Remember Question words
... Law of Conservation of Mass = no detectable gain or loss in mass occurs in chemical reactions. However, the state of a substance may change in a chemical reaction. For example, substances in a chemical reaction can change from solid states to gaseous states but the total mass will not change. Or mor ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass = no detectable gain or loss in mass occurs in chemical reactions. However, the state of a substance may change in a chemical reaction. For example, substances in a chemical reaction can change from solid states to gaseous states but the total mass will not change. Or mor ...
Inorganic Chemistry Lesson 3
... (i.e. a chemical formula of water) means there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in each water molecule. Is the composition of molecules arbitrary, or there is some law that defines it? If such a law does exists, then is it possible to predict composition of molecules? Yes, it is possible ...
... (i.e. a chemical formula of water) means there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in each water molecule. Is the composition of molecules arbitrary, or there is some law that defines it? If such a law does exists, then is it possible to predict composition of molecules? Yes, it is possible ...
Chapter 5: Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table
... • Groups 1A—8A elements are called the representative elements (have a wide range of physical and chemical properties) • Groups 1B—8B elements in the middle of the table are called transition elements (metals) • Bottom rows of elements under the main table are called the inner transition elements (m ...
... • Groups 1A—8A elements are called the representative elements (have a wide range of physical and chemical properties) • Groups 1B—8B elements in the middle of the table are called transition elements (metals) • Bottom rows of elements under the main table are called the inner transition elements (m ...
Chem I Review Part 1
... E. Ernest Rutherford 23. Rutherford's experiment with alpha particle scattering by gold foil established that A. protons are not evenly distributed throughout an atom. B. electrons have a negative charge. C. electrons have a positive charge. D. atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. E. ...
... E. Ernest Rutherford 23. Rutherford's experiment with alpha particle scattering by gold foil established that A. protons are not evenly distributed throughout an atom. B. electrons have a negative charge. C. electrons have a positive charge. D. atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. E. ...
Section 3.2 Atoms and Compounds
... • A given compound always contains the same proportion by mass of the elements of which it is composed. A mixture can have variable composition but the composition of a compound is fixed Does this give us a clue about the nature of matter? ...
... • A given compound always contains the same proportion by mass of the elements of which it is composed. A mixture can have variable composition but the composition of a compound is fixed Does this give us a clue about the nature of matter? ...
Chemical Reactions.
... A compound reacts with oxygen (O2) often produces CO2 & H2O e.x. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) à 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) Note: a combustion reaction can also be a decomposition or a combination reaction ...
... A compound reacts with oxygen (O2) often produces CO2 & H2O e.x. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) à 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) Note: a combustion reaction can also be a decomposition or a combination reaction ...
Chemistry Final - Practice Test I
... A process used to separate sand and water. Filtration An electrical process that can separate water into hydrogen and oxygen. Electrolysis Boiling a chemical and then condensing its vapors. Distillation ...
... A process used to separate sand and water. Filtration An electrical process that can separate water into hydrogen and oxygen. Electrolysis Boiling a chemical and then condensing its vapors. Distillation ...
Unit 2: The Atom
... sound for each particle detected. Different types of radiation required different types of protection. The greater the distance from a radioactive source will give better ...
... sound for each particle detected. Different types of radiation required different types of protection. The greater the distance from a radioactive source will give better ...
chapter3_Sections 1
... • Molecule that consists primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio ...
... • Molecule that consists primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio ...
FXM Rev 1 Key - Grande Cache Community High School
... Rutherford’s model This model formed as a result of the gold foil experiment. It involves a positively charged nucleus with electrons in orbit. It is sometimes called the Planetary Atomic Model. hydrocarbons These are organic compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen. Methane (CH4) is an exam ...
... Rutherford’s model This model formed as a result of the gold foil experiment. It involves a positively charged nucleus with electrons in orbit. It is sometimes called the Planetary Atomic Model. hydrocarbons These are organic compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen. Methane (CH4) is an exam ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
... Atoms of different elements differ by the number of protons in their nucleus. All atoms of an element have the same number of ...
... Atoms of different elements differ by the number of protons in their nucleus. All atoms of an element have the same number of ...
Honors Chemistry
... 5. What are significant figures? How many SF are in 4.500060 cm? 0.0036030 ft? 3.980200 x 1017 mm? 6. What is the rule for SF in calculations such as multiplication, division, addition and subtraction? What is 0.760 cm + 367.8 cm? What is 609 g / 1020 mL? 7. What is the density of a 7.9 lb rock that ...
... 5. What are significant figures? How many SF are in 4.500060 cm? 0.0036030 ft? 3.980200 x 1017 mm? 6. What is the rule for SF in calculations such as multiplication, division, addition and subtraction? What is 0.760 cm + 367.8 cm? What is 609 g / 1020 mL? 7. What is the density of a 7.9 lb rock that ...
ExamView - test.practice.questions.tst
... ____ 21. 3.4 - WWBAT determine the number of valence electrons in an atom... Which of the following atoms has six valence electrons? a. magnesium (Mg) c. sulfur (S) b. silicon (Si) d. argon (Ar) ____ 22. 3.5 - WWBAT identify electronic structure as the primary factor in determining chemical properti ...
... ____ 21. 3.4 - WWBAT determine the number of valence electrons in an atom... Which of the following atoms has six valence electrons? a. magnesium (Mg) c. sulfur (S) b. silicon (Si) d. argon (Ar) ____ 22. 3.5 - WWBAT identify electronic structure as the primary factor in determining chemical properti ...
THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
... with extremely small numbers. • Because of these extremely small masses are very difficult to deal with chemists have developed a method of measuring the mass of an atom relative to the mass of a specific standard. • Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – defined as one-twelfth the mass of carbon-12 atom. • 1 amu ...
... with extremely small numbers. • Because of these extremely small masses are very difficult to deal with chemists have developed a method of measuring the mass of an atom relative to the mass of a specific standard. • Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – defined as one-twelfth the mass of carbon-12 atom. • 1 amu ...
Atoms - Chemistry Land
... Dalton is best known for his atomic theory, which revolutionized the science of chemistry and brought back Democritus’ concept of the atom. ...
... Dalton is best known for his atomic theory, which revolutionized the science of chemistry and brought back Democritus’ concept of the atom. ...
Notes matter energy
... Group IA is the alkali metals. H, which appears in group IA, is a nonmetal. The metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr) are reactive, so they exist in nature as compounds. Alkali metals form +1 ions in compounds, so they also form similar compounds (HBr, NaBr, KBr, ...). A +1 ion has lost one electron. A ...
... Group IA is the alkali metals. H, which appears in group IA, is a nonmetal. The metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr) are reactive, so they exist in nature as compounds. Alkali metals form +1 ions in compounds, so they also form similar compounds (HBr, NaBr, KBr, ...). A +1 ion has lost one electron. A ...
Sample Questions
... 3. The average mass of a carbon atom is 12.011. Assuming you were able to pick up only one carbon unit, the chances that you would randomly get one with a mass of 12.011 is 4. Iron is biologically important in the transport of oxygen by red blood cells from the lungs to the various organs of the bod ...
... 3. The average mass of a carbon atom is 12.011. Assuming you were able to pick up only one carbon unit, the chances that you would randomly get one with a mass of 12.011 is 4. Iron is biologically important in the transport of oxygen by red blood cells from the lungs to the various organs of the bod ...
atoms - Fort Bend ISD
... Materials, when rubbed, can develop a charge difference. This electricity is called “cathode rays” when passed through an evacuated tube (demos). These rays have a small mass and are negative. Thompson noted that these negative subatomic particles were a fundamental part of all atoms. 1) Dalton’s “B ...
... Materials, when rubbed, can develop a charge difference. This electricity is called “cathode rays” when passed through an evacuated tube (demos). These rays have a small mass and are negative. Thompson noted that these negative subatomic particles were a fundamental part of all atoms. 1) Dalton’s “B ...
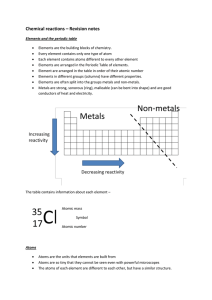
Chemical reactions revision
... You should be able to give the name of the compound formed when different elements combine and tell which elements are present in any simple compound ...
... You should be able to give the name of the compound formed when different elements combine and tell which elements are present in any simple compound ...
1.2 c) Molecular and Empirical Formulas
... Why is the relative atomic mass of hydrogen not exactly 1.00?...due to the existence of ___________________. Hydrogen has _____ isotopes [H-1(normal hydrogen , H-2(deuterium), H-3(tritium)]. Remember, atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of ______________are called isotopes. Mo ...
... Why is the relative atomic mass of hydrogen not exactly 1.00?...due to the existence of ___________________. Hydrogen has _____ isotopes [H-1(normal hydrogen , H-2(deuterium), H-3(tritium)]. Remember, atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of ______________are called isotopes. Mo ...
Chemistry FINAL: CONTENT Review Packet
... _________________ are substances that are made up of two or more elements which are chemically combined _______________________is made from two or more substances that are physically combined The ability to do work is known as ________________ ________________________ are substances that are made up ...
... _________________ are substances that are made up of two or more elements which are chemically combined _______________________is made from two or more substances that are physically combined The ability to do work is known as ________________ ________________________ are substances that are made up ...
Atomic/Nuclear
... The binding energy per nucleon versus atomic number graph peaks at iron. Smaller and larger nuclei have less binding energy per nucleon than iron. If a nucleus with an even atomic number 92 or greater and an odd mass number absorbs a neutron, it can be split into two smaller nuclei with about 3 neut ...
... The binding energy per nucleon versus atomic number graph peaks at iron. Smaller and larger nuclei have less binding energy per nucleon than iron. If a nucleus with an even atomic number 92 or greater and an odd mass number absorbs a neutron, it can be split into two smaller nuclei with about 3 neut ...
Review for Chapter 2
... 1. Dalton’s Atomic Theory says: • Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called “atoms”. • All atoms of the same element are identical. • Compounds contain atoms of different elements combined in whole-number ratios. • Atoms are combined or rearranged in a chemical reaction but they are n ...
... 1. Dalton’s Atomic Theory says: • Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called “atoms”. • All atoms of the same element are identical. • Compounds contain atoms of different elements combined in whole-number ratios. • Atoms are combined or rearranged in a chemical reaction but they are n ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.