology and physics, and chemic ...
Radioactivity
... accomplished by radioactive minerals, such as Uranium. Uranium decays very slowly. Rocks on Earth have been dated to 3.7 bil yrs old Rocks on Moon dated to 4.2 bil yrs old The Earth has been dated to 4.6 bil yrs old ...
... accomplished by radioactive minerals, such as Uranium. Uranium decays very slowly. Rocks on Earth have been dated to 3.7 bil yrs old Rocks on Moon dated to 4.2 bil yrs old The Earth has been dated to 4.6 bil yrs old ...
atomic mass - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... of nitrogen is 14.01. An aluminum atom is how many times heavier than a nitrogen atom? ...
... of nitrogen is 14.01. An aluminum atom is how many times heavier than a nitrogen atom? ...
Atomic and Molecular Structure
... material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc2 ) is small but significant in nuclear reactions. Fusion = atoms come together (H+H=He) Fission = atoms split ...
... material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc2 ) is small but significant in nuclear reactions. Fusion = atoms come together (H+H=He) Fission = atoms split ...
Chapter #2-Newest CPub
... • Law of Mass Conservation: The total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction (Lavoisier). • Law of Definite (or Constant) Composition: No matter what its source, a particular chemical compound is composed of the same elements in the same parts (fractions) by mass (Proust). • T ...
... • Law of Mass Conservation: The total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction (Lavoisier). • Law of Definite (or Constant) Composition: No matter what its source, a particular chemical compound is composed of the same elements in the same parts (fractions) by mass (Proust). • T ...
RXN-4-STUDENTS - Rothschild Science
... element you have NH3 (one nitrogen, three hydrogen)- DON’T mess with these!! Coefficients – small whole number that appears ...
... element you have NH3 (one nitrogen, three hydrogen)- DON’T mess with these!! Coefficients – small whole number that appears ...
Period 6
... • Polymers are long chains of many smaller molecules (monomers). • Monomers are single molecules. • The prefix poly means many and the prefix mono means one. • Polymers can be made of organic compounds such as alcohols, and ...
... • Polymers are long chains of many smaller molecules (monomers). • Monomers are single molecules. • The prefix poly means many and the prefix mono means one. • Polymers can be made of organic compounds such as alcohols, and ...
Chem-130 Test Lecture
... The number of neutrons in the nucleus is given by the mass number minus the atomic number. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Therefore isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. An atom of a specific isotope is called a nuclide. ...
... The number of neutrons in the nucleus is given by the mass number minus the atomic number. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Therefore isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. An atom of a specific isotope is called a nuclide. ...
Final Exam review semester 1
... 1. Ninety-nine percent of all the matter that can be observed in the universe exists as 2. Hydrochloric acid, HCl, is added to solid NaOH. After the reaction is complete, NaCl dissolved in water remains. What are the products of this chemical reaction? ____ ...
... 1. Ninety-nine percent of all the matter that can be observed in the universe exists as 2. Hydrochloric acid, HCl, is added to solid NaOH. After the reaction is complete, NaCl dissolved in water remains. What are the products of this chemical reaction? ____ ...
Atomic Structure
... a) Three isotopes of sulfur are sulfur-32, sulfur33, and sulfur-34. Write the complete symbol for each isotope, including the atomic number and the mass number. b) How many neutrons, protons, and electrons are in Na+ with a mass number of 24? What is its atomic number? ...
... a) Three isotopes of sulfur are sulfur-32, sulfur33, and sulfur-34. Write the complete symbol for each isotope, including the atomic number and the mass number. b) How many neutrons, protons, and electrons are in Na+ with a mass number of 24? What is its atomic number? ...
theory1 (osergienko v1)
... Proust’s Law of Definite Proportions A given compound always contains the same proportions (by mass) of elements regardless of the source For example water H2O must Always have 8 g oxygen Combining with 1 g Hydrogen Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 must Have 16 g Oxygen combining with 1 g Hydrogen ...
... Proust’s Law of Definite Proportions A given compound always contains the same proportions (by mass) of elements regardless of the source For example water H2O must Always have 8 g oxygen Combining with 1 g Hydrogen Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 must Have 16 g Oxygen combining with 1 g Hydrogen ...
Atomic structure - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Proust studied many other compounds and observed that the elements that composed the compounds were always in a certain proportion by mass. This principle is now referred to as the law of definite proportions ...
... • Proust studied many other compounds and observed that the elements that composed the compounds were always in a certain proportion by mass. This principle is now referred to as the law of definite proportions ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry of Life
... Name & describe the subatomic particles of an atom, & indicate which one accounts for the occurrence of isotopes. LT#1 Protons (+), neutrons (0), electrons (-) p & n have mass weight of 1 amu; e- have ~ no mass Isotopes = same atomic # but different #s of neutrons ...
... Name & describe the subatomic particles of an atom, & indicate which one accounts for the occurrence of isotopes. LT#1 Protons (+), neutrons (0), electrons (-) p & n have mass weight of 1 amu; e- have ~ no mass Isotopes = same atomic # but different #s of neutrons ...
Science 9
... What are the properties of ionic compounds? (list 2 properties, and what ionic compounds are made of) ...
... What are the properties of ionic compounds? (list 2 properties, and what ionic compounds are made of) ...
Atomic Structure-1
... Atomic Masses Unified atomic mass unit: a unit that describes the mass of an ...
... Atomic Masses Unified atomic mass unit: a unit that describes the mass of an ...
Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry
... All nuclei contain protons and neutrons (exception - hydrogen-1 has no neutrons). Since protons are positively charged, it would be expected that they would repel and separate, but this does not occur. A force holds them together. The nuclear force is an attractive force that acts between all nuclea ...
... All nuclei contain protons and neutrons (exception - hydrogen-1 has no neutrons). Since protons are positively charged, it would be expected that they would repel and separate, but this does not occur. A force holds them together. The nuclear force is an attractive force that acts between all nuclea ...
Chemistry 1 Revision: Metals and their uses
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
Atom - Malibu High School
... Atomic Mass Know that 1.0 amu is defined as exactly 1/12 the mass of a 126C atom. Carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, therefore 1 proton or 1 neutron = ~1 amu 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10 -24 grams Since the mass mostly depends on # protons and # neutrons, you’d think atomic mass would be a whol ...
... Atomic Mass Know that 1.0 amu is defined as exactly 1/12 the mass of a 126C atom. Carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, therefore 1 proton or 1 neutron = ~1 amu 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10 -24 grams Since the mass mostly depends on # protons and # neutrons, you’d think atomic mass would be a whol ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.